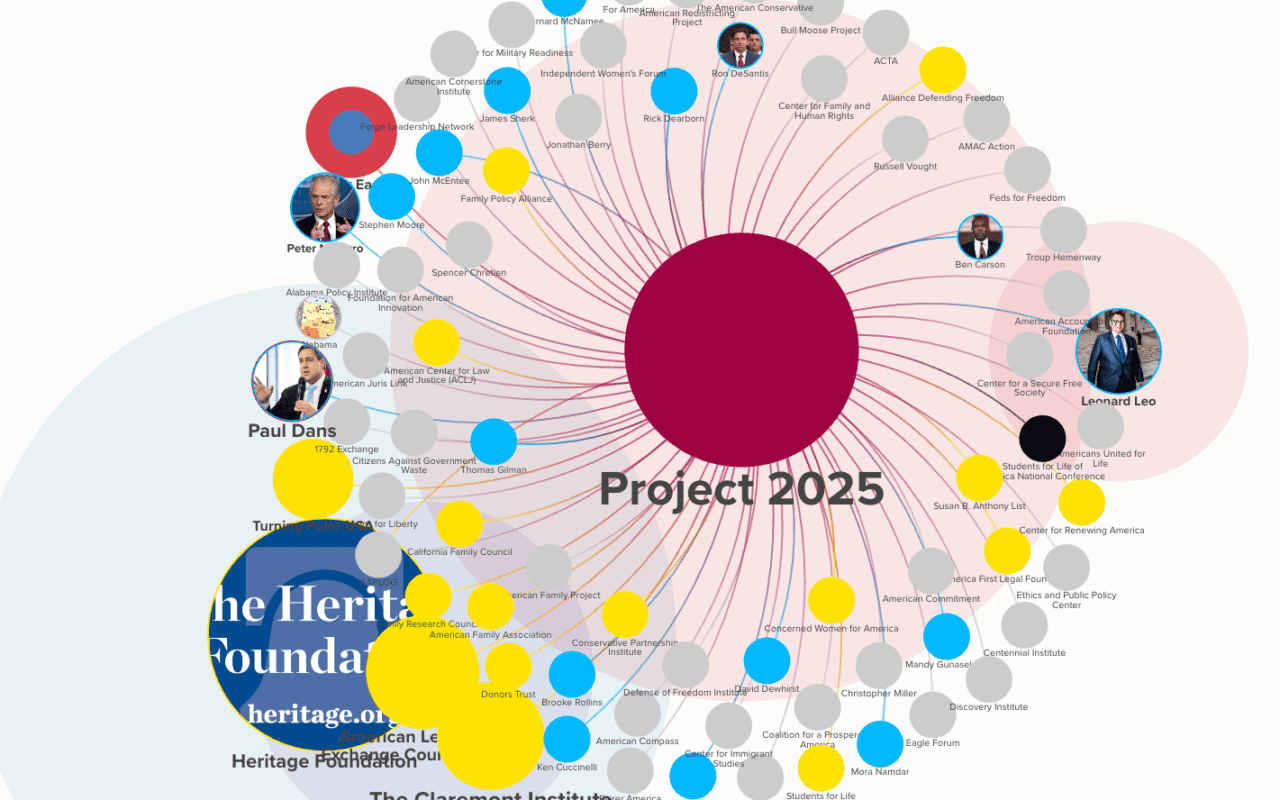
Conspiracy Theory Dictionary: From QAnon to Gnostics
In half a decade we’ve gone from Jeb Bush making a serious run for president to Marjorie Taylor Greene running unopposed and winning a House seat in Georgia. QAnon came seemingly out of nowhere, but taps into a much deeper and older series of conspiracy theories that have surfaced, resurfaced, and been remixed throughout time.
Essentially, QAnon is a recycling of the Protocols of the Elders of Zion conspiracy theory that drove the Nazi ideology and led to the genocide of over 6 million Jews, gypsies, gays, and others who made Hitler mad. It’s a derivative of the global cabal conspiracy theory, and is riddled with the kind of conspiratorial paranoia that led to the deaths of over 75 million people in World War II.
The spread of the QAnon conspiracy theory greatly benefits from historical memory, getting a generous marketing boost from sheer familiarity. It also benefits from an authoritarian mentality growing louder in America, with a predilection for magical thinking and a susceptibility to conspiratorial thinking.

Tales as old as time
Conspiracy theories have been around much longer even than the Protocols — stretching back about as long as recorded history itself. Why do people believe in conspiracy theories? In an increasingly complex world brimming with real-time communication capabilities, the cognitive appeal of easy answers may simply be stronger than ever before.
Anthropologists believe that conspiracy theory has been around for about as long as human beings have been able to communicate. Historians describe one of the earliest conspiracy theories as originating in ancient Mesopotamia, involving a god named Marduk and a goddess called Tiamat — both figures in Babylonian creation mythology.
According to the myth, Marduk defeated Tiamat in battle and created the world from her body — but some ancient Mesopotamians at the time thought that the story was not actually a mere myth, but a political cover-up of a real-life conspiracy in which the followers of Marduk secretly plotted to overthrow Tiamat to seize power.
This “original conspiracy theory” was likely driven by political tensions between city-states in ancient Mesopotamia, although there are very few written records still around to corroborate the origin of the theory or perception of the story at the time. Nevertheless, the Marduk-Tiamat myth is regarded as one of the earliest known examples of widespread belief in conspiracy theories, and it points to the relative commonality and frequency of false narratives throughout history.
Whether deployed purposefully to deceive a population for political advantage, created to exploit people economically, or invented “naturally” as a simple yet satisfying explanation for otherwise complicated and overwhelming phenomena, conspiracy theories are undoubtedly here to stay in culture more broadly for some time to come. We had best get the lay of the land, and understand the language we might use to describe and talk about them.

Conspiracy Theory Dictionary
| 4chan | A notorious internet message board with an unruly culture capable of trolling, pranks, and crimes. |
| 8chan | If 4chan wasn’t raw and lawless enough for you, you could try the even more right-wing “free speech”-haven 8chan while it still stood (now 8kun). Described by its founder Frederick Bennan as “if 4chan and reddit had a baby,” the site is notorious for incubating Gamergate, which morphed into PizzaGate, which morphed into QAnon — and for generally being a cesspool of humanity’s worst stuff. |
| 9/11 truthers | People who believe the attacks on the Twin Towers in New York City in 2001 were either known about ahead of time and allowed to happen, or were intentionally planned by the US government. |
| alien abduction | People who claim to have been captured by intelligent life from another planet, taken to a spaceship or other plane of existence, and brought back — as well as the folks who believe them. |
| American carnage | Evocative of “immense loss” in the Nazi mythology |
| Antifa | Antifa is anti-fascism, so the anti-anti-fascists are just fascists wrapped in a double negative. They are the real cancel culture — and a dangerous one (book burning and everything!). |
| Anti-Semitism | One of history’s oldest hatreds, stretching back to early biblical times |
| Biblical inerrancy | Biblical inerrancy is the doctrine that the Bible, in its original manuscripts, is without error or fault in all its teachings. |
| birtherism | One of Donald Trump‘s original Big Lies — that President Barack Obama wasn’t born in the U.S. and therefore, wasn’t a “legitimate” president. |
| Black Lives Matter | A social justice movement advocating for non-violent civil disobedience in protest against incidents of police brutality and all racially motivated violence against black people. |
| blood libel | A false accusation or myth that Jewish people used the blood of Christians, especially children, in religious rituals, historically used to justify persecution of Jews. |
| child trafficking | The illegal practice of procuring or trading children for the purpose of exploitation, such as forced labor, sexual exploitation, or illegal adoption. |
| Christian Identity | A religious belief system that asserts that white people of European descent are God’s chosen people, often associated with white supremacist and extremist groups. |
| climate change denial | The rejection or dismissal of the scientific consensus that the climate is changing and that human activity is a significant contributing factor. Part of a broader cultural trend of science denialism. |
| The Confederacy | Refers to the Confederate States of America, a group of 11 southern states that seceded from the United States in 1861, leading to the American Civil War, primarily over the issue of slavery. |
| contamination | The presence of an unwanted substance or impurity in another substance, making it unsafe or unsuitable for use. |
| cosmopolitanism | Another term for globalist or internationalist, which are all dog whistles for Jewish people (see also: global cabal, blood libel) |
| Crossing the Rubicon | A phrase that signifies passing a point of no return, derived from Julius Caesar’s irreversible crossing of the Rubicon River in 49 BC, leading to the Roman Civil War. |
| cultural Marxism | Anti-semitic conspiracy theory alleging that Jewish intellectuals who fled the Hitler regime were responsible for infecting American culture with their communist takeover plans and that this holy war is the war the right-wing fights each day. |
| deep state | The idea of a body within the government and military that operates independently of elected officials, often believed to manipulate government policy and direction. |
| DVE | (Domestic Violent Extremism): Refers to violent acts committed within a country’s borders by individuals motivated by domestic political, religious, racial, or social ideologies. |
| fake news | Information that is false or misleading, created and disseminated with the intent to deceive the public or sway public opinion. |
| GamerGate | A controversy that started in 2014 involving the harassment of women in the video game industry, under the guise of advocating for ethics in gaming journalism. |
| George Soros | A Hungarian-American billionaire investor and philanthropist, often the subject of unfounded conspiracy theories alleging he manipulates global politics and economies. |
| Hollywood | The historic center of the United States film industry, often used to refer broadly to American cinema and its cultural influence. |
