In this post, we dive deep into the heart of American political tradition by presenting a complete collection of first presidential inaugural address speeches that have shaped the United States from its inception to the present day. Each speech, a time capsule of its era, is summarized up front (with a link to the full text) to highlight the core messages, visions, and promises made by the presidents at the dawn of their administrations during their first (or singular) inaugural address.
Accompanying these summaries, we’ve included visual opportunities to get a sense of the inauguration speeches “at a glance,” via word clouds and histograms. These are generated from the text of the speeches themselves, to offer a uniquely infovisual perspective on the recurring themes, values, and priorities that resonate through America’s history.
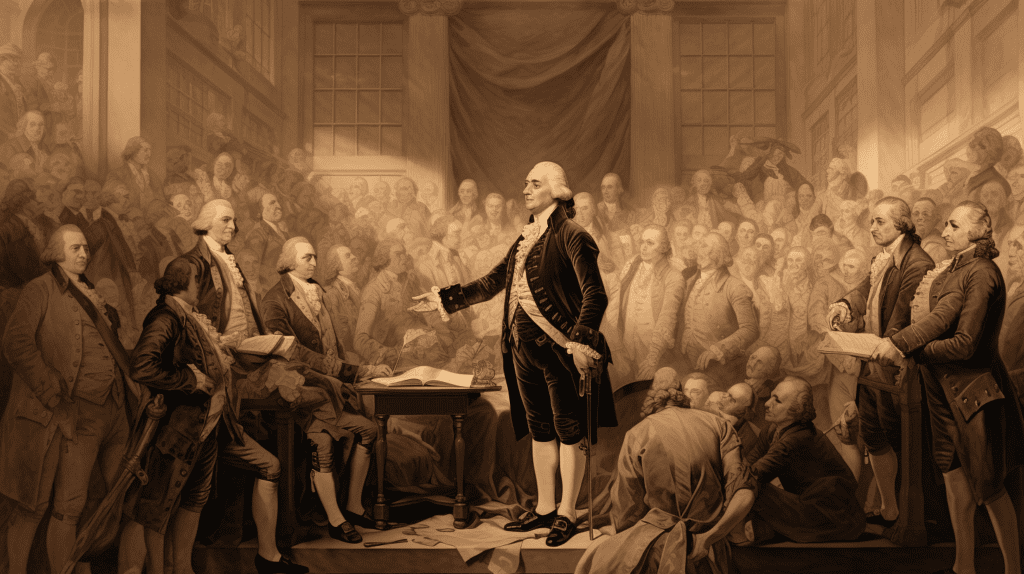

Understanding our history is not just about recounting events; it’s about connecting with the voices that have guided the nation’s trajectory at each pivotal moment. These speeches are more than formalities; they are declarations of intent, reflections of the societal context, and blueprints for the future, delivered at the crossroads of past achievements and future aspirations.
By exploring these speeches, we not only gain insight into the leadership styles and political climates of each period but also engage with the evolving identity of America itself. We can compare the use of language by different presidents in a way that reflects both shifting trends in culture and geopolitics as well as the character and vision of the leaders themselves.
This collection serves as a vital resource for anyone looking to grasp the essence of American political evolution and the enduring principles that continue to inform its path forward.
George Washington inaugural address (1789)
Washington speech summary
George Washington’s inaugural speech, delivered in New York City on April 30, 1789, reflects his reluctance and humility in accepting the presidency. He expresses deep gratitude for the trust placed in him by his fellow citizens and acknowledges his own perceived inadequacies for the monumental task ahead.
Washington emphasizes the importance of divine guidance, national unity, and public virtue, and commits to a government dedicated to the liberties and happiness of the people. He also articulates a vision for a government founded on principles of morality and free governance, highlighting the inseparable link between virtue and happiness. Washington concludes by declining any personal financial benefits from his role as president, reiterating his dedication to public service.
For more details, you can view the full text of the speech in my GitHub respository.
Washington speech word cloud
Washington speech histogram
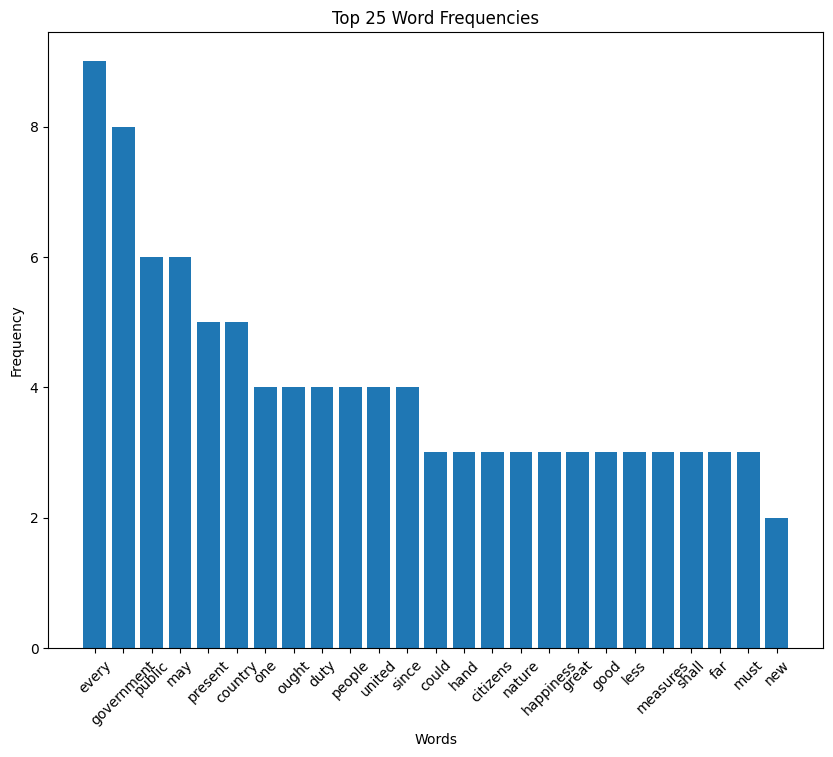
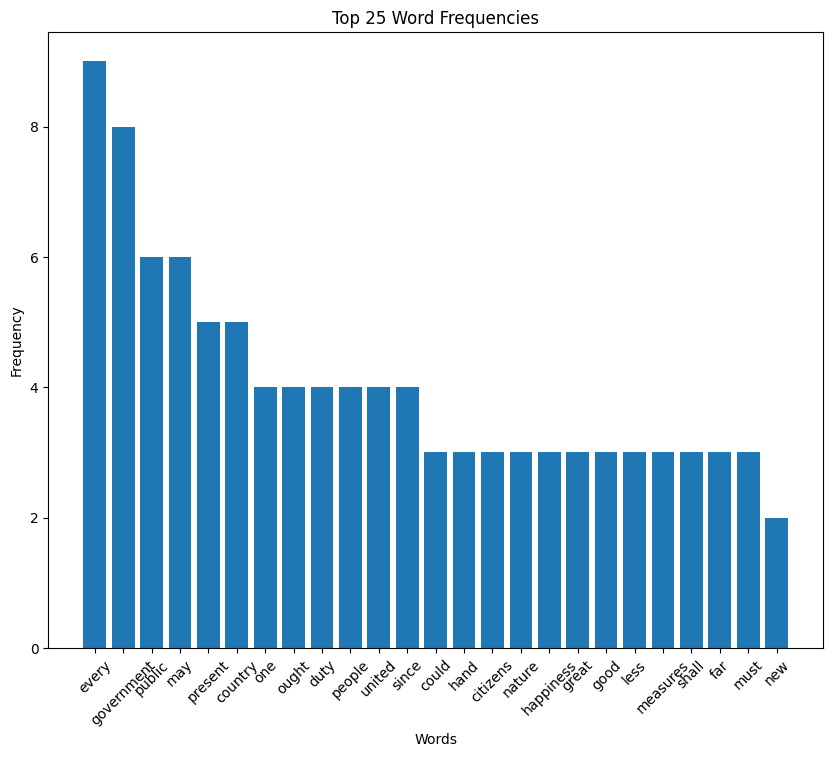
John Adams inaugural address (1797)
Adams speech summary
John Adams’ inaugural address emphasizes the critical choice between submission to foreign rule and independence, highlighting the challenges in forming a new government. He discusses the early weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation, the eventual creation of a more robust Constitution, and his support for it.
Adams praises the Constitution’s design, reflects on his role in its adoption, and commits to upholding it. He stresses the importance of fair elections, national unity, and adherence to constitutional principles, expressing hope for America’s future under this governance system.
For the full text, you can visit the original speech in my GitHub repository.
Adams speech word cloud

Adams speech histogram
Thomas Jefferson inaugural address (1801)
Jefferson speech summary
Thomas Jefferson‘s First Inaugural Address in 1801 emphasizes unity, respect for majority rule while protecting minority rights, and adherence to republican principles. He acknowledges the challenges of the presidency and pledges to support the Constitution, promote justice, maintain peace, and encourage economic freedom.
Jefferson advocates for a frugal government that avoids unnecessary burdens on labor and prioritizes the welfare of the people. He commits to serving with humility and seeks the support and indulgence of the American people for any errors in judgment during his tenure.
For the full text, you can visit this link.
Jefferson speech word cloud
Jefferson speech histogram
James Madison inaugural address (1809)
Madison speech summary
James Madison, in his first inaugural address, emphasized the honor and responsibility of being called to serve by his country. He recognized the unique challenges of the period, including international tensions and domestic prosperity.
Madison expressed commitment to maintaining peace, justice, and neutrality in foreign affairs, while also cherishing republican institutions and the Constitution. He advocated for economic prudence, the reduction of public debt, and the promotion of agriculture, commerce, and science. Madison sought to follow the exemplary services of his predecessors, particularly relying on the intelligence and virtue of fellow citizens and divine guidance for support.
For the full text, you can visit the source.
Madison speech word cloud


Madison speech histogram
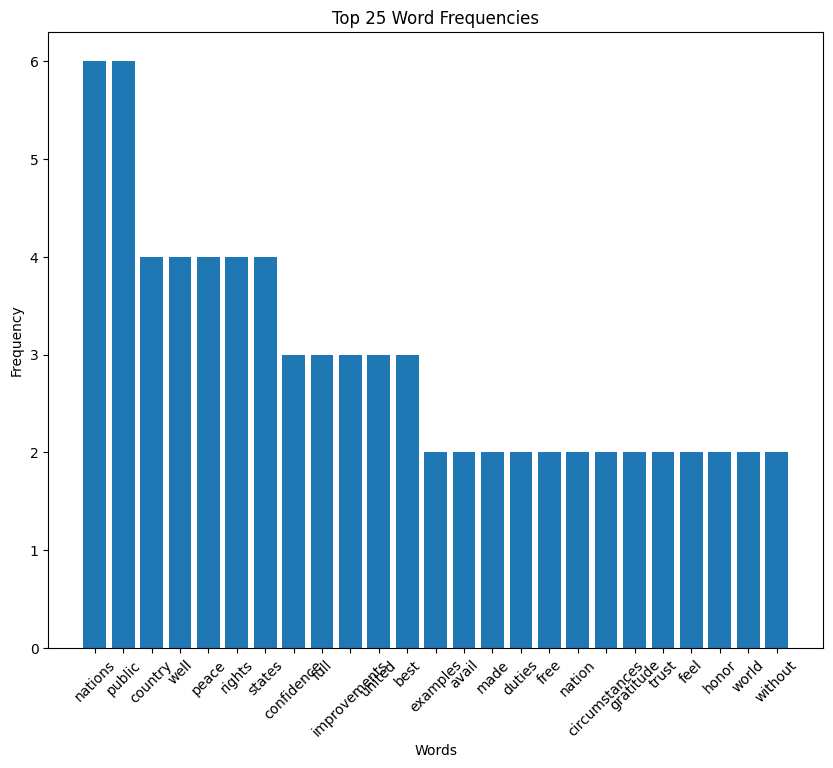
James Monroe inaugural address (1817)
Monroe speech summary
James Monroe’s first inaugural address emphasizes the strength and prosperity of the United States under self-governance, highlighting the nation’s successful navigation through challenges, both domestic and foreign — referring specifically in part to the War of 1812, or the “second war for American independence,” that the US had recently won (again) against the British. Monroe reflects on the country’s rapid growth, the happiness of its citizens, and the prosperity under the Constitution.
He commits to maintaining peace, promoting national unity, and safeguarding the nation against external threats. Monroe also stresses the importance of preparing for defense and fostering harmony and prosperity through infrastructure and domestic industry support.
For the full speech, you can visit it on GitHub.
