There was a weird controversy that set in after the events of the white nationalist Unite the Right rally in Charlottesville, VA in which a neo-Nazi 8chan bottomfeeder killed Heather Heyer by running her over with his car, while injuring 19 others. It was a shocking moment for the nation and all Trump had to say about it was they condemned violence “on many sides, on many sides” — though there were only two sides, and only one of those two sides had killed someone.
A couple of days later he managed to get through a scripted teleprompter statement explicitly condemning white supremacists and neo-Nazis only to walk it back again and then double down on it the following day, saying “The statement I made on Saturday, the first statement, was a fine statement… What I’m saying is this: You had a group on one side and you had a group on the other, and they came at each other with clubs—and it was vicious and it was horrible. You had some very bad people in that group, but you also had people that were very fine people, on both sides.”
First of all, both sides did not have clubs. One side had tiki torches and a car that killed someone while the other side was armed with hymnals and homemade signage. Secondly — where were those “other” fine people? The vagueness allows for almost any interpretation — were some of the people with clubs “very fine” despite beating others about the head? Were some of the people who didn’t have clubs themselves but were cheering on the people with clubs “fine people”? Maybe there was a gathering of small invisible fairies merely caught up in the shuffle and Trump wanted to just make sure that possibility didn’t get overlooked and this innocent group of delicate souls unnecessarily besmirched?
The primary chosen “debunk” that detractors ended up going with from the wet clay of Trump’s stilted statement alleges that the *other* side Trump meant by “both” were simply innocent local townsfolk objecting to the removal of a statue of their beloved hero Robert E. Lee. Besides the fact that the right-wing has failed to this day to produce a shred of evidence that such people were even there, and the inconvenient reality that the rally was openly marketed as a white supremacist event, organized by avowed white nationalist organizations, it doesn’t even matter if they could produce such evidence — because those people are still not very fine! Robert E. Lee was a traitor to the United States and exalting him is not good!
In fact, Robert E. Lee was a terrible human being whose noble cause was maintaining his ownership of other human beings — as well as a shitty general who paid zero attention to the battle after giving a set of static orders and hoping God would sort out the rest. All he had to do was defend the borders of his baby white homeland, but he was an arrogant showboat who couldn’t keep it in his pants and had to go attacking Pennsylvania for no good reason.
He was also a senseless butcher who had the highest casualty rate of the entire war, being so reckless with his soldiers’ lives that he may as well have fed them into a woodchipper. He chewed through his entire army of 100,000 only 14 months into the campaign and by the war’s end had effectively annihilated his original army multiple times over through cumulative losses, as well as obliterating a whopping 30% of the total Confederate forces overall despite leading only one army in one theater.
He was overconfident and mean-spirited like the rest of his Confederate compadres, feeling that his natural superiority would win the day without much effort. He was trounced and the moral bankruptcy of the Confederacy defeated, but to this day the spirit of the “Lost Cause” animates an unholy miasma of sadistic trolls, anti-government whackjobs (who nevertheless guzzle Trump’s emissions), and stone cold psychopaths who feel the “Cause” — aka white supremacy — is still worth fighting for.
The Confederacy lost. But the ideology — the conviction that some people are simply born to rule over others, that cruelty is strength, that losing doesn’t mean you were wrong — has never died. It just went underground, waiting, simmering. And in Charlottesville, it walked openly in the streets again — wearing khakis and carrying torches, feeling emboldened enough to show its face.
This movement of treasonous trolls had to lick its wounds and bide(n) its time between 2021 and 2025, but true to his word (for once), when Senile Orange Grandpa conned enough noobs to retake the White House in 2024, he pardoned all the January 6 rioters on day one. Including, of course, hundreds of avowed white nationalists from groups he had claimed — fleetingly — to disavow. Including their leaders, among the rare breed of individuals who have ever been convicted of seditious conspiracy in the history of this country, each serving up to 20-year sentences. And including violent thugs who beat Capitol police officers with bats, flagpoles, their own stolen shields, and numerous blunt objects on hand.
People who maced, pepper sprayed, bear sprayed, and electrocuted law enforcement with their own tasers. Folks who committed the obvious crime, broadcast live to the whole world, of breaking and entering at multiple entry points, including overwhelming a line of officers with a physical siege — then rampaged through the halls of Congress defiling, destroying, and stealing irreplaceable historical objects and defecating on lawmakers’ desks. And after all this, they fled the scene and hid from law enforcement — despite having collectively livestreamed the entiretiy of it and posting thousands of “trophy shots” on social media themselves, on top of being filmed by TV cameras from news organizations around the globe.
Then they lied about it. They continue to lie about it. President Trump continues to lie about it. The Republican Party continues to lie about it. A day which resulted in the deaths of 5 law enforcement officers and injuries to 150 more members of the “blue line.”
And yet.
We are to believe.
