Inequality is the difference in measures of economic well-being between individuals in a group, among groups in a population, or among countries. Also known as economic inequality; inclusive of both income inequality and wealth inequality.
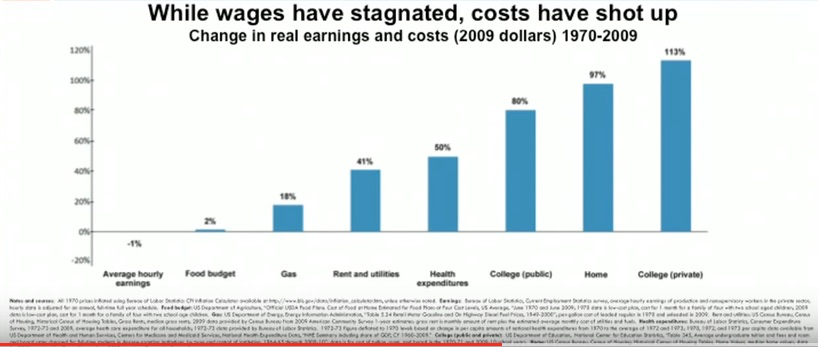
In the United States, the data broadly shows shared economic growth and prosperity in the post-WWII period until the 1970s, when things begin to take a turn: economic growth slowed and income inequality began to increase. For the past 40-50 years, income growth for lower and middle class Americans has stagnated while income growth at the top of the distribution remained growing strongly. Meanwhile as wages have stagnated, costs have risen dramatically, especially in key universal areas like housing, utilities, health care, and education.
Wealth is even more greatly concentrated than income. A recent Oxfam report found that the world’s richest 62 people control as much wealth as the bottom half of the entire population of the planet. In the U.S., the richest 20% of families owned about 89% of the country’s wealth as of 2013 figures.
Those at the top of the wealth distribution who benefit financially from the growing inequality find numerous ways to justify the architecture of the system, and retain much of the power and control over its design. Yet an overwhelming majority of the available historical and present-day data indicates that stark income inequality has wide-ranging negative effects on societies as a whole, from exacerbating social ills to deleterious effects on basic human needs.
Related effects
- Endangers the basic viability of democracy by concentrating power vs. distributing it broadly
- Social Security shortfall
- Hinders and can even destroy social mobility
- Negative effects on population health, lifespan, and basic social values/contracts
- Rising Gini coefficient
Further resources
- Pew Research Center research on income inequality
Comments are closed.