The Echo Chamber of Deceit: Right-Wing Media Outlets, Disinformation, and the Conspiracy Industrial Complex
In an era where truth is increasingly under siege, disinformation has become a weapon of mass confusion—and no faction wields it with more fervor than the vast right-wing media machine. From fringe conspiracy theorists lurking in dark corners of the internet to mainstream outlets that once feigned journalistic credibility, these media entities have mastered the art of crafting narratives that distort, divide, and deceive.
But the effects of this disinformation aren’t limited to a few misguided souls. These conspiracy-laden outlets drive real-world consequences, spreading chaos and undermining democratic institutions with each clickbait headline and manufactured outrage. Whether fueling distrust in elections, amplifying extremist ideologies, or fostering a sense of victimhood among their audiences, these outlets play a pivotal role in shaping the political landscape—and not for the better.
In this post, we’ll dive into some of the most notorious right-wing media outlets pushing disinformation and conspiracy theories, exploring how they have built empires of falsehoods and what it means for a society increasingly untethered from reality (for the antidote to this list, please see our set of curated trusted expert sources on political and historical topics).
Building Empires of Falsehoods
These right-wing media outlets have built empires of falsehoods by capitalizing on two critical factors: the erosion of trust in traditional media and the increasing polarization of political discourse. As public faith in mainstream journalism wanes, largely due to relentless attacks branding them as “fake news” or “liberal bias,” alternative outlets step into the vacuum. They promise their audiences “unfiltered truth” but deliver carefully curated content designed to inflame rather than inform. The business model thrives on sensationalism—conspiracy theories and emotionally charged stories that draw clicks, shares, and ad revenue. Whether it’s the undermining of election results, promoting COVID-19 misinformation, or fostering anti-government sentiment, these outlets operate in an ecosystem where outrage is profitable, and facts are malleable.
For a society increasingly untethered from reality, the implications are grave. When large swaths of the public are consistently exposed to a parallel universe of disinformation, the ability to engage in reasoned discourse or even agree on basic facts erodes. This creates a fertile ground for extremism, where misinformation is weaponized to radicalize, isolate, and enrage. Civic institutions that rely on trust and shared reality—elections, the judiciary, and public health—are undermined, weakening the very foundation of democracy. In a world where conspiracy theories and falsehoods become the currency of political influence, society drifts ever closer to a reality in which truth is irrelevant, and power is achieved through manipulation and division.

Let’s take a look at some of the most egregious offenders on the right, who routinely eschew any interest in journalistic integrity or independent verification of facts or sources and instead have a tendency to, well, make shit up (or enable bad shit to happen on their platforms).
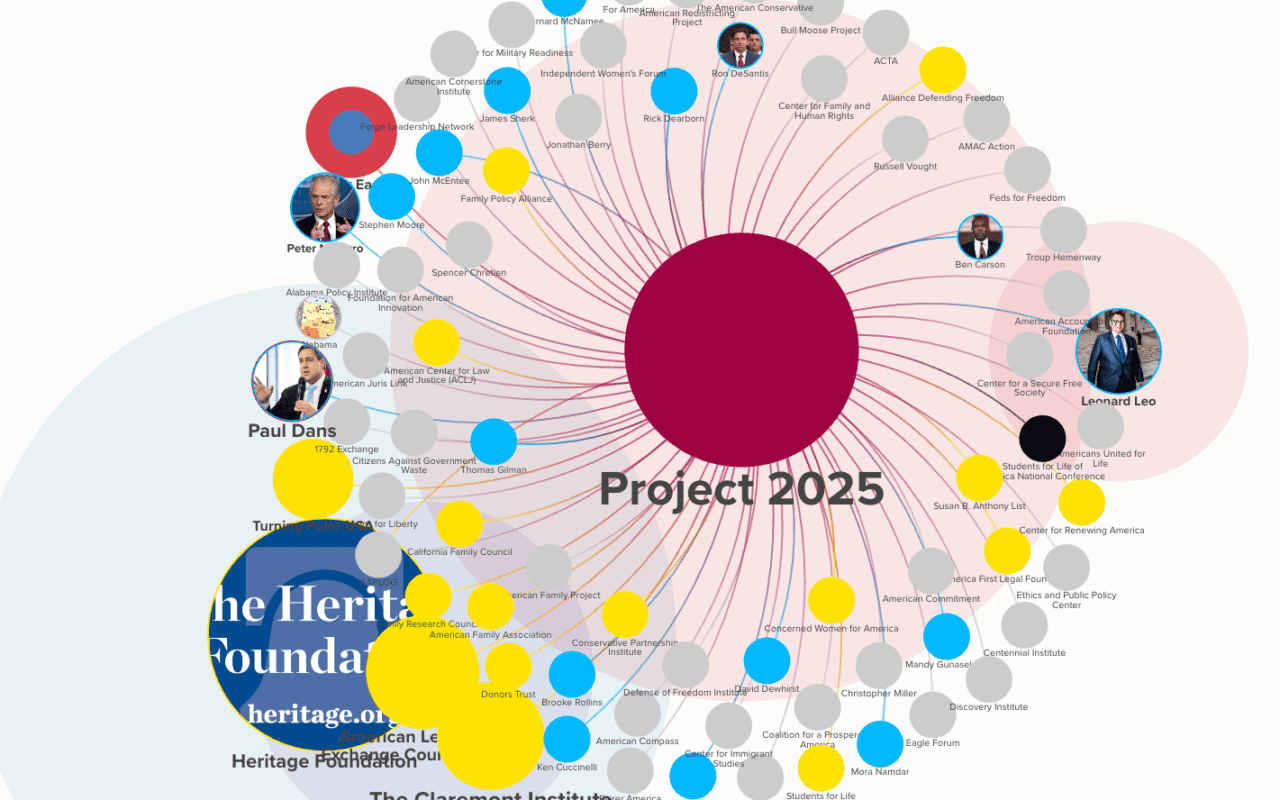
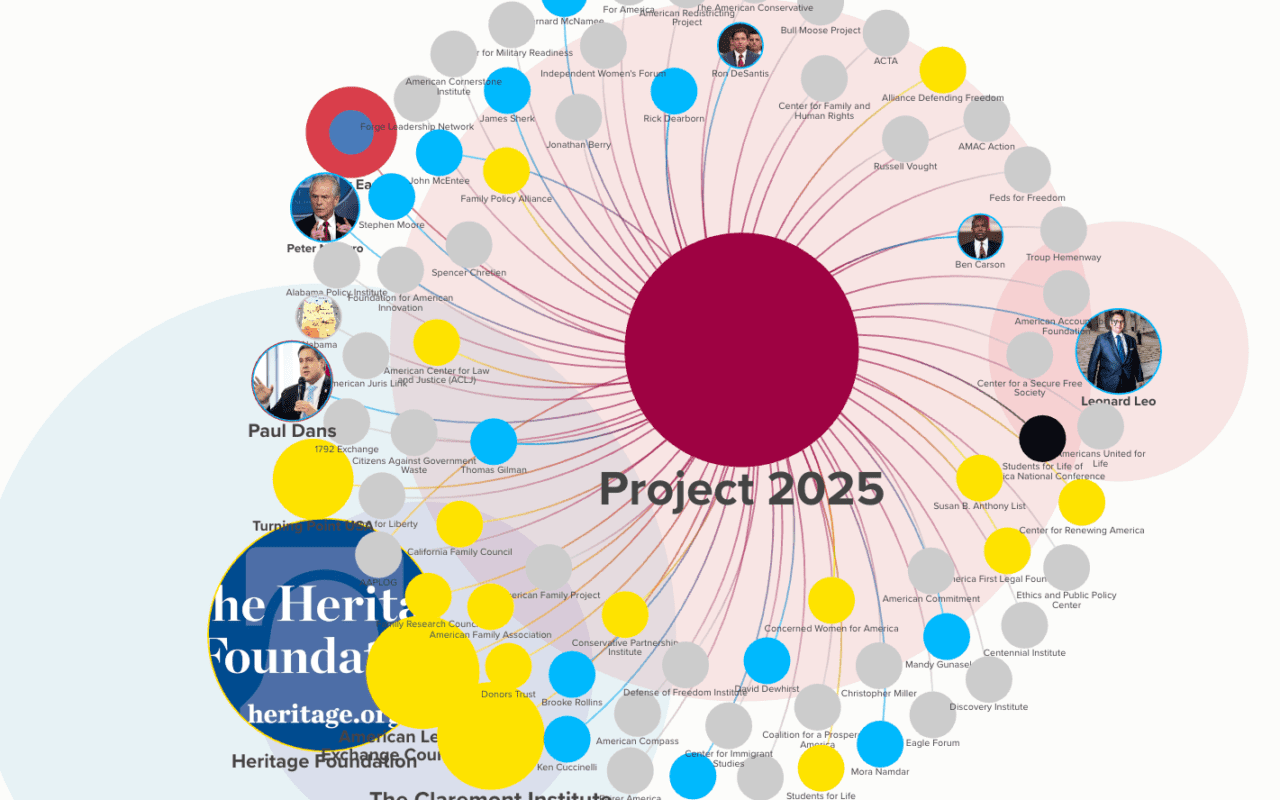
Right-Wing Media Outlets
| Outlet or Individual | Description |