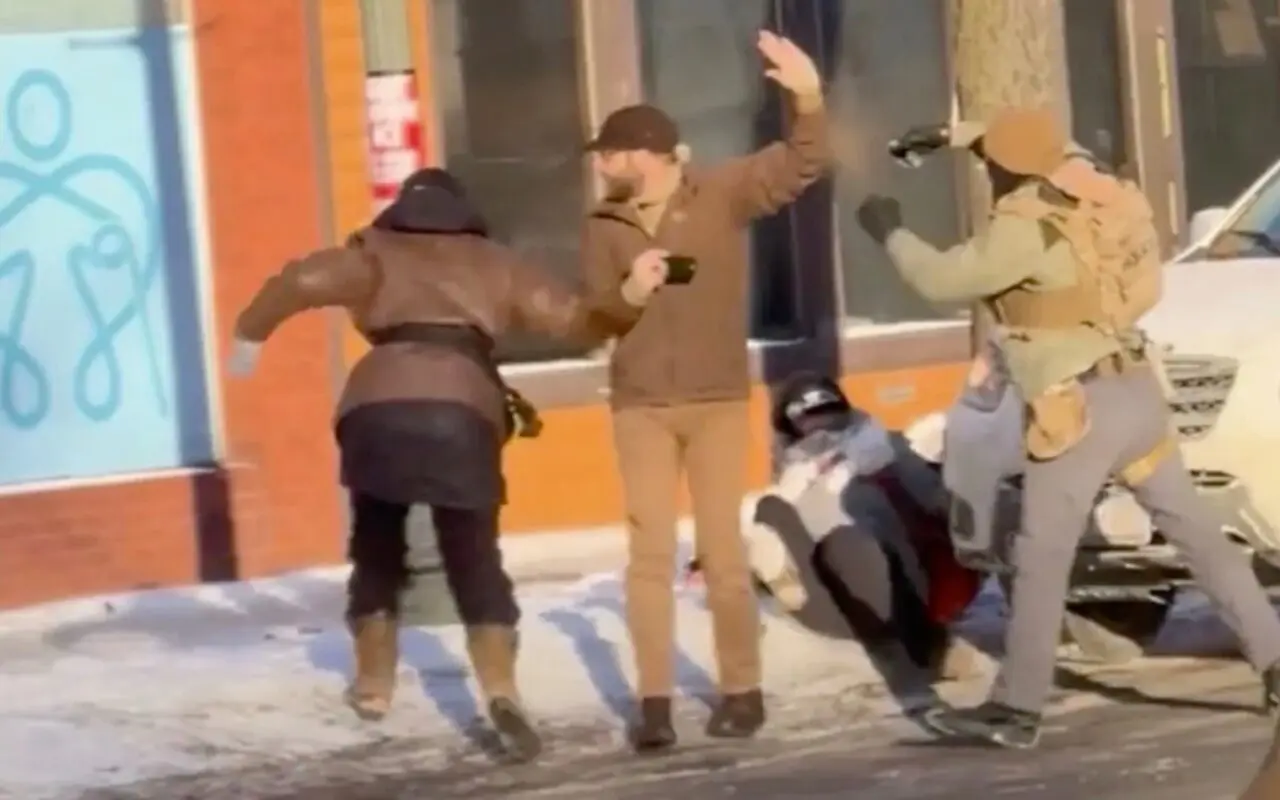
That Alex Pretti deserved to die because law enforcement found him “threatening.”
While standing at the side of the road, with a hand waved in a gesture of surrender, and looking away from the scene over his shoulder out of concern for an individual in distress.
