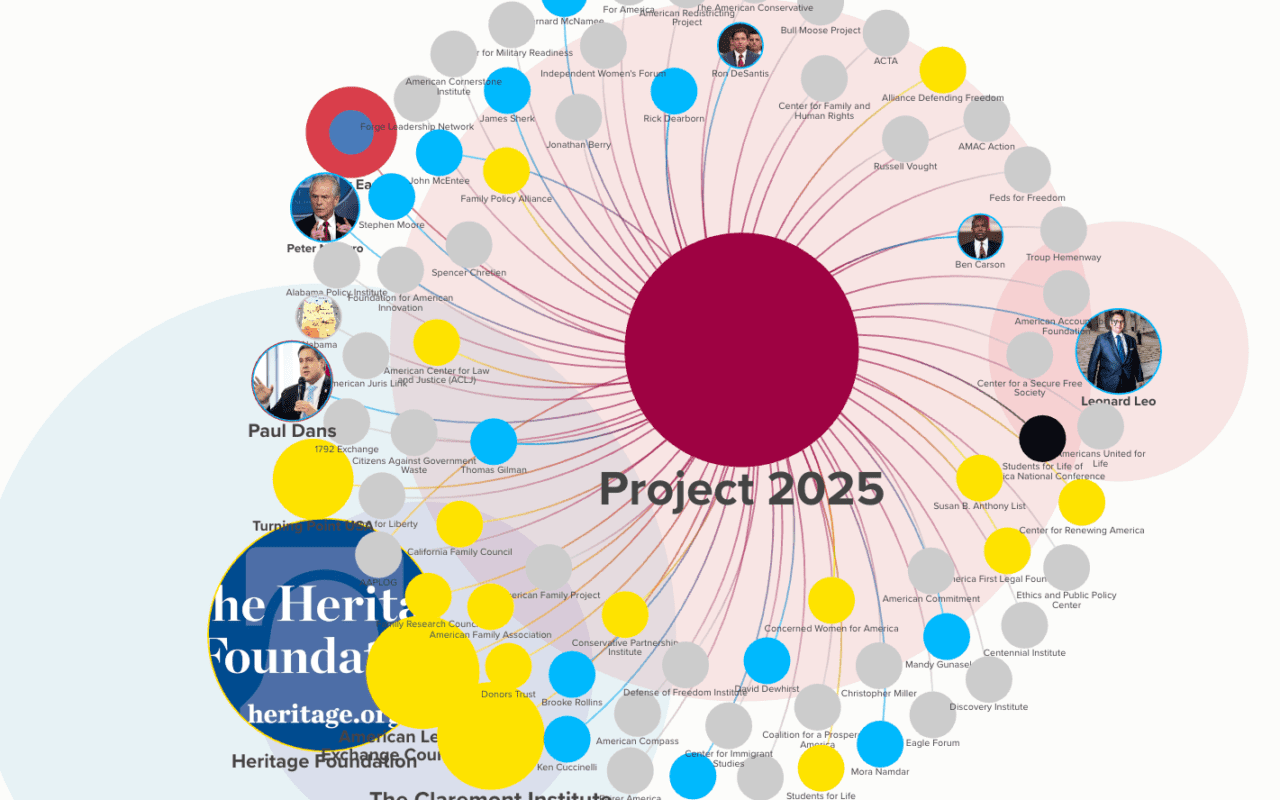
In this post, we dive deep into the heart of American political tradition by presenting a complete collection of first presidential inaugural address speeches that have shaped the United States from its inception to the present day. Each speech, a time capsule of its era, is summarized up front (with a link to the full text) to highlight the core messages, visions, and promises made by the presidents at the dawn of their administrations during their first (or singular) inaugural address.
Accompanying these summaries, we’ve included visual opportunities to get a sense of the inauguration speeches “at a glance,” via word clouds and histograms. These are generated from the text of the speeches themselves, to offer a uniquely infovisual perspective on the recurring themes, values, and priorities that resonate through America’s history.

Understanding our history is not just about recounting events; it’s about connecting with the voices that have guided the nation’s trajectory at each pivotal moment. These speeches are more than formalities; they are declarations of intent, reflections of the societal context, and blueprints for the future, delivered at the crossroads of past achievements and future aspirations.
By exploring these speeches, we not only gain insight into the leadership styles and political climates of each period but also engage with the evolving identity of America itself. We can compare the use of language by different presidents in a way that reflects both shifting trends in culture and geopolitics as well as the character and vision of the leaders themselves.
This collection serves as a vital resource for anyone looking to grasp the essence of American political evolution and the enduring principles that continue to inform its path forward.
George Washington inaugural address (1789)
Washington speech summary
George Washington’s inaugural speech, delivered in New York City on April 30, 1789, reflects his reluctance and humility in accepting the presidency. He expresses deep gratitude for the trust placed in him by his fellow citizens and acknowledges his own perceived inadequacies for the monumental task ahead.
Continue reading Presidential Inaugural Address Mega List