| 4chan | Since its launch in 2003, 4chan has become a key platform in shaping internet subculture, particularly through its creation and dissemination of memes. The site operates as an anonymous imageboard, with users posting on a wide range of topics, from anime to politics. With over 22 million unique monthly visitors, 4chan remains one of the most influential and controversial online communities, often cited for both its creative output and its association with extremist content. |
| 8chan | Known for its alt-right extremism and ties to mass shootings, 8chan was crucial in spreading conspiracy theories like QAnon. Banned and later rebranded as 8kun, the platform gained notoriety during the Gamergate controversy, attracting users banned from other platforms. |
| Alex Jones | Founder of InfoWars, a prominent conspiracy theorist known for promoting various false claims and conspiracy theories. |
| Alexander Marlow | Editor-in-chief of Breitbart News, known for maintaining the site’s far-right editorial stance. |
| American News | American News is a conservative news outlet that focuses on pro-Republican content. With a significant online presence, it engages a large conservative audience, contributing to the polarization of political discourse in the U.S. through its right-leaning coverage. |
| American Renaissance | White supremacist website run by Jared Taylor. |
| Andrew Anglin | White supremacist who started the Daily Stormer in response to Obama‘s election |
| Ben Shapiro | Former Breitbart columnist and founder of The Daily Wire |
| Blaze TV | Glenn Beck’s network |
| Breitbart News | Online news site known for its right-wing perspectives. Former chairman Steve Bannon; funded by Robert Mercer. |
| Cassandra Fairbanks | Cassandra Fairbanks is a political activist and journalist best known for her support of Donald Trump. Previously a Bernie Sanders supporter, she has worked for outlets like the Russian Sputnik News and The Gateway Pundit. |
| Chanel Rion | Chief White House correspondent for OANN, known for her conservative reporting and support of Trump. |
| Charles Hurt | Opinion editor of The Washington Times, known for his conservative political commentary. |
| Christopher Ruddy | CEO of Newsmax and significant figure in operational and editorial direction. |
| Daily Stormer | White supremacist, neo-Nazi website founded by Andrew Anglin in reaction to Obama’s election. |
| Dan Bongino | Dan Bongino is a prominent American conservative commentator, radio host, and author. His background includes serving as an NYPD officer from 1995 to 1999, followed by a distinguished career as a US Secret Service agent, where he worked on the Presidential Protective Division under both the Bush and Obama administrations. Bongino is highly educated, with a BS and MS from Queens College and an MBA from Penn State. His popular show, “The Dan Bongino Show,” attracted about 8.5 million listeners as of October 2021, ranking second among those vying to succeed Rush Limbaugh. He has authored several New York Times bestsellers, including Spygate: The Attempted Sabotage of Donald J. Trump, and hosted “Unfiltered with Dan Bongino” on Fox News until April 2023 |
| Drudge Report | The Drudge Report is a U.S.-based news aggregation website founded by Matt Drudge, known for breaking the Clinton-Lewinsky scandal. The site consists primarily of links to stories from other news outlets and was once considered conservative, though its political leanings have been questioned since 2019. |
| EndingtheFed | Popularized by Ron Paul, Ending the Fed advocates for eliminating the Federal Reserve, criticizing it for contributing to inflation and financial crises. The platform is closely aligned with Tea Party movements from 2008 to 2012. |