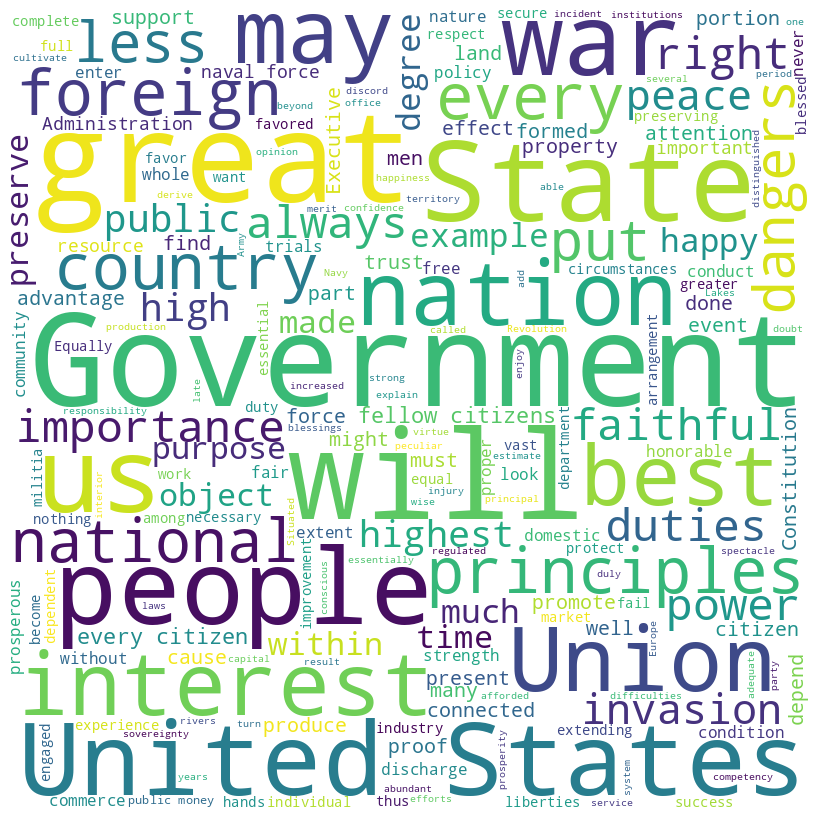
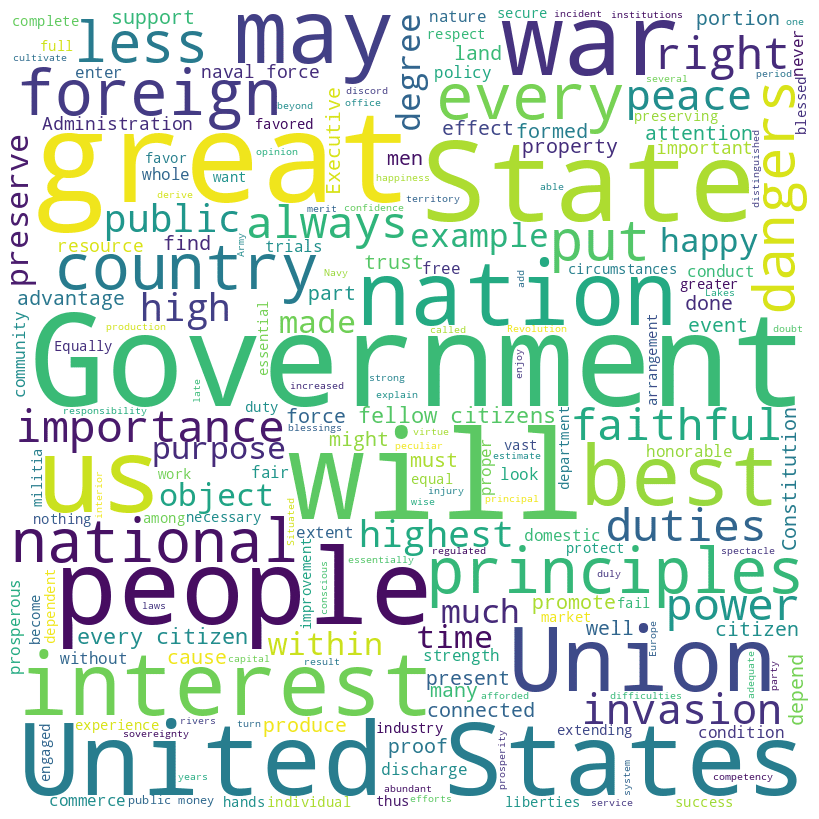
Monroe speech word cloud
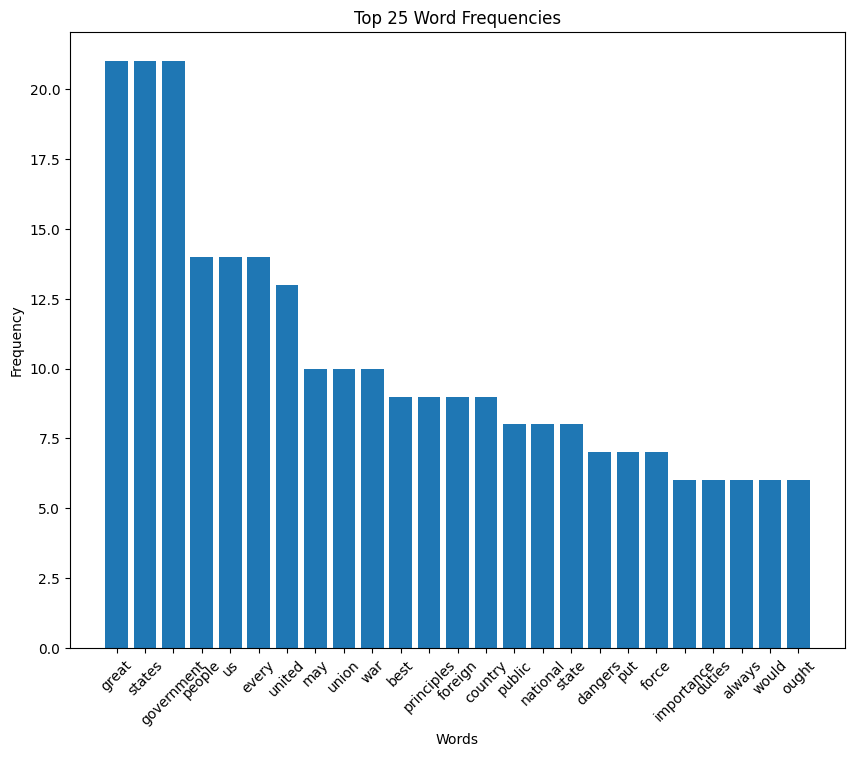
Monroe speech histogram
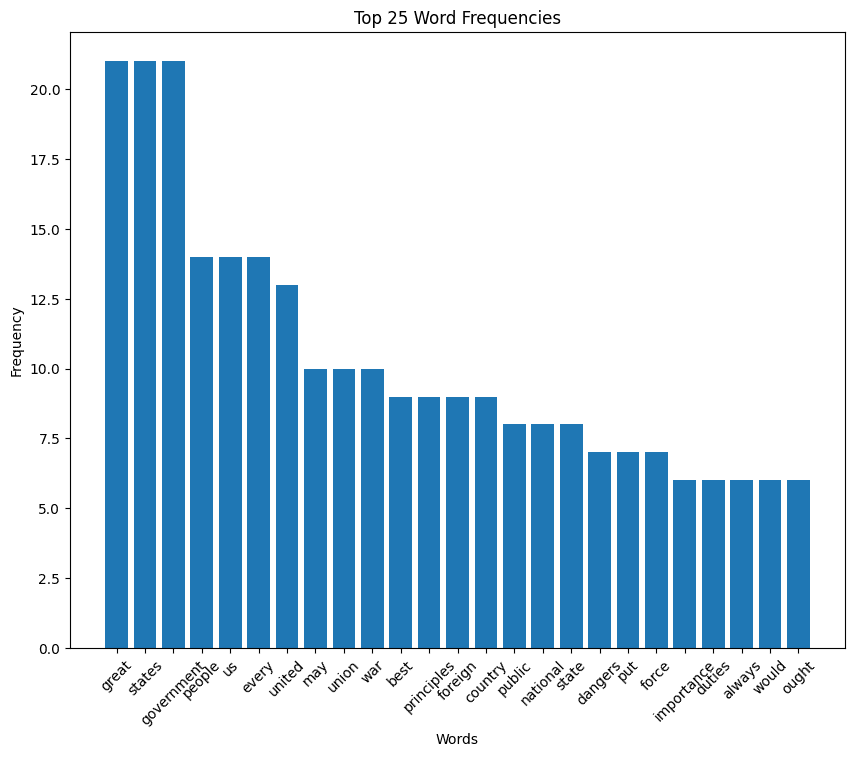
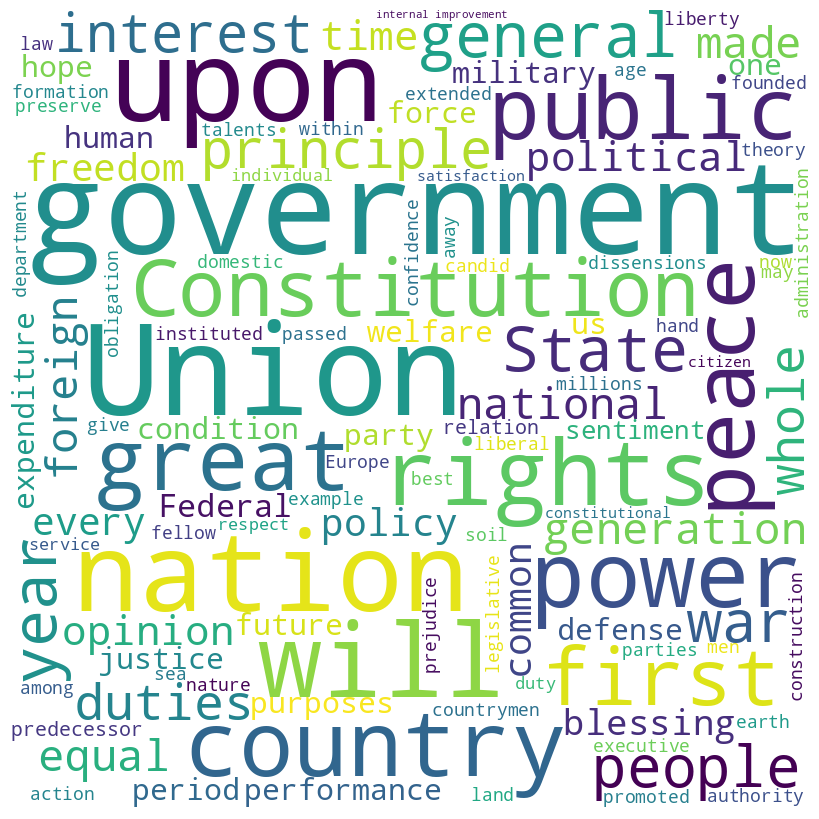
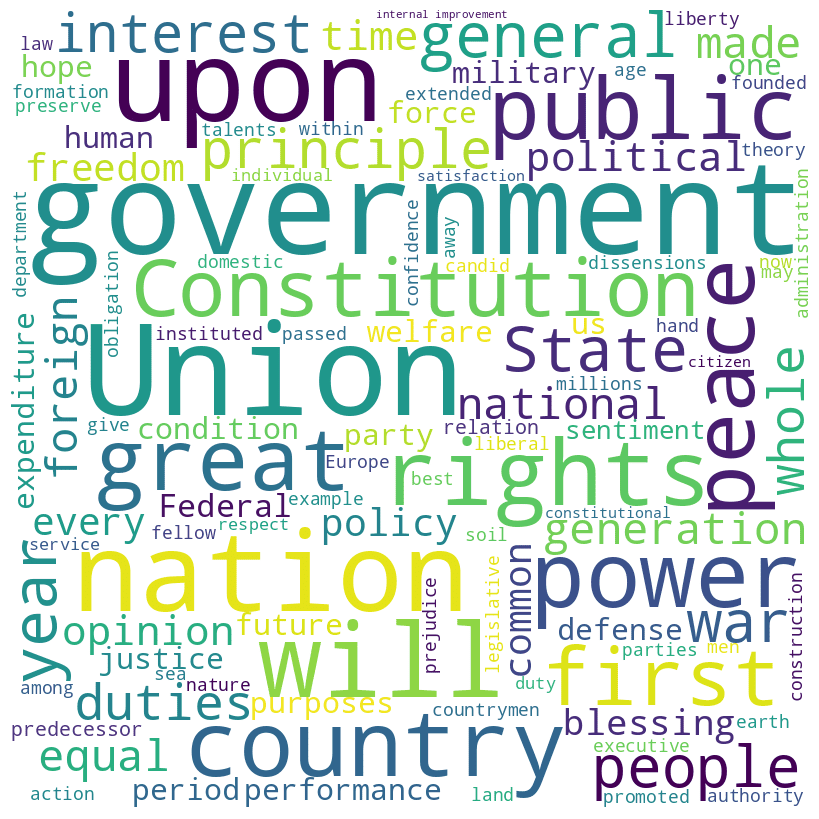
John Quincy Adams inaugural address (1825)
Adams speech summary
John Quincy Adams, in his inaugural speech of 1825, pledged to uphold the U.S. Constitution and its principles, emphasizing the duty to transmit an unimpaired legacy to future generations. He celebrated the growth and successes of the nation under the Constitution, including expansion, commerce, and liberty, while acknowledging challenges like internal dissensions and external injustices.
Adams called for unity and the dismissal of partisan prejudices, stressing the importance of internal improvements and the role of government in promoting the general welfare and securing liberty for all.
For the full speech, you can visit the original text on GitHub.