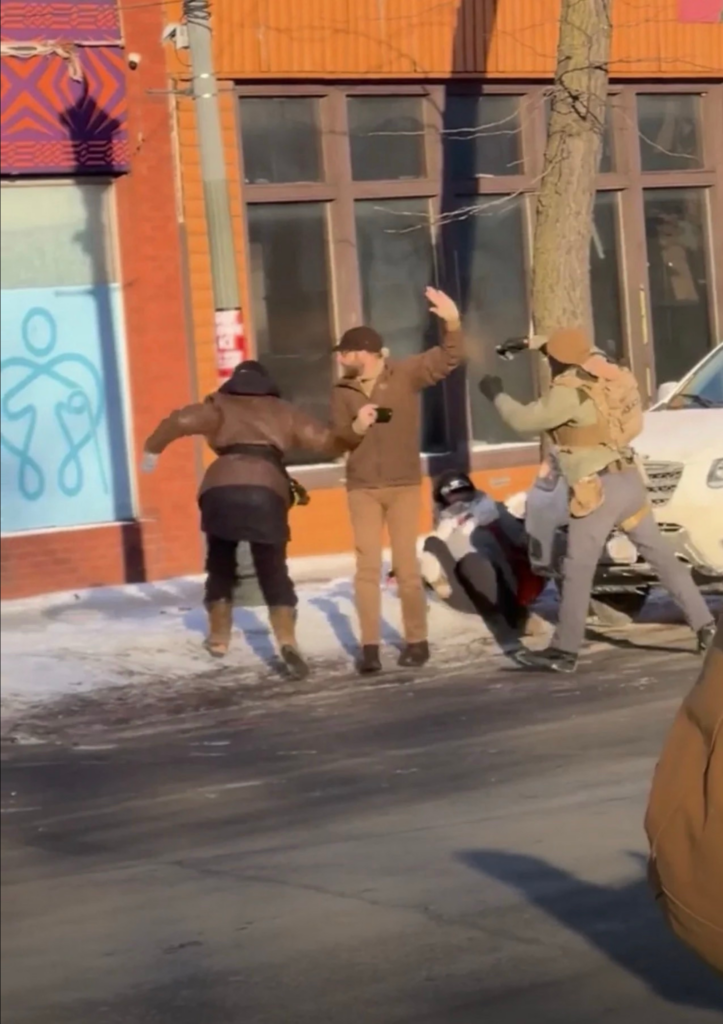
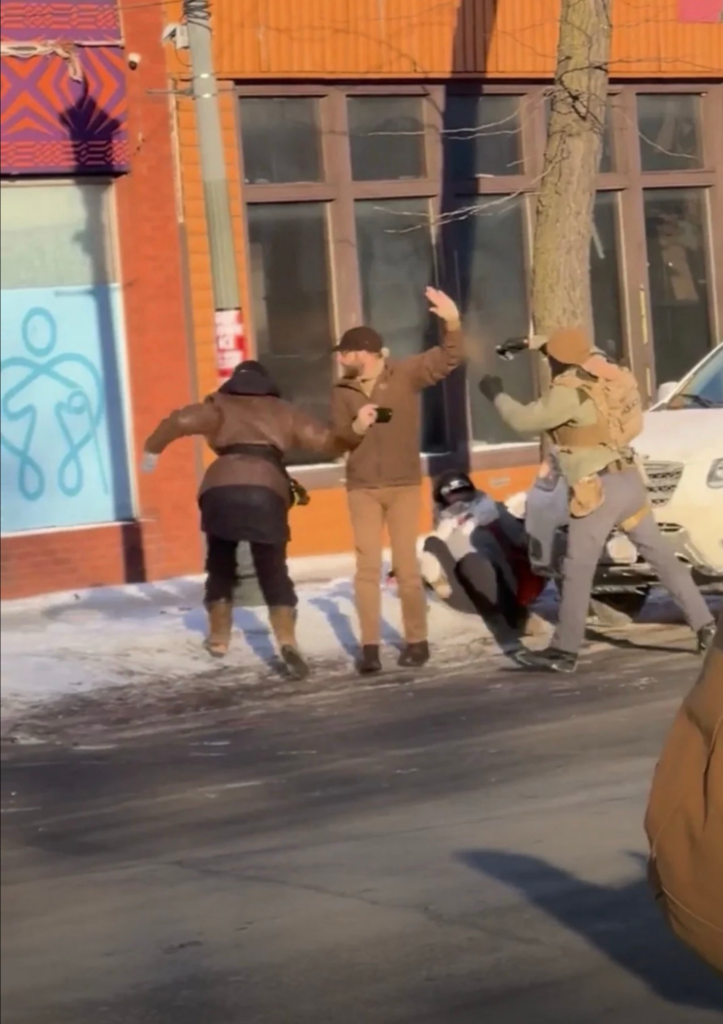


No. We call bullshit. We know these ghost skins have no trouble killing one of their own from the killing of Renee Good, regardless of whatever Great Replacement idiocracy they espouse about the white race — if you get in their way, killing you is perhaps the one unbiased act they will perform free of bigotry to anyone who disagrees with them. Because if they happen to possess an ounce of shame, they never let a molecule of it leak out in public.
People with no shame may skirt the technical bounds of the law at times in order to prolong their abuse of the system, but completely disrespecting the spirit of the law inevitably leads them to break it. If they get away with it, they do it more. If they get caught, they double down. Blame the victim. Blame the media. Blame Biden. Blame Obama. Blame Clinton. Assert absurd moral authority based on a trash heap ideology that shifts like a toxic oil spill and makes no sense. State that plainly true facts are wrong and obviously thin lies are inarguable truths. Behave like the most morally depraved psychopaths online and in public, exalting violence and relishing petty revenge, smearing the names of random bystanders they shot in the street mere minutes ago, and generally treating human life as political toys for them to play with, or a casual game of Call of Duty IRL — all in the name of Jesus.
It is vile. It is a blackened pile of steaming horseshit smeared across the nation. It is a moral stain being done in our name that we will never, ever, ever, ever in the history of history live down — that this is happening here. That we allowed this to happen here. That we are allowing this to happen here. We must not allow this to happen here.