| Epoch Times | A multi-language outlet founded by Chinese Americans associated with Falun Gong, known for its critical stance on the Chinese Communist Party, staunch support for Trump, and echoing of the Big Lie about Election 2020. |
| Fox News | Major cable news network known for its right-wing slant and influential conservative commentary. Fox News was found liable in a defamation lawsuit brought by Dominion Voting Systems, resulting in a settlement of nearly $1 billion after the network repeatedly aired false claims that Dominion’s voting machines were used to rig the 2020 presidential election. |
| Free Beacon | Founded in 2012, The Washington Free Beacon is a conservative news website known for its investigative reporting. Although aligned with conservative viewpoints, it has been criticized for publishing potentially misleading content. |
| Gateway Pundit | The Gateway Pundit is a far-right website founded in 2004, notorious for publishing falsehoods and hoaxes. In 2021, it was demonetized by Google. The site expanded significantly during the 2016 election and has faced multiple defamation lawsuits, leading to a Chapter 11 filing. |
| Gavin McInnes | Co-founder of Vice Media in 1994 and the Proud Boys in 2016 |
| Greg Kelly | Notable host on Newsmax, known for his conservative views and support of Donald Trump. |
| InfoWars | Founded in 1999 by Alex Jones, InfoWars is notorious for promoting conspiracy theories like the New World Order and the Sandy Hook shooting “hoax,” for which it was ordered to pay $1.5 billion in damages. In 2024, InfoWars is scheduled to auction its assets as part of bankruptcy proceedings. |
| Jared Taylor | Jared Taylor is an American white supremacist and the editor of American Renaissance magazine. He founded the New Century Foundation to promote racial advocacy and hosts the annual American Renaissance Conference. Taylor has been widely accused of promoting racist ideologies. |
| Jordan Peterson | Jordan Peterson is a Canadian clinical psychologist, professor emeritus at the University of Toronto, and bestselling author who has gained widespread recognition for both his work in psychology and his often controversial views on cultural and political issues. His book 12 Rules for Life: An Antidote to Chaos became an international bestseller, selling over 5 million copies and being translated into more than 45 languages, propelling him to global fame as a public intellectual. Peterson has built a substantial online following, with over 7 million subscribers on his YouTube channel, where he shares lectures and discussions on psychology, philosophy, and culture. He gained notoriety for his opposition to Canada’s Bill C-16, which added gender identity and expression as protected categories, a stance that sparked both support and criticism. |
| Judicial Watch | A conservative watchdog group founded in 1994, Judicial Watch is known for its FOIA lawsuits targeting Democratic administrations. Under president Tom Fitton, it has been labeled by the SPLC as an anti-government extremist group, despite its significant influence in conservative circles. |
| Kathryn Limbaugh | Kathryn over some responsibilities for managing his media empire following her husband Rush Limbaugh’s death. |
| Larry Beasley | President and CEO of The Washington Times, overseeing the newspaper’s conservative editorial direction. |
| Laura Ingraham | Prime-time opinion host on Fox News, known for her conservative viewpoints and outspoken criticism of liberal policies. |