Adams speech word cloud
Adams speech histogram
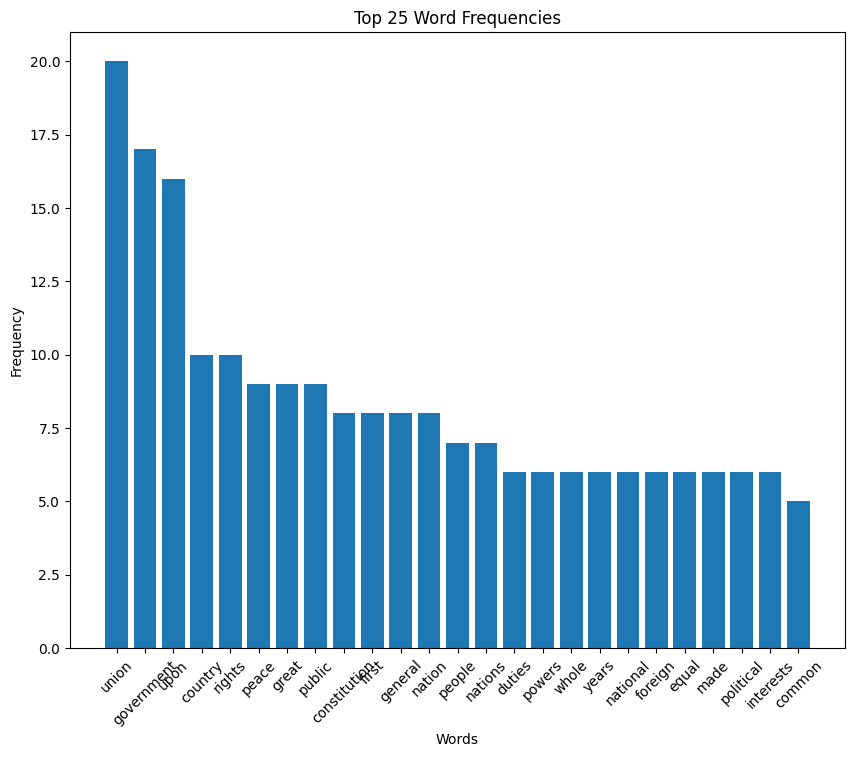
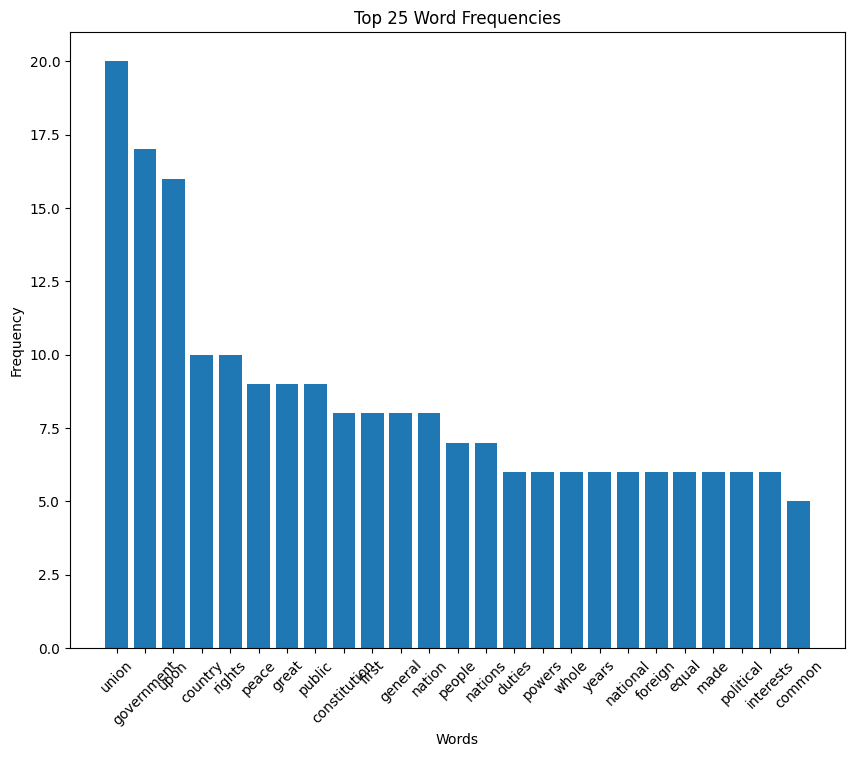
Andrew Jackson inaugural address (1829)
Jackson speech summary
In his first inaugural address, Andrew Jackson outlines his commitment to serving the American people with humility and dedication, emphasizing adherence to the Constitution, prudent foreign policy, and fiscal responsibility. He advocates for equal support of agriculture, commerce, and manufacturing, stresses the importance of internal improvements and education, and prioritizes a strong national defense with a focus on the militia.
Jackson also pledges to respect Native American rights and addresses the need for governmental reform, particularly in the civil service system, to ensure integrity and efficiency in governance. For the full text, you can visit the original on GitHub.
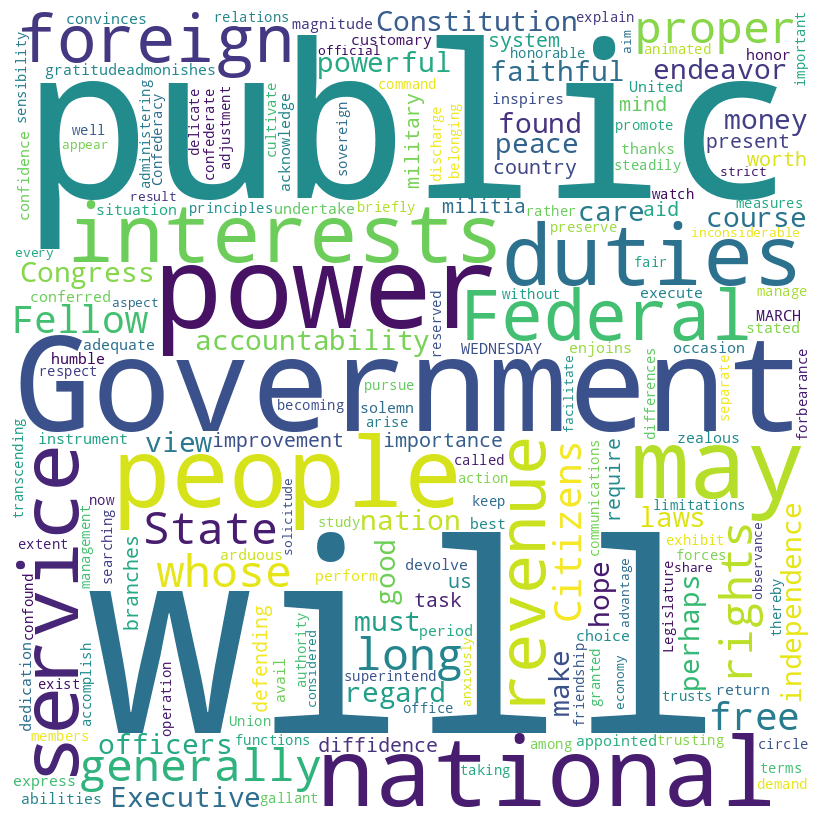
Jackson speech word cloud

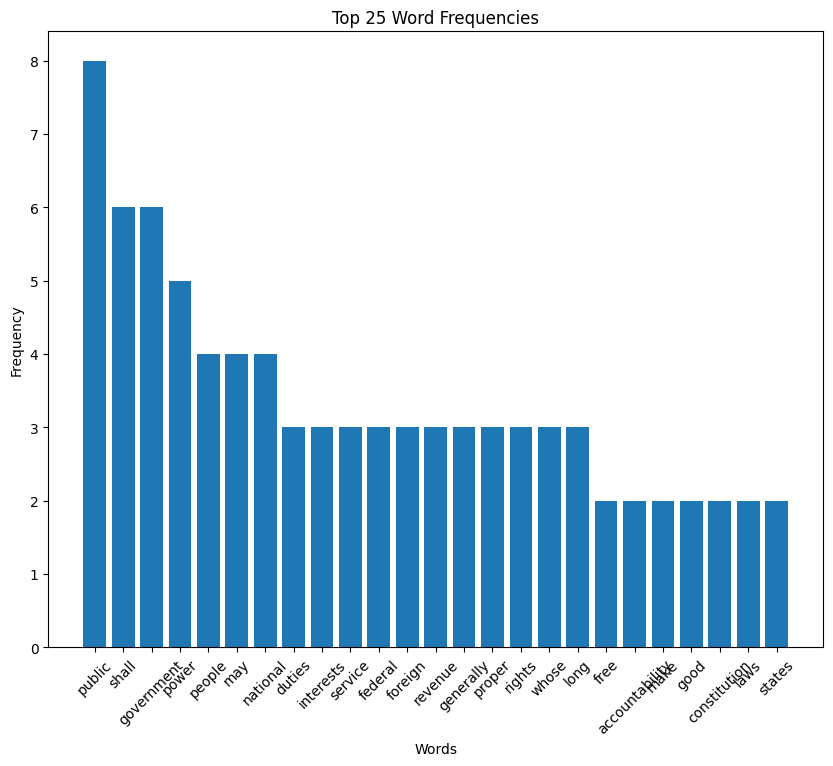
Jackson speech histogram
Martin Van Buren inaugural address (1837)
Van Buren speech summary
Martin Van Buren’s inaugural speech emphasizes the importance of adhering to the principles and compromises established by the Constitution, the significance of unity and cooperation across different government branches and states, and the need to maintain the institutions that have ensured the nation’s prosperity and stability. He acknowledges the challenges and responsibilities of his presidency, expressing reliance on the support of the people and divine providence.
Van Buren also addresses the contentious issue of slavery, advocating for a stance of non-interference by Congress in states where it exists, in line with his previously stated positions.
For the full text of the speech, you can visit my GitHub repository for the original.
Van Buren speech word cloud
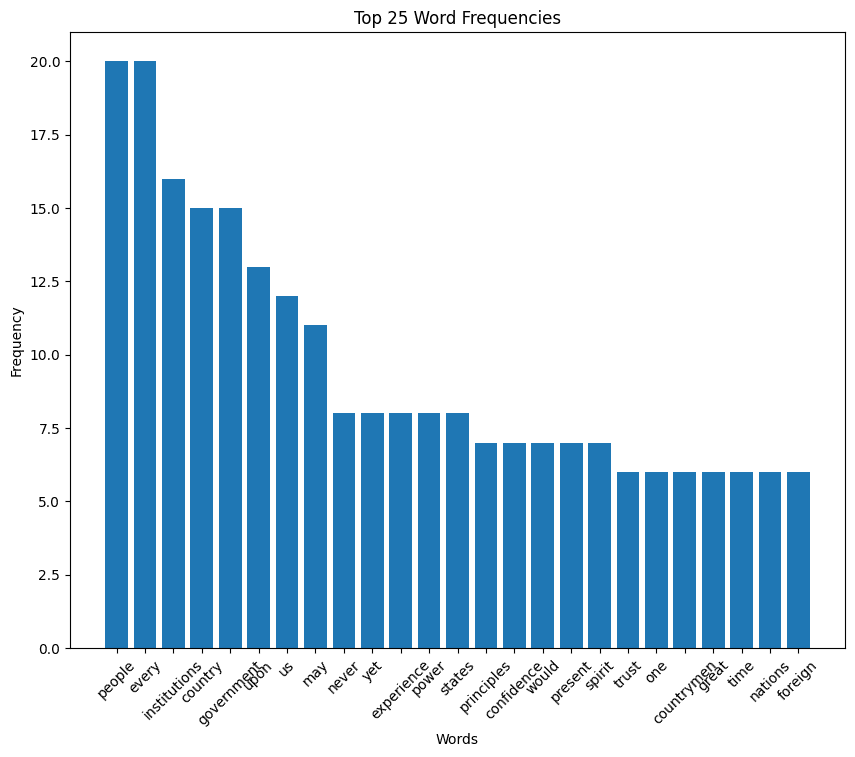
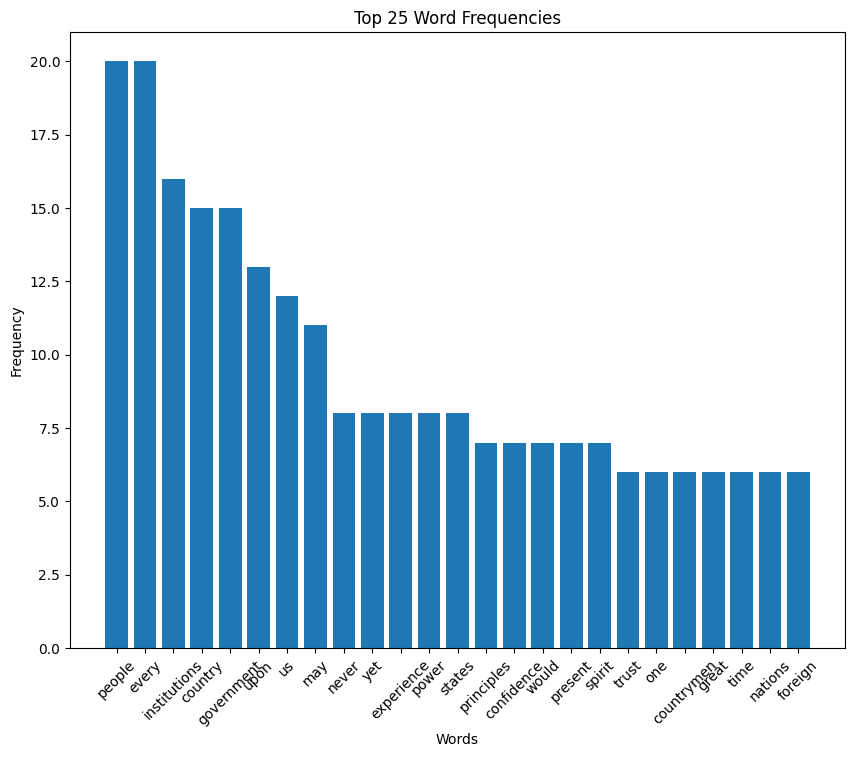
Van Buren speech histogram
William Henry Harrison inaugural address (1841)
Harrison speech summary
William Henry Harrison’s inaugural address outlines his principles and intentions as President. He would go on to have the shortest presidency in US history, dying of pneumonia he developed shortly after delivering this lengthy statement to the nation — just 32 days into his term.
Harrison emphasizes the need for adherence to the Constitution, the importance of democratic governance, and the dangers of concentrated power. Harrison also discusses the role of the executive branch, advocating for a limited term for the Presidency and cautioning against the misuse of executive power and patronage. He calls for a careful interpretation of the Constitution, fiscal responsibility, and a focus on the general welfare of the people, highlighting the importance of public opinion and constitutional amendments in shaping governance.
For the full text, you can visit the original in my GitHub repository.
Harrison speech word cloud
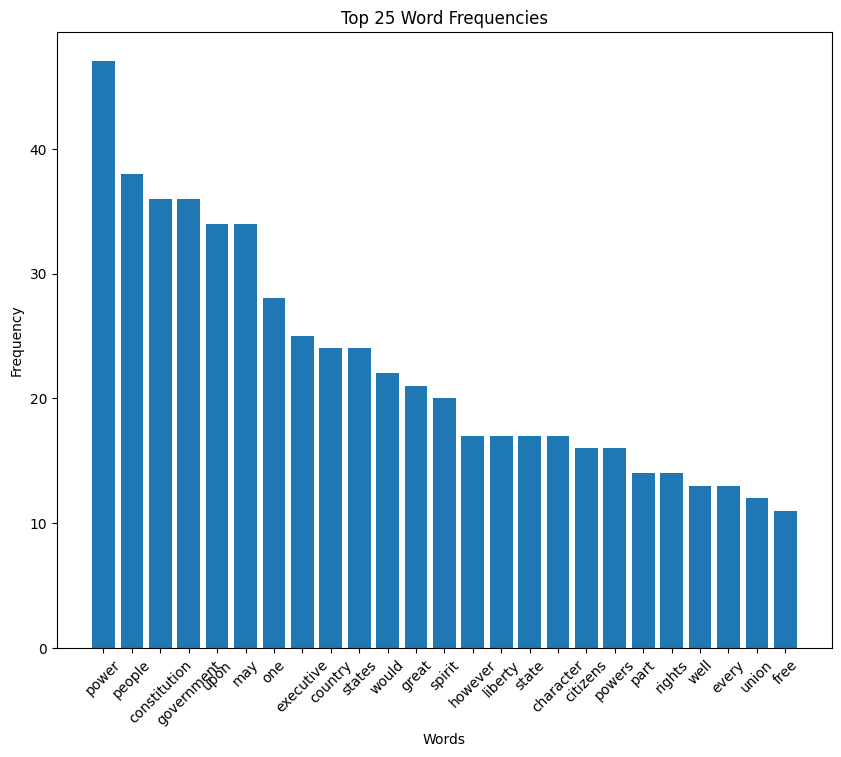
Harrison speech histogram
James K. Polk inaugural address (1845)
Polk speech summary
In his speech, James K. Polk outlines his vision and priorities for his presidency, touching upon several key areas:
- Territorial Expansion: Polk emphasizes the importance of territorial expansion as a means to ensure the nation’s security and prosperity. He is known for his expansionist policies, which later led to significant territorial acquisitions such as the Oregon Territory and parts of what is now the southwestern United States.
- Foreign Policy and Trade: He advocates for peaceful relations and commerce with foreign nations but also stresses the importance of defending American interests. Polk highlights the significance of trade and the need for fair and open commerce between nations.
- Domestic Policy and Economy: Polk discusses his views on the role of the federal government, advocating for a limited government that intervenes minimally in the lives of its citizens. He also addresses the economy, including the need for a stable currency and responsible fiscal policies.
- National Unity: Throughout his address, Polk calls for national unity and the importance of adhering to the principles of the Constitution. He emphasizes the need for all regions of the country to work together for the common good.
- Slavery: While Polk does not directly address the issue of slavery in his inaugural speech, his presidency would later be marked by this contentious issue, particularly as territorial expansion raised questions about the extension of slavery into new territories.
Polk’s presidency is often remembered for its accomplishments in territorial expansion, which played a significant role in shaping the future of the United States. His inaugural address sets the tone for these priorities and reflects the optimism and challenges of the era.
Read the full text of the original in my GitHub repository.
Polk speech word cloud

Polk speech histogram
Zachary Taylor inaugural address (1849)
Taylor speech summary
In his speech, Taylor emphasizes several key points that reflect the concerns and aspirations of the United States during his time in office. Here’s a summary:
- Unity and the Preservation of the Constitution: Taylor begins by expressing his gratitude for the trust placed in him by the American people and pledges to preserve, protect, and defend the Constitution. He emphasizes the importance of unity among the states and the need for all government officials to be guided by the Constitution.
- Federal Government and States’ Rights: He acknowledges the debate over the scope of powers between the federal government and the states. Taylor affirms his belief in a strict interpretation of the Constitution, suggesting that the federal government should exercise only those powers clearly granted to it by the Constitution, leaving all others to the states and the people.
- Domestic Policy and Internal Improvements: Taylor supports prudent management of public affairs and fiscal responsibility. He advocates for a government that is simple and efficiently managed, focusing on the common good. Taylor also mentions the importance of internal improvements and infrastructure development but cautions against unnecessary government expenditure.
- Foreign Policy: On foreign affairs, Taylor promotes a peaceful and diplomatic approach, maintaining honorable and friendly relations with other nations. He emphasizes the principle of non-interference in the internal matters of other countries and the importance of international law and treaties.
- Military and National Defense: Taylor, a military leader himself, underscores the significance of maintaining a strong defense posture for national security. He highlights the need for a well-regulated militia and a capable military to defend the country against external threats.
- Slavery and Territorial Expansion: While he does not explicitly address the contentious issue of slavery in his inaugural address, the context of his presidency is marked by tensions over slavery and its expansion into new territories. Taylor’s leadership would later be tested by these issues, although they are not directly confronted in his speech.
- Closing Remarks: Taylor concludes his address by invoking divine guidance and expressing his hope for the country’s prosperity and the well-being of its people. He acknowledges the challenges ahead and pledges to serve with integrity and dedication.
Taylor’s inaugural address reflects the concerns of a nation on the cusp of major social and political changes. His emphasis on constitutional principles, states’ rights, and fiscal responsibility, along with a cautious approach to foreign policy, underscores the themes of his presidency in the mid-19th century American context.
Taylor speech word cloud
Taylor speech histogram
Franklin Pierce Inaugural Address (1853)
Pierce speech summary
Franklin Pierce’s inaugural address, delivered on March 4, 1853, emphasizes his humility and sense of responsibility in assuming the presidency. He acknowledges the nation’s confidence in him while recognizing the weight of his obligations.
Pierce reflects on the United States’ growth and strength since its founding, highlighting the importance of adhering to constitutional principles and maintaining national unity. He advocates for peaceful expansion and non-interference in foreign territories, stresses the importance of military readiness without large standing armies, and pledges to uphold the Constitution and the rights of states and individuals.
Pierce also reaffirms his commitment to enforcing the Compromise of 1850 — obliquely referring to the issue of slavery — and expresses hope for the resolution of sectional tensions, underlining the necessity of national reliance on divine guidance for security and prosperity.
For a more detailed reading, you can view the original text on GitHub.
Pierce speech word cloud
Pierce speech histogram
James Buchanan inaugural address (1857)
Buchanan speech summary
In his inaugural address, new President James Buchanan touches upon several key points and themes that were relevant to the United States at that time. Here’s a summary of the main points from his speech:
- Unity and Sectionalism: Buchanan speaks about the importance of maintaining the Union and addressing the sectional differences that threatened it. He emphasizes the need for harmony and cooperation among the various states and regions.
- Constitution and Slavery: He discusses the contentious issue of slavery, advocating for the rights of states as outlined in the Constitution. Buchanan supports the idea that states should decide on the matter of slavery within their own borders, referencing the ongoing legal case (Dred Scott v. Sandford) that was pending a Supreme Court decision at the time of his inauguration.
- Territorial Expansion: Buchanan mentions the expansion of the United States’ territory, expressing a desire to see the nation grow. However, he insists that any expansion should not disturb the peace or create conflict among the existing states, especially concerning the issue of slavery.
- Foreign Policy: He talks about foreign relations, stating his intention to maintain peaceful and friendly interactions with other nations. Buchanan expresses a commitment to respecting the sovereignty and rights of other countries.
- Domestic Policy and Administration Goals: Buchanan outlines his goals for domestic policy, including the improvement of infrastructure and the administration of justice. He emphasizes the importance of adhering to the Constitution and the laws of the land.
- Appeal for Unity: Throughout the speech, Buchanan appeals to the American people’s sense of unity and patriotism. He calls for an end to the bitter sectionalism that had been growing in the country and asks for the support of the American people in preserving the Union.
Buchanan’s inaugural address reflects the challenges and concerns facing the United States on the eve of the Civil War. He attempts to address the divisive issues of the time, particularly slavery, with a call for adherence to the Constitution and legal process. However, his presidency would ultimately see an increase in the tensions that led to the Civil War.
Buchanan speech word cloud
Buchanan speech histogram
Abraham Lincoln inaugural address (1861)
Lincoln speech summary
Abraham Lincoln’s First Inaugural Address, delivered on March 4, 1861, seeks to reassure the nation amidst the secession crisis, after the Confederate states took the unprecedented step of leaving the Union. Lincoln emphasizes his commitment to not interfere with slavery in states where it exists and underscores the perpetual nature of the Union, arguing that no state can lawfully secede.
He advocates for compliance with existing laws, including the return of fugitive slaves, and calls for calm and patience to resolve national differences. Lincoln concludes by appealing for unity and the avoidance of conflict, emphasizing that Americans are not enemies but friends.
Lincoln speech word cloud
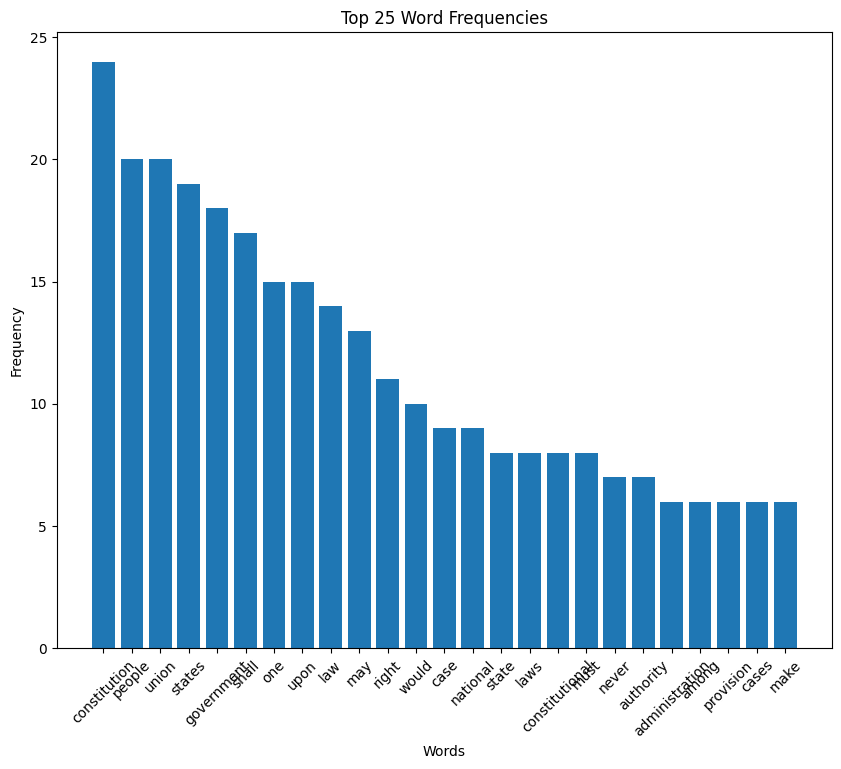
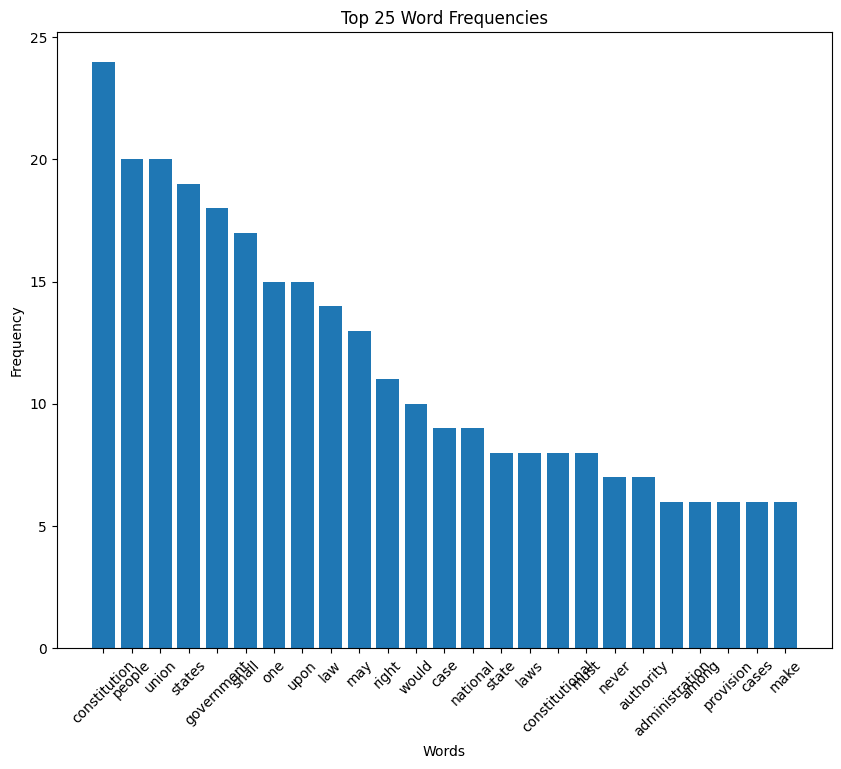
Lincoln speech histogram
Ulysses S. Grant inaugural address (1869)
Grant speech summary
In his inaugural speech, Ulysses S. Grant discusses his commitment to faithfully executing the duties of the presidency without personal bias, emphasizing the importance of enforcing laws equitably, addressing the nation’s debt, and promoting economic stability. He advocates for gold-backed government debt repayment, fiscal responsibility, and the support of commerce and industry recovery.
