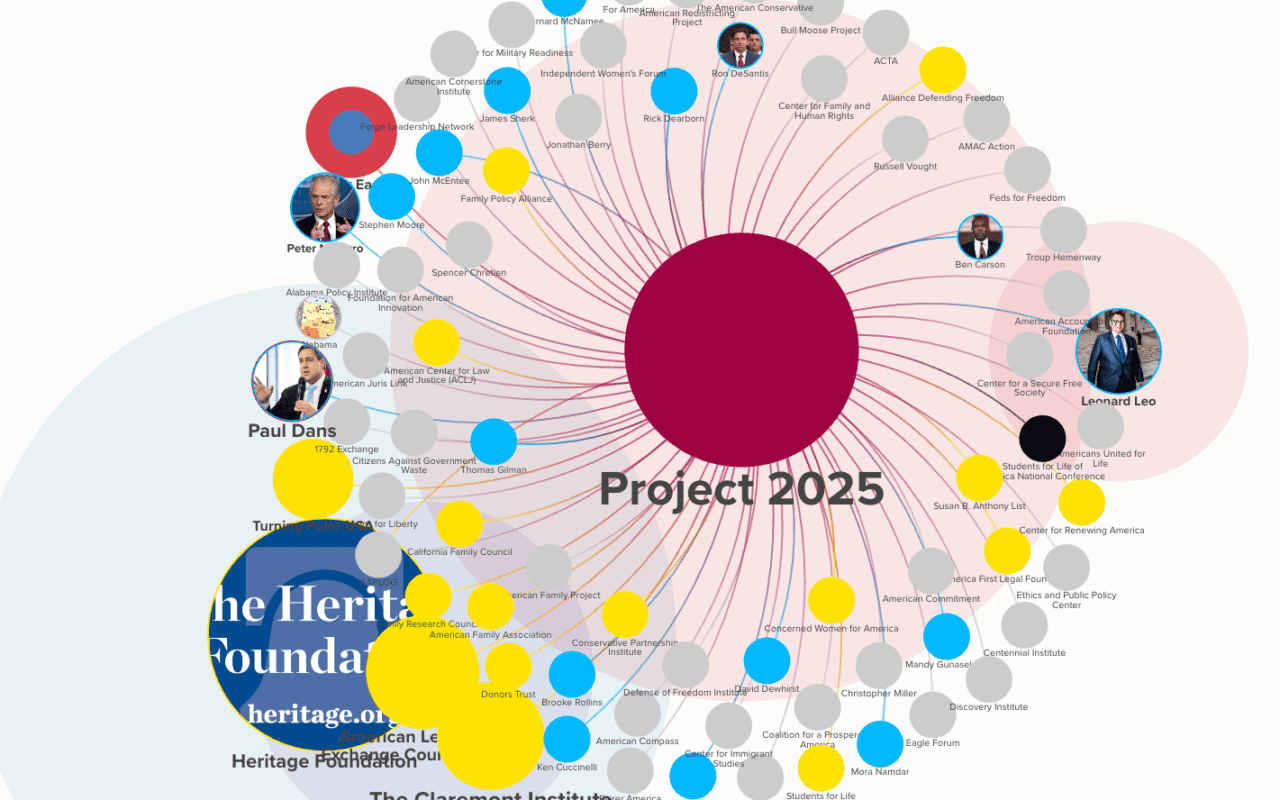
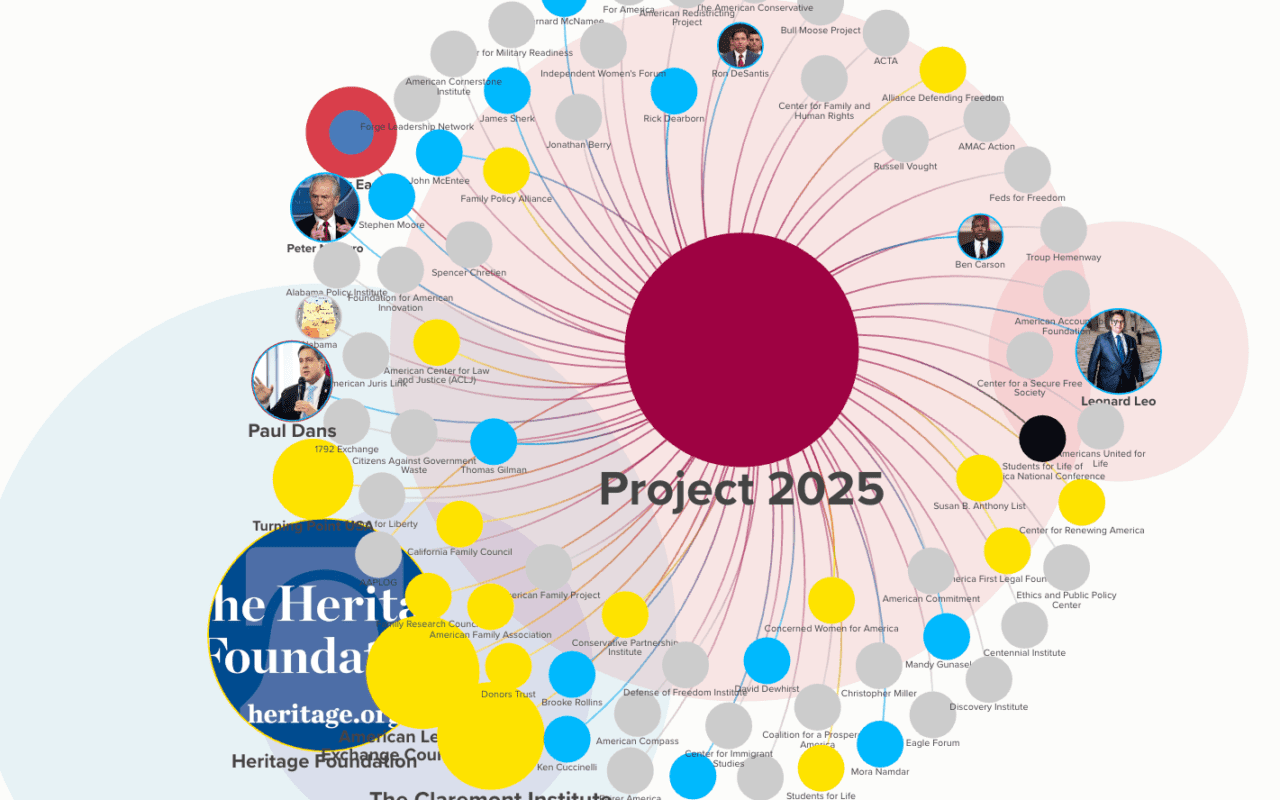
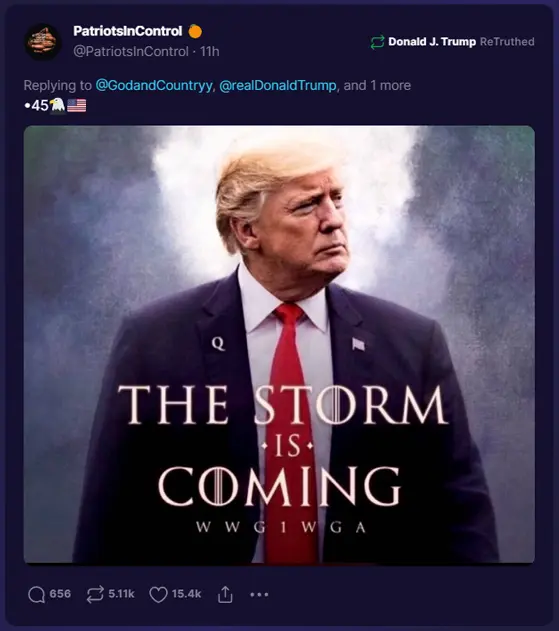
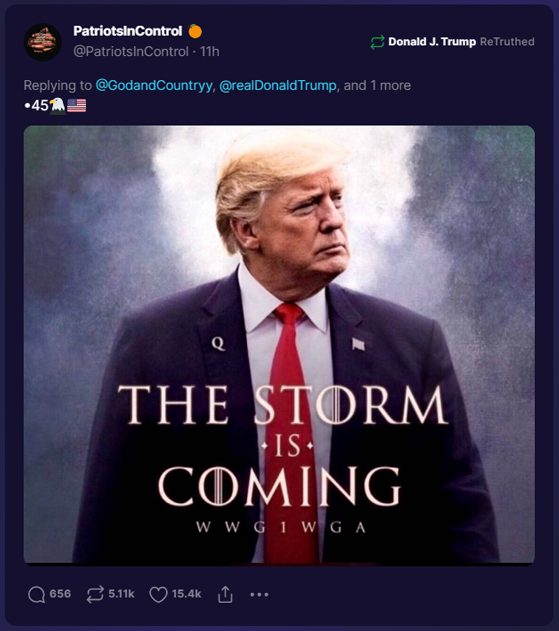
If we want to know what’s going on today, we need to understand what happened yesterday. This list will give us just a start:
- The Federalist Papers — A collection of 85 articles and essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay promoting the ratification of the United States Constitution, offering insight into the ideologies that shaped the foundation of American governance.
- A People’s History of the United States (Howard Zinn) — An alternative take on American history from the perspective of ordinary people rather than political leaders, focusing on the struggles of workers, women, African Americans, and the indigenous populations.