| Mike Cernovich | Mike Cernovich is an American right-wing social media personality and conspiracy theorist known for his involvement in #Gamergate and his segments on ‘The Alex Jones Show.’ He initially associated with the alt-right but now identifies with the new right, frequently promoting controversial views on free speech and engaging in inflammatory rhetoric. |
| Neil Patel | Co-founder and publisher of The Daily Caller, focusing on conservative news and commentary. |
| Newsmax | Newsmax is a conservative news and opinion media company founded in 1998. In 2014, it launched a cable television channel that reaches approximately 75 million households. The network is known for its right-wing and far-right leanings as well as its staunch pro-Trump coverage. |
| One America News Network (OANN) | OANN (One America News Network) is a far-right, pro-Trump cable news channel founded on July 4, 2013. Based in San Diego, it reaches an audience of 150,000 to 500,000 viewers and heavily relies on AT&T networks for revenue. The channel is known for promoting conspiracy theories and misinformation. |
| Parler | Parler, launched in 2018, is a social media platform promoting free speech, attracting predominantly right-wing users and Trump supporters. It saw a user surge during and after the 2020 U.S. presidential election amid accusations of censorship by mainstream platforms. The platform was removed from app stores following its role in organizing the January 6th Capitol riot but plans a relaunch in 2024. |
| RedState | RedState, founded in 2004 and owned by Salem Media Group, is a leading conservative blog known for its political activism and organizing events. The site has undergone staffing changes, notably during Trump’s presidency when critics of Trump were dismissed. |
| RedState Watcher | Founded in 2004, RedState Watcher is a conservative blog operated by Townhall Media, known for its right-wing bias and opinion pieces. It has a strong alignment with the Salem Media Group’s conservative perspectives. |
| Richard Spencer | Former Editor of the racist rag Taki’s Magazine and an early figure in the alt-right. |
| Right Wing Tribune | Right Wing Tribune is known for its right-wing propaganda and election season misinformation. It has been criticized for amplifying conspiracy theories and sensationalist stories that align with extreme conservative narratives. |
| Robert Herring, Sr. | Founder and CEO of One America News Network (OANN), known for its conservative, pro-Trump coverage. |
| Rumble | Rumble is a video-sharing platform launched in 2013 that positions itself as an alternative to YouTube, particularly for creators who feel they are censored or deplatformed by mainstream platforms. Rumble gained popularity among conservative, right-leaning, and libertarian creators, though it markets itself as a platform that champions “free speech” and content that may not fit with the guidelines of other social media giants. |
| Rupert Murdoch | Australian media mogul and founder of Fox and key influencer in the Fox News network’s overall direction. |
| Rush Limbaugh (deceased) | Original host and pioneering figure in conservative talk radio, known for his influential and controversial views. One of the first in a wave of political right-wing “shock jocks.” |
| Sean Hannity | Fox News host known for his strong conservative viewpoints, significant influence in right-wing media, and close relationship with Trump. |
| Steve Bannon | Former executive chairman of Brietbart News and a key figure in shaping the outlet’s editorial stance. |
| Stormfront | Founded by former KKK leader Don Black in 1996, Stormfront was the first major online hate site, centered on white nationalism. It has attracted over 300,000 registered users, with the site repeatedly taken down for violating hate speech policies. |
| Suzanne Scott | CEO of Fox News Media, overseeing all aspects of the network’s operations and editorial direction. |
| Taki’s Magazine | Taki’s Magazine, founded on February 5, 2007 by Taki Theodoracopulos, is known for its extreme right-wing political stance. The publication has drawn criticism for its racially controversial content and its backing of individuals associated with white nationalism, while continuing to publish provocative material critical of political correctness. |
| Tenet Media | Tenet Media is a far-right media organization implicated in Russian influence campaigns in the United States. It has been linked to the promotion of disinformation, especially around political elections and controversial social issues. The platform is currently under investigation by the DOJ for its involvement in spreading foreign-backed propaganda. Operating primarily through social media and online outlets, Tenet Media targets conservative audiences with sensationalized content that aligns with extreme right-wing views. |
| The Babylon Bee | The Babylon Bee is a conservative Christian satirical website that publishes parody news stories with a right-wing perspective, often targeting liberal politics, secular culture, and progressive social movements. While its content is intentionally fictional, it has frequently been mistaken for real news due to its style and tone (not unlike a The Onion for the right-wing). |
| The Daily Caller | The Daily Caller, founded in 2010 by Tucker Carlson and Neil Patel with funding from conservative businessman Foster Friess, was launched as a right-leaning alternative to The Huffington Post. It aims to provide news and opinion content from a conservative perspective. Alongside its for-profit media site, The Daily Caller also operates a non-profit arm, The Daily Caller News Foundation, which has raised concerns about potential conflicts of interest and tax issues. Despite early claims of ideological independence, the outlet has been criticized for publishing misleading stories and engaging in partisan reporting. In 2020, Tucker Carlson sold his ownership stake, leaving Neil Patel as the majority owner. |
| The Daily Wire | The Daily Wire, an American conservative media company founded in 2015 by Ben Shapiro and Jeremy Boreing, has rapidly grown into a major player in digital media. By 2019, it ranked as the sixth-leading English-language publisher on Facebook, drawing massive engagement. The company surpassed $100 million in annual revenue in early 2022 and employed 150 people. Expanding its reach, The Daily Wire launched DailyWire+ in June 2022, offering video on demand for its popular content, including podcasts and video productions. Notably, “The Ben Shapiro Show” became the second most listened-to podcast in the U.S. by March 2019. |
| The Right Stuff | Largest white nationalist podcast network in the US. |
| The Rush Limbaugh Show | Long considered a staple of conservative talk radio, influential in shaping right-wing discourse. |
| The Sean Hannity Show | Radio show mixing news and conservative commentary, hosted by Sean Hannity. |
| The Washington Examiner | A conservative news outlet founded in Washington, D.C., the Washington Examiner transitioned from a daily newspaper to a weekly magazine in 2013. Owned by oil magnate Philip Anschutz, it is known for its right-leaning coverage and is often rated as having a “Lean Right” bias. |
| The Washington Times | Newspaper known for its conservative editorial content and often conspiratorial perspectives. |
| Tim Pool | Tim Pool is an independent journalist and political commentator who gained initial fame for his on-the-ground reporting during the Occupy Wall Street protests in 2011. Over time, Pool has shifted to a right-leaning stance, often criticized for promoting conspiracy theories and misinformation, particularly surrounding elections and COVID-19. He runs a popular YouTube channel where he discusses current events, frequently framing issues in a way that appeals to conservative and libertarian audiences. Though he claims to be politically independent, his content often aligns with right-wing perspectives, leading to accusations of bias. |
| True Pundit | True Pundit is a far-right fake news website known for promoting baseless conspiracy theories, especially regarding mass shootings and political figures. Operating with a “well-known modus operandi” of publishing unverified stories, the site ceased publishing new content in 2021. |
| Truthfeed | Truthfeed is a far-right news outlet notorious for publishing conspiracy theories and misinformation. Known for its strong right-wing bias, the platform has been criticized for aligning with conservative political agendas and contributing to a controversial media landscape dominated by conspiracy-driven narratives. |
| Truth Social | Truth Social is a social media platform launched by President Donald Trump as an alternative to mainstream networks, positioning itself as a “free speech” haven for conservatives. It has become a hub for right-wing users, featuring political content that often echoes Trump’s messaging and grievances against perceived censorship. |
| Tucker Carlson | Co-founder of The Daily Caller, no longer actively involved but was instrumental in the site’s creation. Went on to have a career as a Fox pundit before being abruptly terminated following the January 6 coup attempt and Dominion lawsuit. |
| VDARE | Founded in 1999 by Peter Brimelow, VDARE is a far-right website that advocates for strict immigration policies and is widely associated with white nationalism and white supremacy. The site has long been a platform for anti-immigration rhetoric, often intertwined with racist ideologies. Despite its influence in far-right circles, VDARE announced a suspension of its operations in July 2024, marking a potential end to its two-decade presence in the online white nationalist movement. |
| WikiLeaks | Launched by Julian Assange in 2006, WikiLeaks is renowned for leaking classified documents, including U.S. diplomatic cables and military logs, sparking debates on government transparency. It gained prominence for releasing DNC emails obtained from Russian hackers during the 2016 election, with Assange expressing a controversial preference for a GOP victory over Hillary Clinton. |
| YourNewsWire | Founded in 2014, YourNewsWire is a clickbait website infamous for promoting conspiracy theories and fake news, including some of the most shared hoaxes on social media. Despite being debunked over 80 times, the site remains a significant source of misinformation. |
| Zero Hedge | Zero Hedge is a far-right libertarian financial blog known for its bearish investment outlook and promotion of Austrian School economics. In addition to financial news, the site expanded into political content, often promoting conspiracy theories. Zero Hedge has been accused of spreading Russian propaganda and misinformation, especially regarding the coronavirus pandemic. It was banned from Google Ads in 2020 but was later reinstated. |