The term “hoax” is derived from “hocus,” a term that has been in use since the late 18th century. It originally referred to a trick or deception, often of a playful or harmless nature. The essence of a hoax was its capacity to deceive, typically for entertainment or to prove a point without malicious intent. Over time, the scope and implications of a hoax have broadened significantly. What was once a term denoting jest or trickery has morphed into a label for deliberate falsehoods intended to mislead or manipulate public perception.
From playful deception to malicious misinformation
As society entered the age of mass communication, the potential reach and impact of hoaxes expanded dramatically. The advent of newspapers, radio, television, and eventually the internet and social media platforms, transformed the way information—and misinformation—circulated. Hoaxes began to be used not just for amusement but for more nefarious purposes, including political manipulation, financial fraud, and social engineering. The line between a harmless prank and damaging disinformation and misinformation became increasingly blurred.
The political weaponization of “hoax”
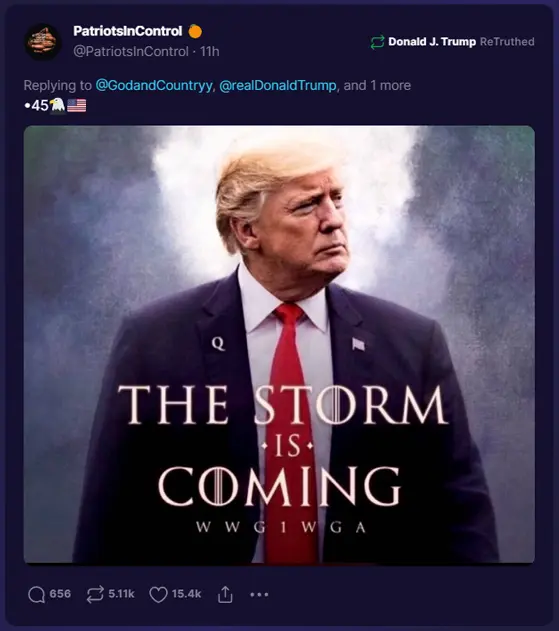
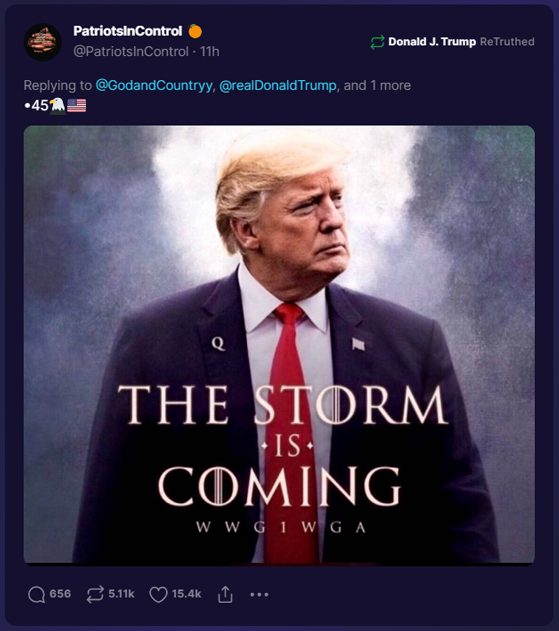
In the contemporary political landscape, particularly within the US, the term “hoax” has been co-opted as a tool for disinformation and propaganda. This strategic appropriation has been most visible among certain factions of the right-wing, where it is used to discredit damaging information, undermine factual reporting, and challenge the legitimacy of institutional findings or scientific consensus. This application of “hoax” serves multiple purposes: it seeks to sow doubt, rally political bases, and divert attention from substantive issues.

This tactic involves labeling genuine concerns, credible investigations, and verified facts as “hoaxes” to delegitimize opponents and minimize the impact of damaging revelations. It is a form of gaslighting on a mass scale, where the goal is not just to deny wrongdoing but to erode the very foundations of truth and consensus. By branding something as a “hoax,” these actors attempt to preemptively dismiss any criticism or negative information, regardless of its veracity.
Case Studies: The “Hoax” label in action
High-profile instances of this strategy include the dismissal of climate change data, the denial of election results, and the rejection of public health advice during the COVID-19 pandemic. In each case, the term “hoax” has been employed not as a description of a specific act of deception, but as a blanket term intended to cast doubt on the legitimacy of scientifically or empirically supported conclusions. This usage represents a significant departure from the term’s origins, emphasizing denial and division over dialogue and discovery.
The impact on public discourse and trust
The strategic labeling of inconvenient truths as “hoaxes” has profound implications for public discourse and trust in institutions. It creates an environment where facts are fungible, and truth is contingent on political allegiance rather than empirical evidence. This erosion of shared reality undermines democratic processes, hampers effective governance, and polarizes society.
Moreover, the frequent use of “hoax” in political discourse dilutes the term’s meaning and impact, making it more difficult to identify and respond to genuine instances of deception. When everything can be dismissed as a hoax, the capacity for critical engagement and informed decision-making is significantly compromised.
Moving Forward: Navigating a “post-hoax” landscape
The challenge moving forward is to reclaim the narrative space that has been distorted by the misuse of “hoax” and similar terms. This involves promoting media literacy, encouraging critical thinking, and fostering a public culture that values truth and accountability over partisanship. It also requires the media, educators, and public figures to be vigilant in their language, carefully distinguishing between genuine skepticism and disingenuous dismissal.
The evolution of “hoax” from a term denoting playful deception to a tool for political disinformation reflects broader shifts in how information, truth, and reality are contested in the public sphere. Understanding this transformation is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern informational landscape and for fostering a more informed, resilient, and cohesive society.