| Illuminati | A term often associated with various conspiracy theories that allege a secret society controlling world affairs, originally referring to the Bavarian Illuminati, an Enlightenment-era secret society. |
| InfoWars | A controversial far-right media platform known for promoting conspiracy theories, disinformation, and misinformation, hosted by clinical narcissist Alex Jones. |
| JFK assassination | The assassination of President John F. Kennedy on November 22, 1963, in Dallas, Texas, an event surrounded by numerous conspiracy theories regarding the motives and identities of the assassins. |
| John Birch Society | The QAnon of its day (circa 1960s), this extreme right-wing group was theoretically about anti-communist ideals but espoused a host of conspiracy theories and outlandish beliefs. |
| lamestream media | Derogatory term for any media that isn’t right-wing media. |
| leftist apocalypse | A hyperbolic term used by some critics to describe a scenario where leftist or progressive policies lead to societal collapse or significant negative consequences. |
| Makers and Takers | A right-wing economic dichotomy used to describe individuals or groups who contribute to society or the economy (makers) versus those who are perceived to take from it without contributing (takers). See also: Mudsill Theory, trickle down economics, supply side economics, Reaganomics, Libertarianism |
| micro-propaganda machine | MPM: Refers to the use of targeted, small-scale dissemination of propaganda, often through social media and other digital platforms, to influence public opinion or behavior. |
| motivated reasoning | The cognitive process where individuals form conclusions that are more favorable to their preexisting beliefs or desires, rather than based on objective evidence. |
| New World Order | A conspiracy theory that posits a secretly emerging totalitarian world government, often associated with fears of loss of sovereignty and individual freedoms. (see also, OWG, ZOG) |
| nullification | A constitutional “theory” put forth by southern states before the Civil War that they have the power to invalidate any federal laws or judicial decisions they consider unconstitutional. It’s never been upheld by the federal courts. |
| One World Government | The concept of a single government authority that would govern the entire world, often discussed in the context of global cooperation or, conversely, as a dystopian threat in conspiracy theories. (see also: NWO, ZOG) |
| PizzaGate | A debunked and baseless conspiracy theory alleging the involvement of certain U.S. political figures in a child sex trafficking ring, supposedly operated out of a Washington, D.C., pizzeria. |
| post-truth | Refers to a cultural and political context in which debate is framed largely by appeals to emotion disconnected from the details of policy, and by the repeated assertion of talking points to which factual rebuttals are ignored. |
| PR | public relations |
| propaganda | Information, especially of a biased or misleading nature, used to promote a political cause or point of view. |
| Protocols of the Elders of Zion | Forged anti-semitic document alleging a secret Jewish child murder conspiracy used by Hitler to gin up support for his regime. |
| PsyOps | Psychological operations: Operations intended to convey selected information and indicators to audiences to influence their emotions, motives, objective reasoning, and ultimately the behavior of governments, organizations, groups, and individuals. Used as part of hybrid warfare and information warfare tactics in geopolitical (and, sadly, domestic) arenas. |
| QAnon | A baseless conspiracy theory alleging that a secret cabal of Satan-worshipping pedophiles is running a global child sex-trafficking ring and plotting against former U.S. President Donald Trump. |
| Q Drops | Messages or “drops” posted on internet forums by “Q,” the anonymous figure at the center of the QAnon conspiracy theory, often cryptic and claiming to reveal secret information about a supposed deep state conspiracy. |
| reactionary modernism | A term that describes the combination of modern technological development with traditionalist or reactionary political and cultural beliefs, often seen in fascist ideologies. |
| Reichstag fire | An arson attack on the Reichstag building (home of the German parliament) in Berlin on February 27, 1933, which the Nazi regime used as a pretext to claim that Communists were plotting against the German government. |
| Rothschilds | A wealthy Jewish family of bankers, often subject to various unfounded conspiracy theories alleging they control global financial systems and world events. |
| sock puppets | Online identities used for purposes of deception, such as to praise, defend, or support a person or organization while appearing to be an independent party. |
| “Stand back and stand by” | A phrase used by former U.S. President Donald Trump during a presidential debate, which was interpreted as a call to readiness by the Proud Boys, a far-right and neo-fascist organization that seemed to answer his calling during the riot and coup attempt at the Capitol on January 6, 2021. |
| The Storm | Within the context of QAnon, a prophesied event in which members of the supposed deep state cabal will be arrested and punished for their crimes. |
| WikiLeaks | WikiLeaks is a controversial platform known for publishing classified and secret documents from anonymous sources, gaining international attention for its major leaks. While it has played a significant role in exposing hidden information, its release of selectively edited materials has also contributed to the spread of conspiracy theories related to American and Russian politics. |
| ZOG | ZOG (Zionist Occupation Government): A conspiracy theory claiming that Jewish people secretly control a country, particularly the United States, while the term itself is antisemitic and unfounded. |