- The Rise and Fall of American Growth (Robert J. Gordon) — An in-depth analysis by economist Robert J. Gordon, which argues that the rapid economic growth experienced by the United States from 1870 to 1970 was a unique period unlikely to be repeated, highlighting how innovation affected living standards.
- Black Reconstruction in America (W. E. B. DuBois) — This seminal work challenges the prevailing narrative of the Reconstruction era, arguing that African Americans were active agents in the fight for their rights and the rebuilding of the South following the Civil War.
- Fraud of the Century (Jr. Roy Morris) — A detailed account of the 1876 U.S. presidential election between Rutherford B. Hayes and Samuel J. Tilden, focusing on the controversial electoral practices and compromises that ultimately led to Hayes’s presidency.
- The Second Coming of the KKK (Linda Gordon) — A historical exploration of the Ku Klux Klan’s resurgence in the early 20th century, detailing how it expanded beyond the South, influencing national politics and American society.
- The Robber Barons (Matthew Josephson) — This book provides a critical look at the late 19th-century industrialists and financiers known as the Robber Barons, examining their business practices, wealth accumulation, and impacts on American society and economy.
- Thieves of State: Why Corruption Threatens Global Security (Sarah Chayes) — Chayes’ book argues that systemic corruption in government and public institutions is a critical driver of global instability, fueling extremism and conflict. Chayes explores how corrupt practices undermine governance and security, leading to widespread disillusionment and violence.
- Plutocracy in America: How Increasing Inequality Destroys the Middle Class and Exploits the Poor (Ronald P. Formisano) — This book examines how growing economic inequality in the United States concentrates wealth and power among a small elite, eroding democracy and undermining the middle class. Formisano argues that this increasing plutocracy exploits the poor and threatens the nation’s social and political stability.
- The Big Sort: Why the Clustering of Like-Minded American Is Tearing Us Apart (Bill Bishop) — Bishop’s work explores how Americans increasingly self-segregate into communities of like-minded individuals, leading to greater political polarization and division. The book argues that this geographic and ideological sorting undermines social cohesion and exacerbates cultural and political conflicts in the United States.
- The Lonely Crowd: A Study of the Changing American Character (David Riesman) — This sociological classic explores how shifts in American society have led individuals to become more other-directed, driven by peer approval rather than internal values, reshaping the national character.
- Present Shock: When Everything Happens Now (Douglas Rushkoff) — Rushkoff examines how the digital age’s constant immediacy disrupts our sense of time, leading to anxiety, distraction, and a collapse of long-term thinking in modern culture.
- Life Inc: How Corporatism Conquered the World, and How We Can Take It Back (Douglas Rushkoff) — This book critiques the rise of corporatism, showing how corporations have infiltrated every aspect of life and offering strategies for reclaiming autonomy in a hyper-commercialized world.
- Captive Audience: The Telecom Industry and Monopoly Power in the New Gilded Age (Susan Crawford) — Crawford analyzes the telecom industry’s monopolistic control over internet access in America, highlighting how this corporate dominance stifles innovation, competition, and public welfare.
- Too Big To Know (David Weinberger) — Weinberger explores how the vast, decentralized nature of knowledge in the digital age is transforming expertise, showing that traditional gatekeepers of knowledge are being replaced by more dynamic, networked ways of understanding.
- Caste: The Origins of Our Discontents (Isabel Wilkerson) — Explores the unspoken social hierarchy in America, comparing it to the caste systems in India and Nazi Germany. Wilkerson argues that this deeply ingrained caste system shapes every aspect of American life, perpetuating racial inequality and injustice.
- Bring the War Home: The White Power Movement and Paramilitary America (Kathleen Belew) — Examines how the white power movement in the United States mobilized in the aftermath of the Vietnam War, blending military tactics and white supremacist ideology. Belew argues that this movement coalesced into a violent, paramilitary force, posing a significant and ongoing threat to American democracy.
- Stamped from the Beginning: The Definitive History of Racist Ideas in America (Ibram X. Kendi) — The book traces the origins and evolution of racist ideas throughout American history. Kendi argues that these ideas were deliberately crafted to justify and maintain racial inequality, shaping policies and social norms that continue to impact the nation today.
- And the Band Played on: Politics, People, and the AIDS Epidemic (Randy Shilts) — Chronicles the early years of the AIDS epidemic, highlighting how political indifference, prejudice, and bureaucratic failures allowed the disease to spread unchecked. Shilts argues that these systemic failures contributed to the unnecessary loss of thousands of lives and shaped the public health response to the crisis.
Support independent booksellers
Support indie bookshops by buying the following 99 titles on Bookshop: