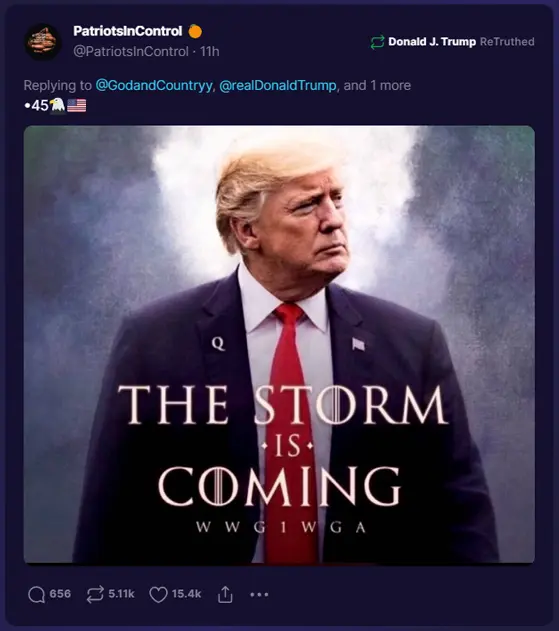
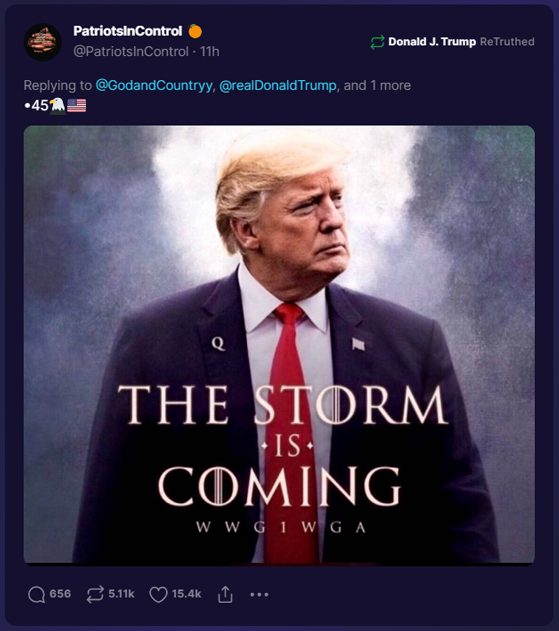
“Source amnesia” is a psychological phenomenon that occurs when an individual can remember information but cannot recall where the information came from. In the context of media and disinformation, source amnesia plays a crucial role in how misinformation spreads and becomes entrenched in people’s beliefs. This overview will delve into the nature of source amnesia, its implications for media consumption, and strategies for addressing it.
Understanding source amnesia
Source amnesia is part of the broader category of memory errors where the content of a memory is dissociated from its source. This dissociation can lead to a situation where individuals accept information as true without remembering or critically evaluating where they learned it. The human brain tends to remember facts or narratives more readily than it does the context or source of those facts, especially if the information aligns with pre-existing beliefs or emotions. This bias can lead to the uncritical acceptance of misinformation if the original source was unreliable but the content is memorable.
Source amnesia in the media landscape
The role of source amnesia in media consumption has become increasingly significant in the digital age. The vast amount of information available online and the speed at which it spreads mean that individuals are often exposed to news, facts, and narratives from myriad sources, many of which might be dubious or outright false. Social media platforms, in particular, exacerbate this problem by presenting information in a context where source credibility is often obscured or secondary to engagement.
Disinformation campaigns deliberately exploit source amnesia. They spread misleading or false information, knowing that once the information is detached from its dubious origins, it is more likely to be believed and shared. This effect is amplified by confirmation bias, where individuals are more likely to remember and agree with information that confirms their pre-existing beliefs, regardless of the source’s credibility.
Implications of source amnesia
The implications of source amnesia in the context of media and disinformation are profound. It can lead to the widespread acceptance of false narratives, undermining public discourse and trust in legitimate information sources. Elections, public health initiatives, and social cohesion can be adversely affected when disinformation is accepted as truth due to source amnesia.
The phenomenon also poses challenges for fact-checkers and educators, as debunking misinformation requires not just presenting the facts but also overcoming the emotional resonance and simplicity of the original, misleading narratives.
Addressing source amnesia
Combating source amnesia and its implications for disinformation requires a multi-pronged approach, focusing on education, media literacy, and critical thinking. Here are some strategies:
- Media Literacy Education: Teaching people to critically evaluate sources and the context of the information they consume can help mitigate source amnesia. This includes understanding the bias and reliability of different media outlets, recognizing the hallmarks of credible journalism, and checking multiple sources before accepting information as true.
- Critical Thinking Skills: Encouraging critical thinking can help individuals question the information they encounter, making them less likely to accept it uncritically. This involves skepticism about information that aligns too neatly with pre-existing beliefs or seems designed to elicit an emotional response.
- Source Citing: Encouraging the practice of citing sources in media reports and social media posts can help readers trace the origin of information. This practice can aid in evaluating the credibility of the information and combat the spread of disinformation.
- Digital Platforms’ Responsibility: Social media platforms and search engines play a crucial role in addressing source amnesia by improving algorithms to prioritize reliable sources and by providing clear indicators of source credibility. These platforms can also implement features that encourage users to evaluate the source before sharing information.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Governments and NGOs can run public awareness campaigns highlighting the importance of source evaluation. These campaigns can include guidelines for identifying credible sources and the risks of spreading unverified information.
Source amnesia is a significant challenge in the fight against disinformation, making it easy for false narratives to spread unchecked. By understanding this phenomenon and implementing strategies to address it, society can better safeguard against the corrosive effects of misinformation.
It requires a concerted effort from individuals, educators, media outlets, and digital platforms to ensure that the public remains informed and critical in their consumption of information. This collective action can foster a more informed public, resilient against the pitfalls of source amnesia and the spread of disinformation.