Grant also highlights the need for national unity, the resumption of specie payments, and the importance of civil rights, including advocating for the ratification of the fifteenth amendment to secure suffrage for all citizens. He calls for patience and collective effort towards national harmony, underscoring the role of divine guidance in achieving these goals.
For a full read of the speech, you can visit the original text on GitHub.
Grant speech word cloud
Grant speech histogram
Rutherford B. Hayes inaugural address (1877)
Hayes speech summary
Rutherford B. Hayes’s inaugural address in 1877 emphasized unity and reconciliation post-Civil War, focusing on civil rights protection, local self-government, and racial harmony following the end of slavery.
Hayes advocated for economic recovery, education for all, civil service reform, and a non-interference foreign policy. Hayes called for cooperation beyond party lines, emphasizing the national welfare over partisan interests and proposing a single six-year presidential term without reelection to reduce political strife.
For the full text of the speech, you can visit my GitHub repository.
Hayes speech word cloud
Hayes speech histogram
James A. Garfield inaugural address (1881)
Garfield speech summary
James A. Garfield’s inaugural speech, delivered on March 4, 1881, reflects on a century of American history, emphasizing the triumphs of liberty and law. He discusses the evolution of the U.S. Constitution, its role in expanding freedom, and the challenges and successes of the Union, particularly through the Civil War.
Garfield highlights the importance of education, the integration of African Americans into society, and the need for honest, free elections. He advocates for economic stability, agricultural support, industrial growth, and the improvement of transportation. Finally, he addresses religious freedom, the civil service, and calls for unity and progress under the Constitution and divine guidance.
Garfield speech word cloud
Garfield speech histogram
Grover Cleveland inaugural address (1885)
Cleveland speech summary
Grover Cleveland’s first inaugural address emphasizes a commitment to public service, the importance of democratic principles, and the need for a government that serves all people equally. He discusses the significance of responsibly executing the will of the people, adheres to a policy of non-intervention in foreign affairs, and stresses the importance of civil service reform and fiscal responsibility.
Cleveland also calls for national unity, respect for the Constitution, and attention to the welfare of all citizens, including the protection and education of Native Americans and the enforcement of laws against polygamy and unfair labor competition.
Cleveland speech word cloud
Cleveland speech histogram
Benjamin Harrison inaugural address (1889)
Harrison speech summary
Harrison’s address covers several key themes and priorities of his administration, reflecting the political and social climate of the late 19th century. Here’s a summary:
- Appreciation and Humility: Harrison begins by expressing his gratitude for the trust placed in him by the American people and acknowledges the responsibility and challenges that come with the presidency.
- Constitution and Governmental Principles: He emphasizes the importance of the Constitution, the rule of law, and the need for a government that is both strong and just. Harrison also touches upon the balance of power between the different branches of government and the roles of the federal and state governments.
- Economic Policies: Harrison advocates for economic policies that would encourage growth and prosperity. He discusses tariffs, trade, and the need to protect American industries and labor. He supports a taxation system that is fair and provides sufficient revenue for the government without burdening the people.
- Civil Service Reform: He calls for reforms in the civil service to ensure that government positions are filled based on merit rather than political affiliation, emphasizing the need for efficiency and integrity in public service.
- Veterans’ Affairs: Harrison pays tribute to the veterans of the Civil War, stressing the nation’s obligation to care for those who have served and sacrificed for their country.
- Foreign Policy: He outlines a foreign policy based on peace, diplomacy, and the protection of American interests abroad. Harrison expresses a desire for friendly relations with other nations while maintaining a strong national defense.
- Education and Social Issues: The address highlights the importance of education, moral values, and the welfare of the nation’s citizens. Harrison expresses concern for social issues, including the rights and conditions of workers and the need for social reform.
- National Unity and Patriotism: Finally, Harrison calls for national unity, patriotism, and a commitment to the common good. He emphasizes the strength derived from diversity and the importance of working together for the nation’s prosperity and well-being.
Benjamin Harrison’s inaugural address sets forth his vision for his presidency, focusing on governance, economic prosperity, social reform, and national unity. It reflects the issues and concerns of the United States at the turn of the 20th century and lays out Harrison’s priorities and policies for his term in office.
Harrison speech word cloud

Harrison speech histogram
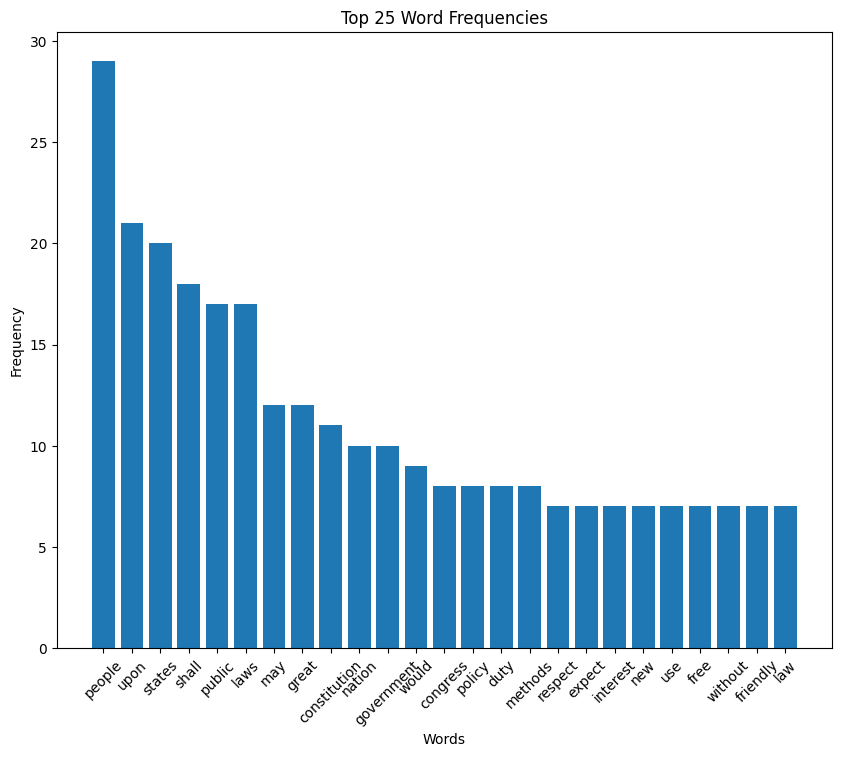
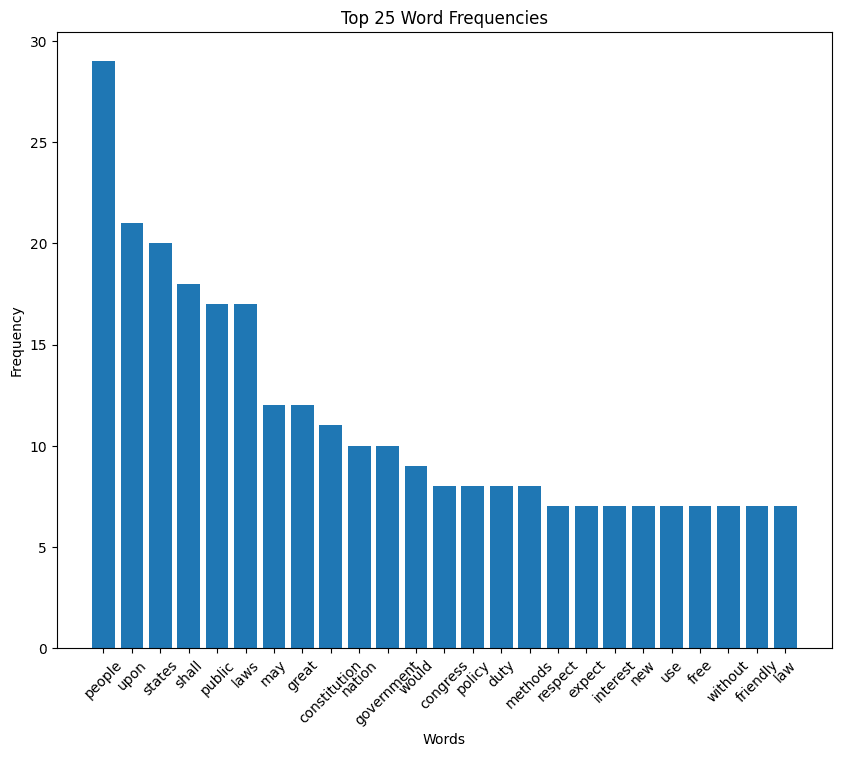
William McKinley inaugural address (1897)
McKinley speech summary
William McKinley’s inaugural address in 1897 emphasized economic reform, advocating for a protective tariff to support American industries and the maintenance of the gold standard to ensure currency stability. He called for fiscal responsibility and a balanced budget, highlighting the need for revenue reform to prevent government debt.
McKinley also supported international bimetallism and proposed the creation of a commission to review financial laws. Furthermore, he emphasized national unity and the adherence to principles of free speech, education, and law and order, while promoting a foreign policy of non-interference and peace.
McKinley speech word cloud
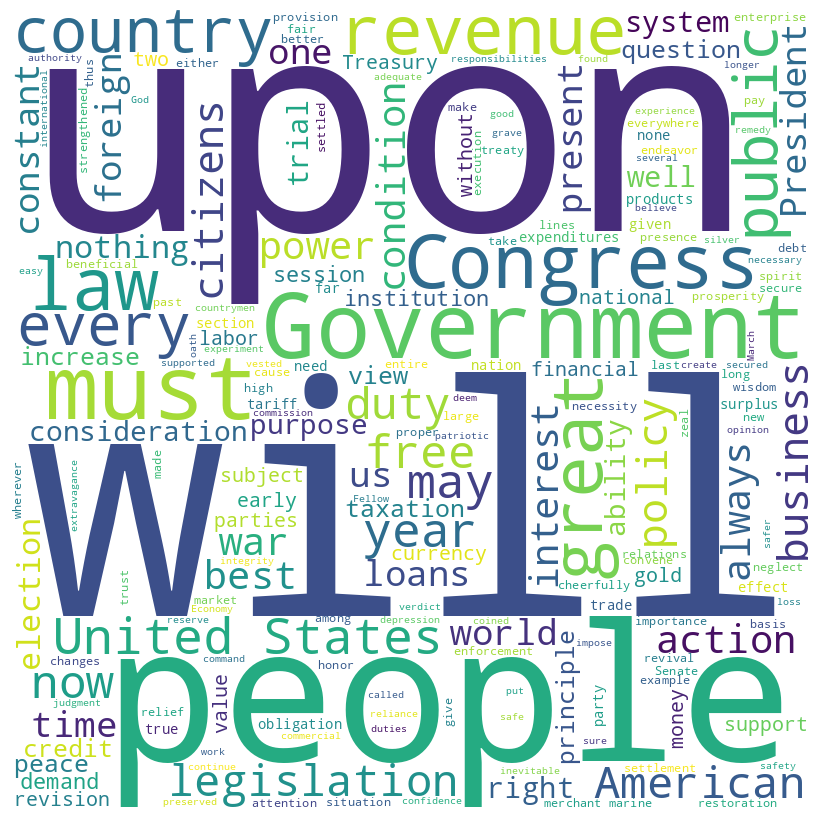
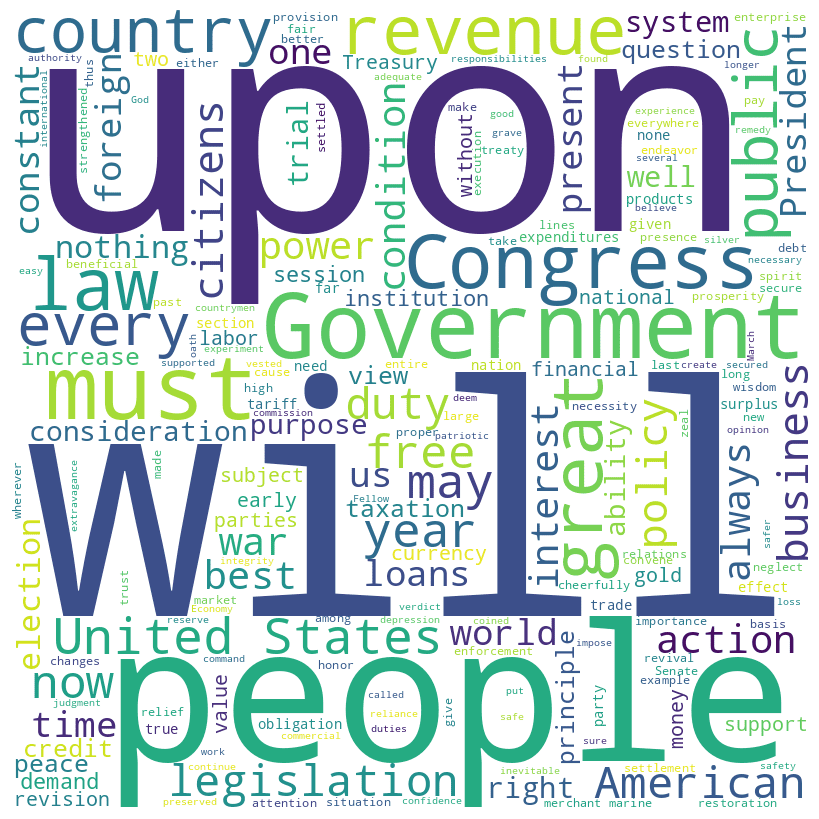
McKinley speech histogram
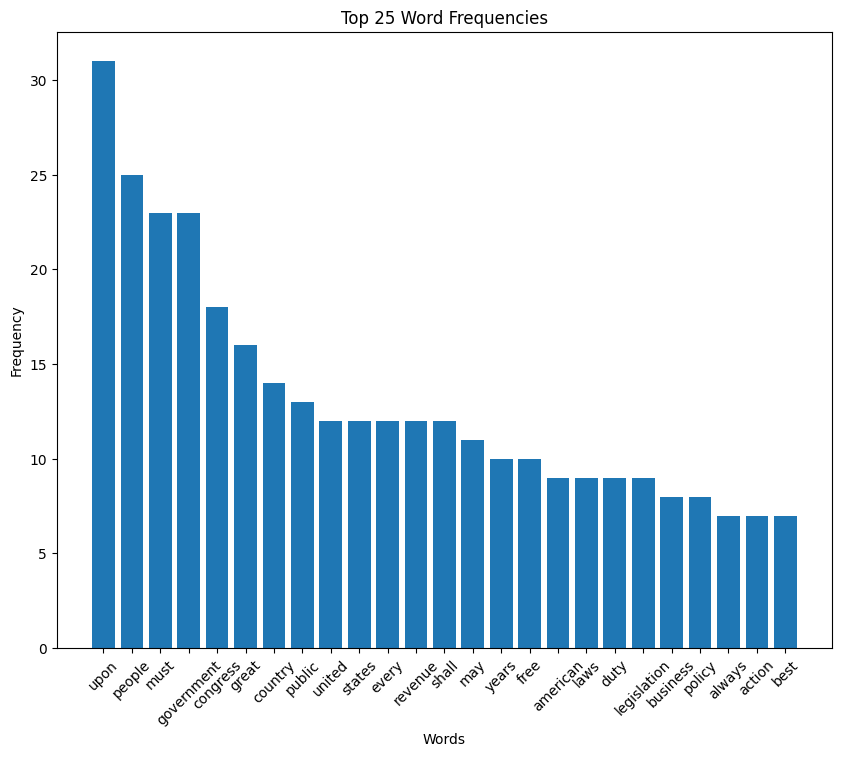
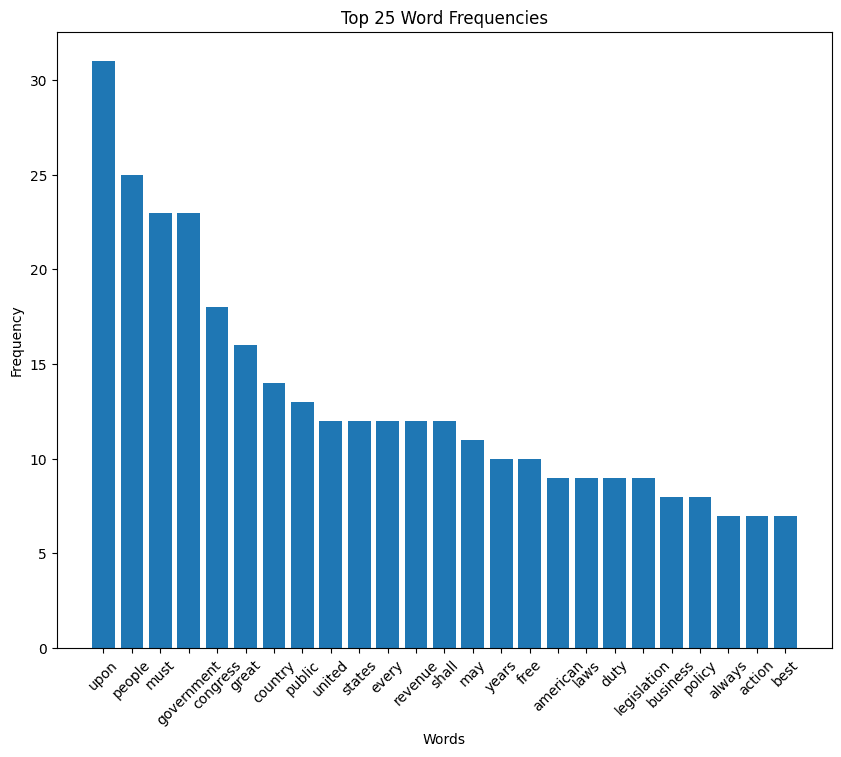
Teddy Roosevelt inaugural address (1905)
Roosevelt speech summary
In his 1905 inaugural address, Theodore Roosevelt spoke to the nation with a tone of humility and responsibility. He emphasized the unique position of the United States, blessed with prosperity and tasked with a moral and civic duty to use its greatness responsibly.
Roosevelt called for a commitment to justice, righteousness, and peace in both domestic and international relations, stressing the importance of acting with honor and strength. He highlighted the challenges of modern life and the need for courage, intelligence, and devotion to ideals, urging Americans to uphold the legacy of the Republic’s founders and to pass on a fortified heritage to future generations.
Roosevelt speech word cloud
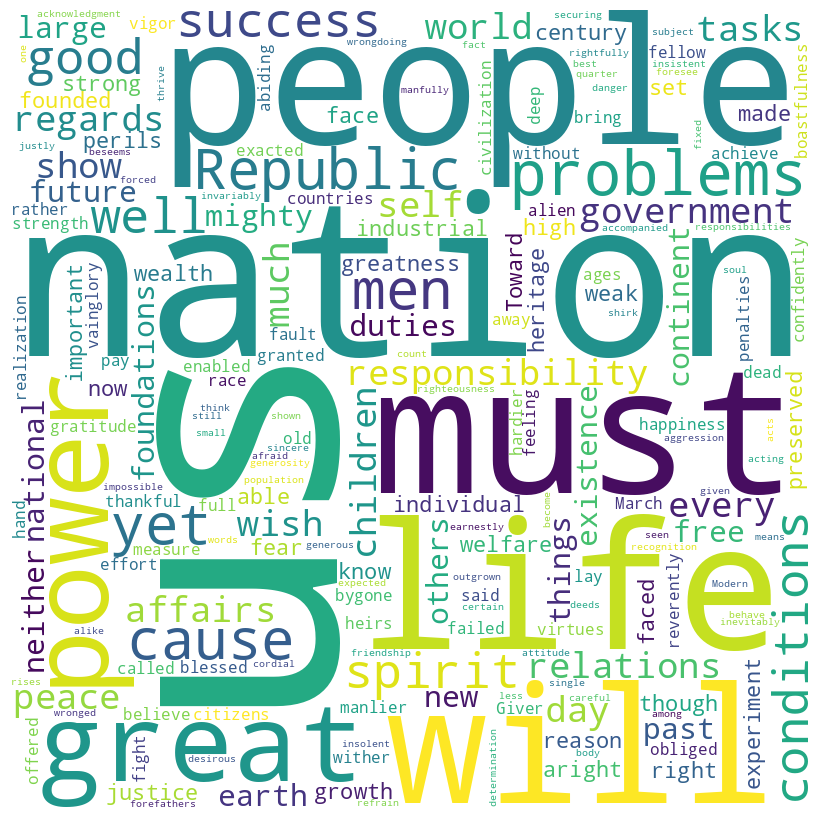
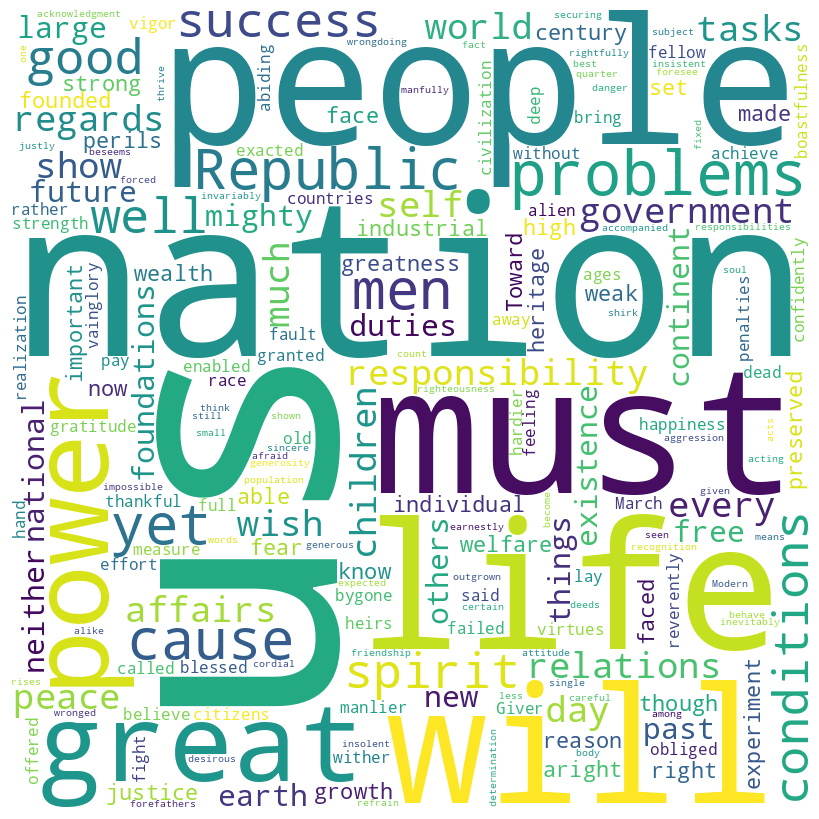
Roosevelt speech histogram
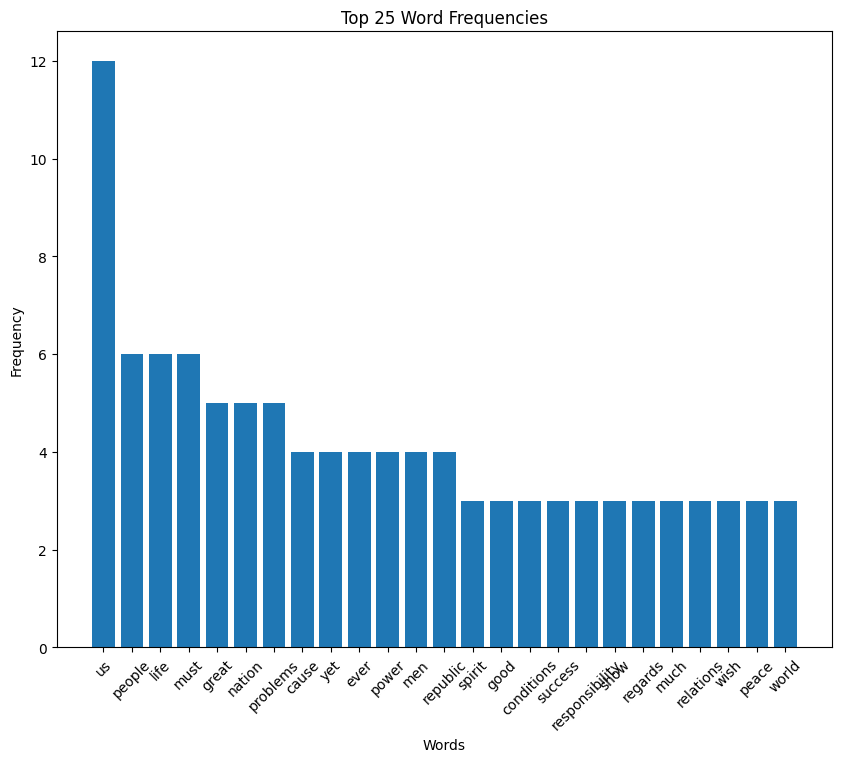
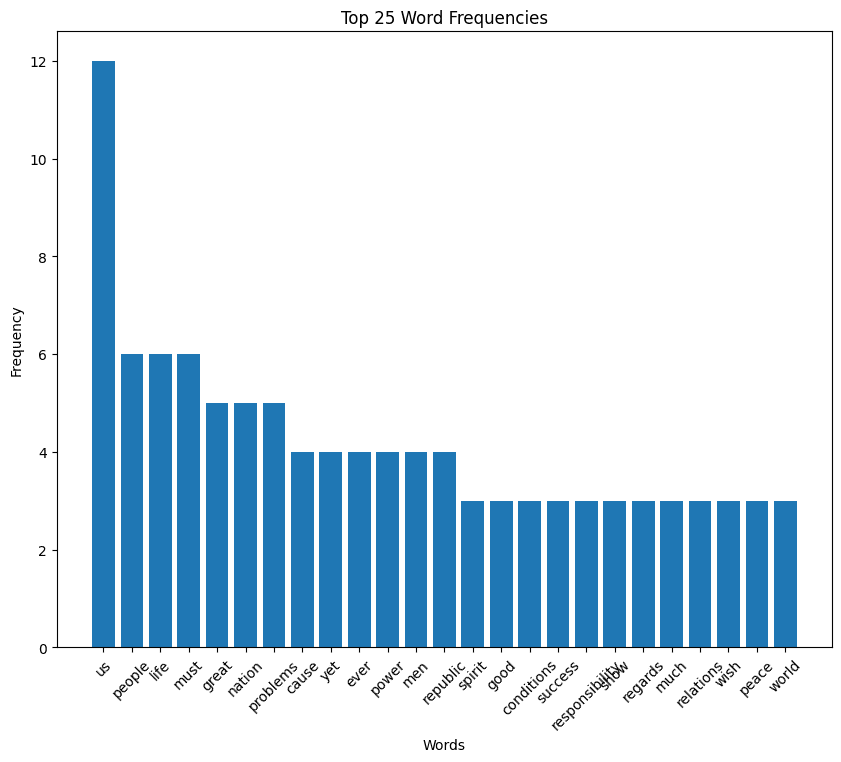
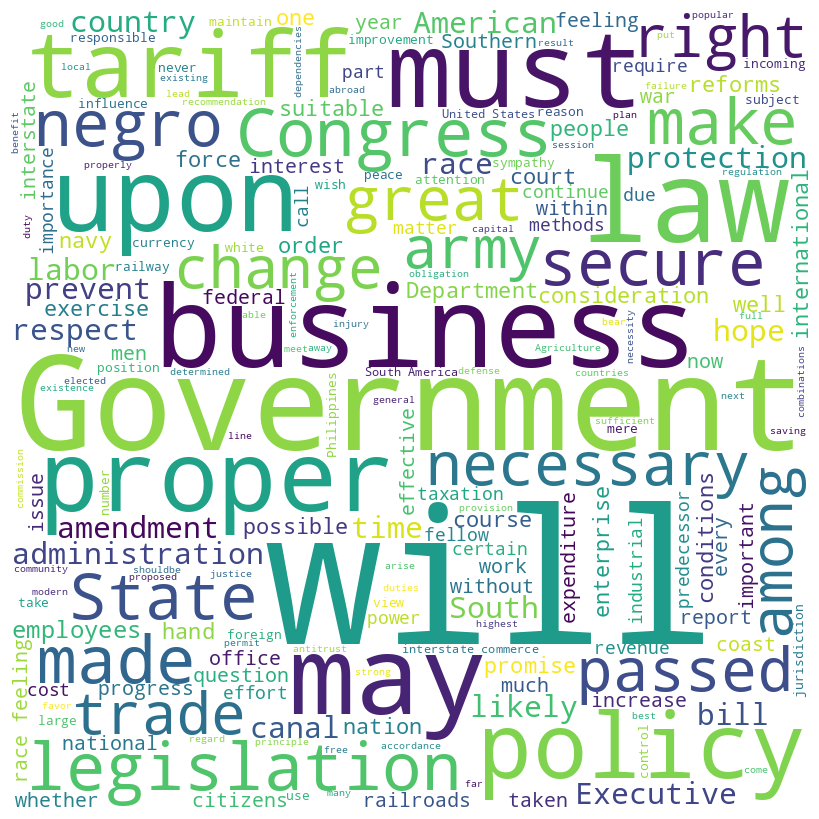
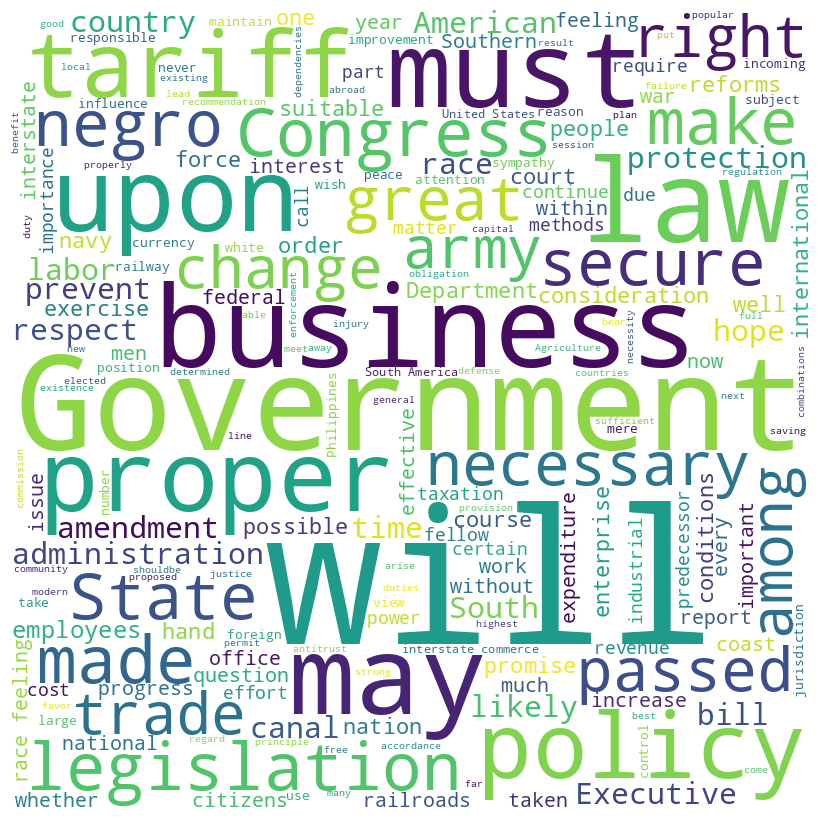
William Howard Taft inaugural address (1909)
Taft speech summary
William H. Taft’s inaugural address focuses on his commitment to continuing and enhancing the reforms initiated by his predecessor, especially those targeting the abuses of large corporations and improving interstate commerce regulations. He emphasizes the importance of further legislative and executive action to ensure economic stability, fair business practices, and the protection of legitimate business against monopolies.
Taft also outlines plans for tariff revision, advocating for adjustments to secure adequate revenue and protect American industries, and stresses the importance of maintaining a strong military and naval presence for national security and international respect.
Taft speech word cloud
Taft speech histogram
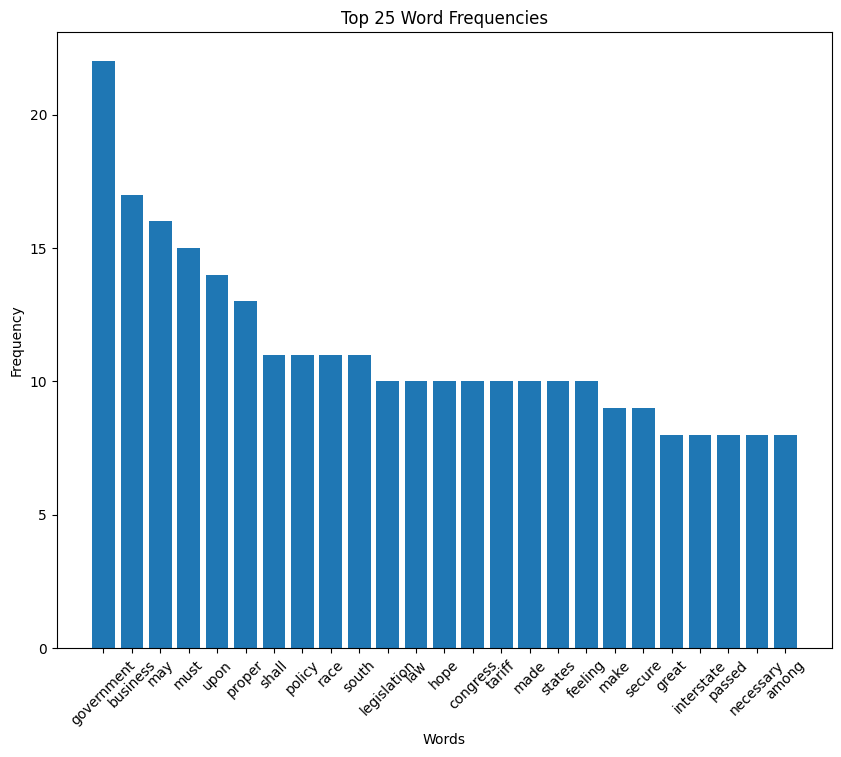
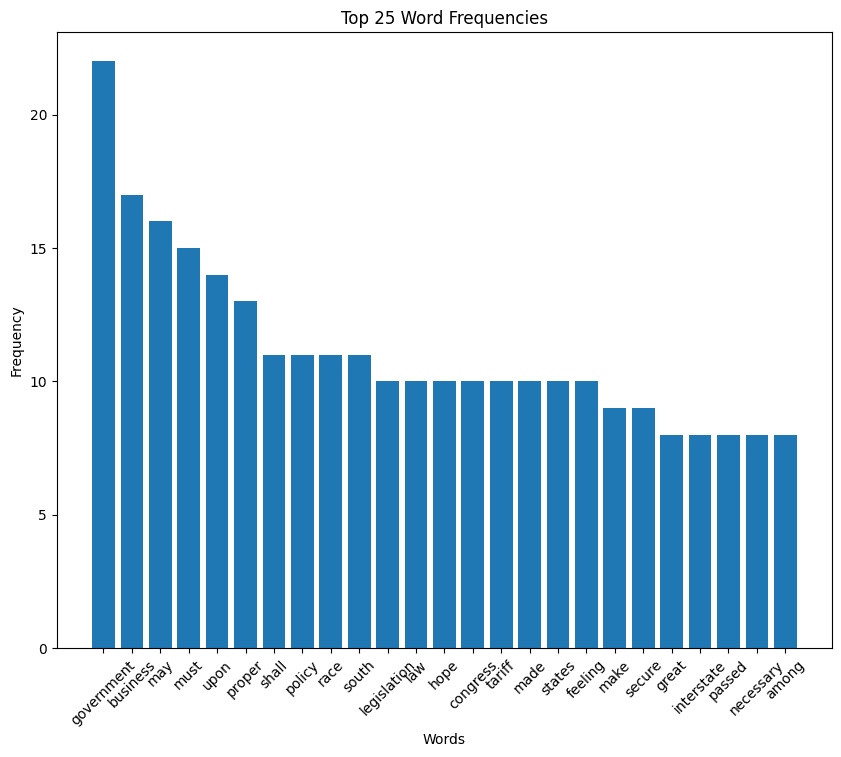
Woodrow Wilson inaugural address (1913)
Wilson speech summary
Woodrow Wilson’s inaugural speech on March 4, 1913, emphasizes a transformative vision for America, highlighting a shift towards Democratic governance and a critique of past industrial and governmental excesses. He calls for a renewal focused on justice, economic reform, and societal well-being, stressing the importance of addressing labor conditions, conservation, and equitable economic systems.
Wilson frames this change as a moral and practical duty, urging unity and action to rectify inequalities and promote a healthier, more just society.
You can read the full speech on GitHub.
Wilson speech word cloud
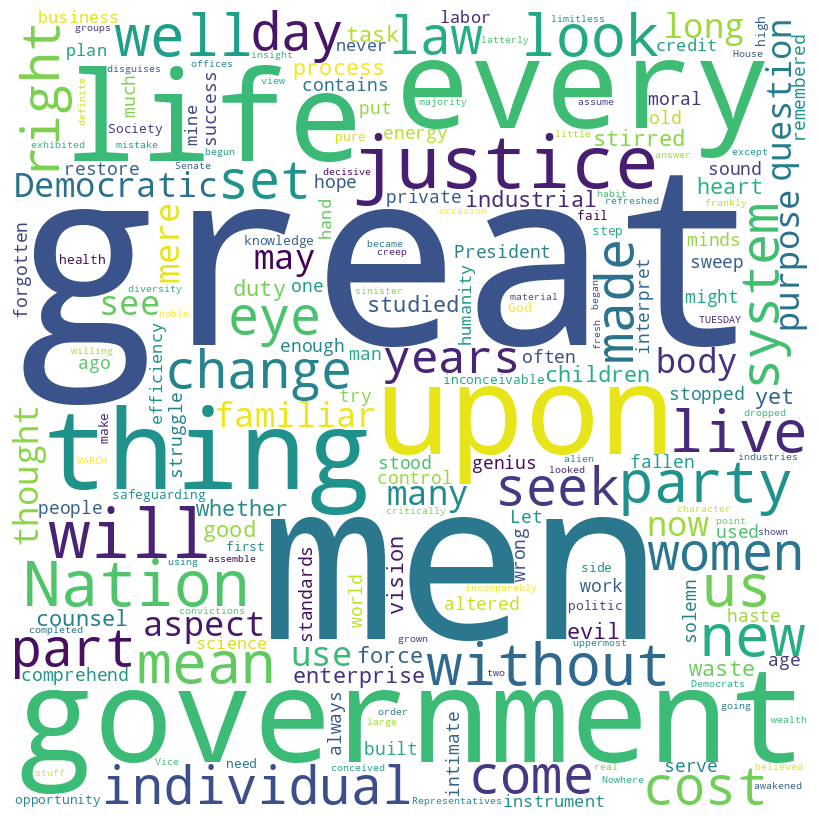
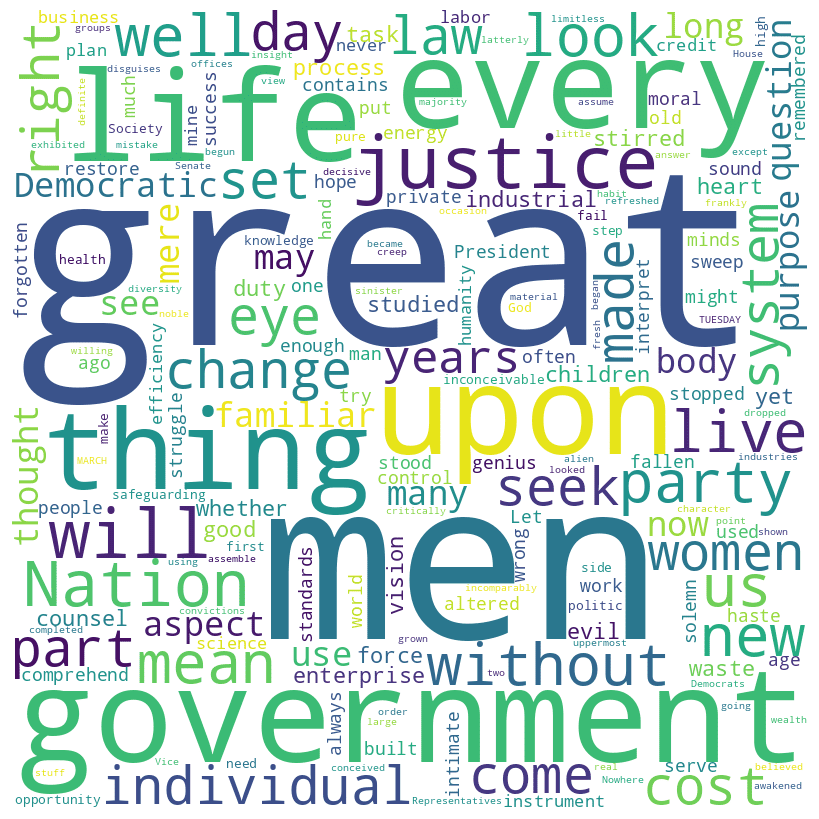
Wilson speech histogram
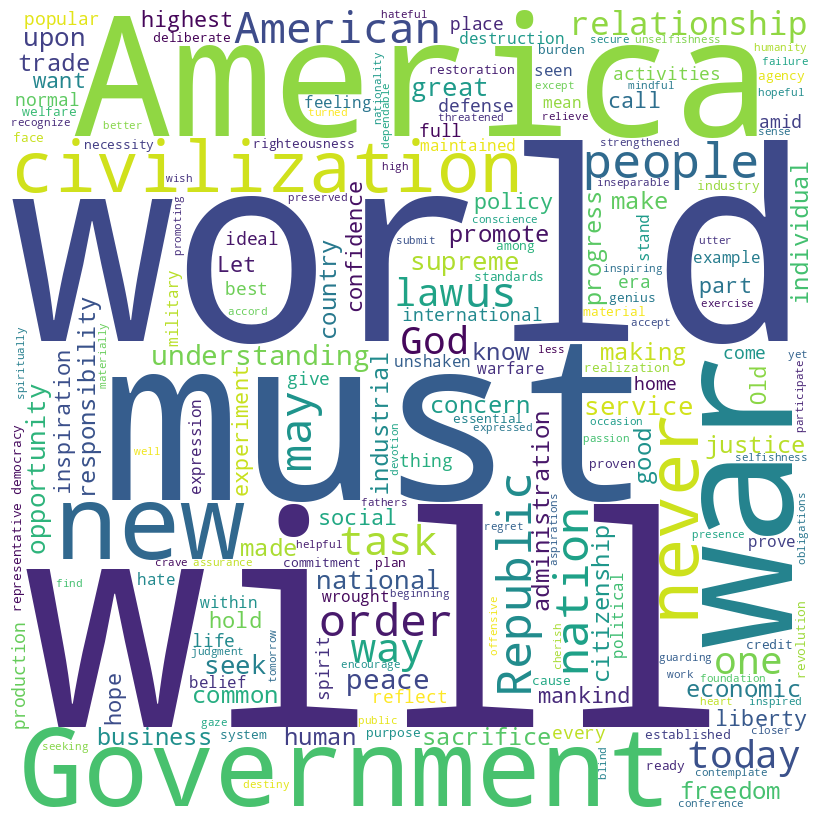
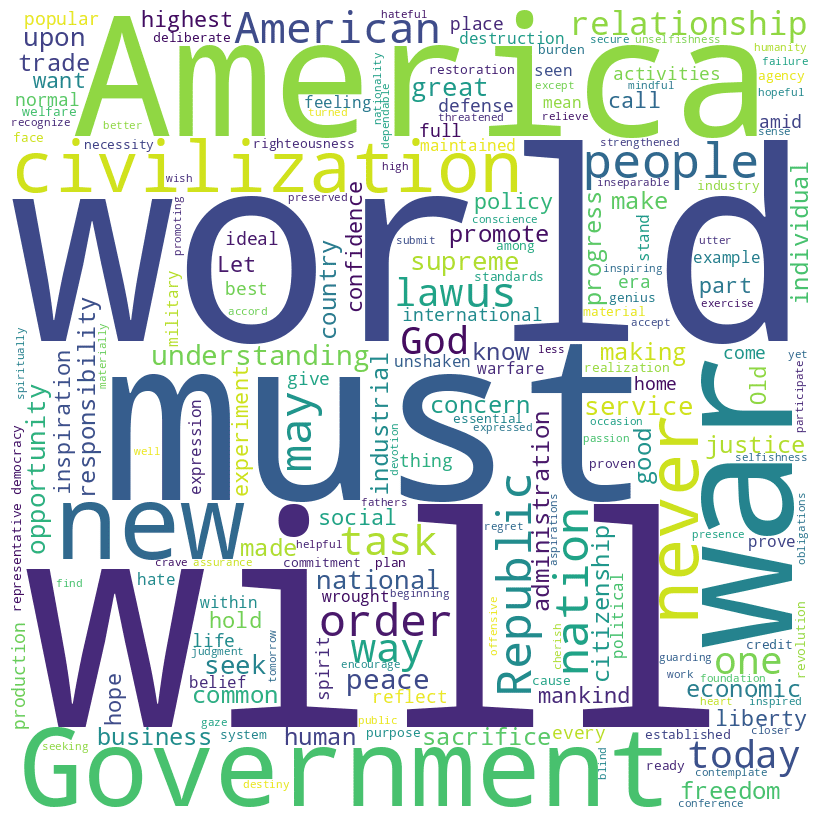
Warren G. Harding inaugural address (1921)
Harding speech summary
Warren G. Harding’s inaugural address, delivered on March 4, 1921, emphasizes hope and resilience after the end of World War I. He champions liberty, representative government, and non-involvement in Old World affairs, advocating for America to focus on its own destiny and independence.
Harding rejects military alliances and economic obligations that compromise national sovereignty. He calls for disarmament, international cooperation without compromising American principles, and a return to normalcy post-war — with a focus on economic readjustment, fiscal responsibility, and unity. Harding envisions an America that promotes peace, justice, and prosperity both domestically and internationally.
For a more detailed exploration, you can read the full text on GitHub.
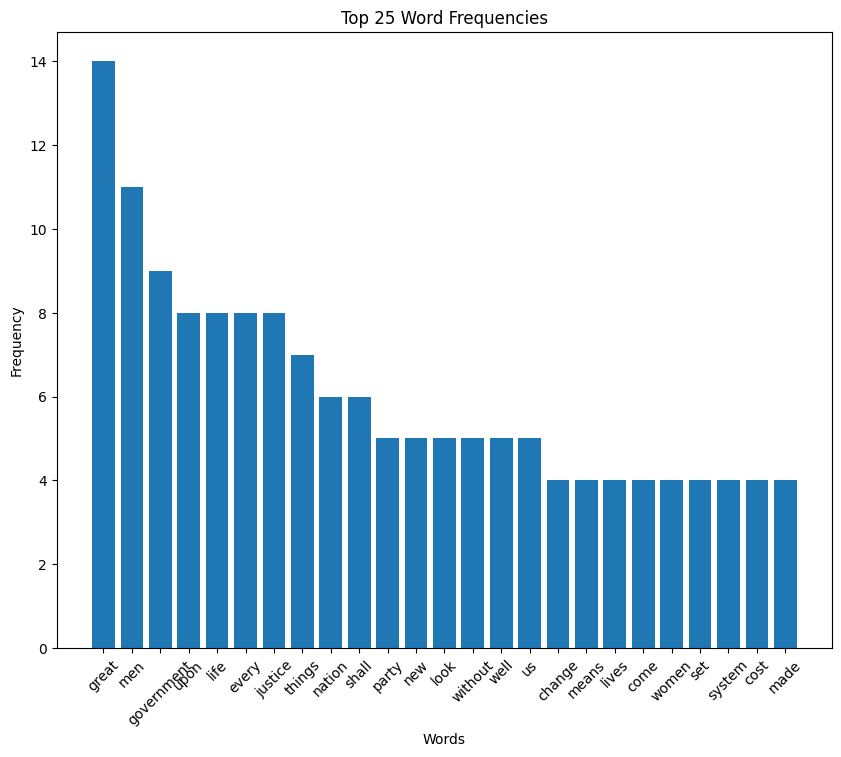
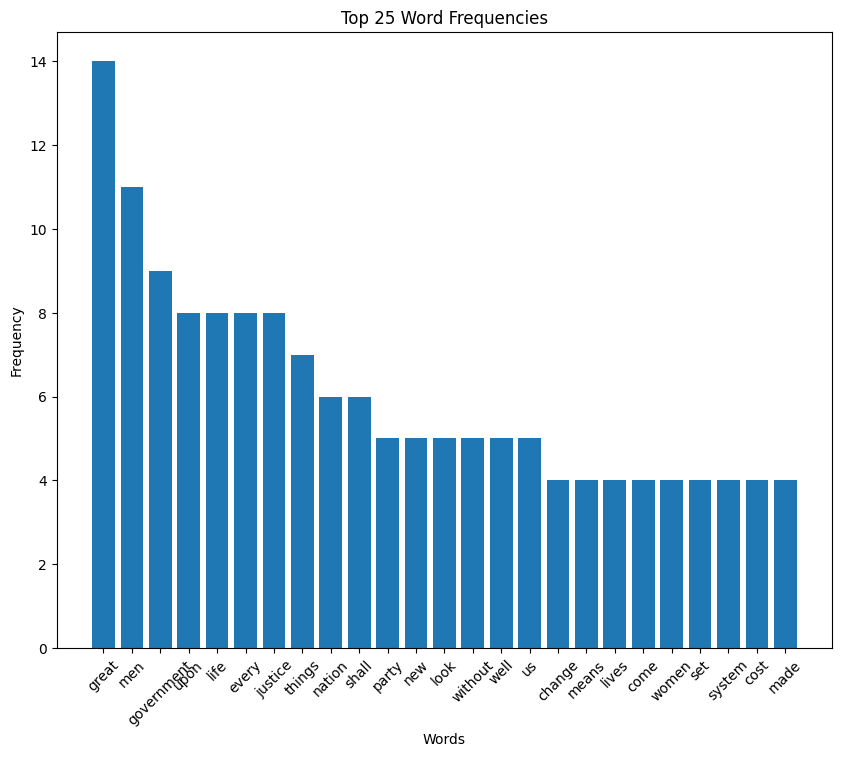
Harding speech word cloud
Harding speech histogram
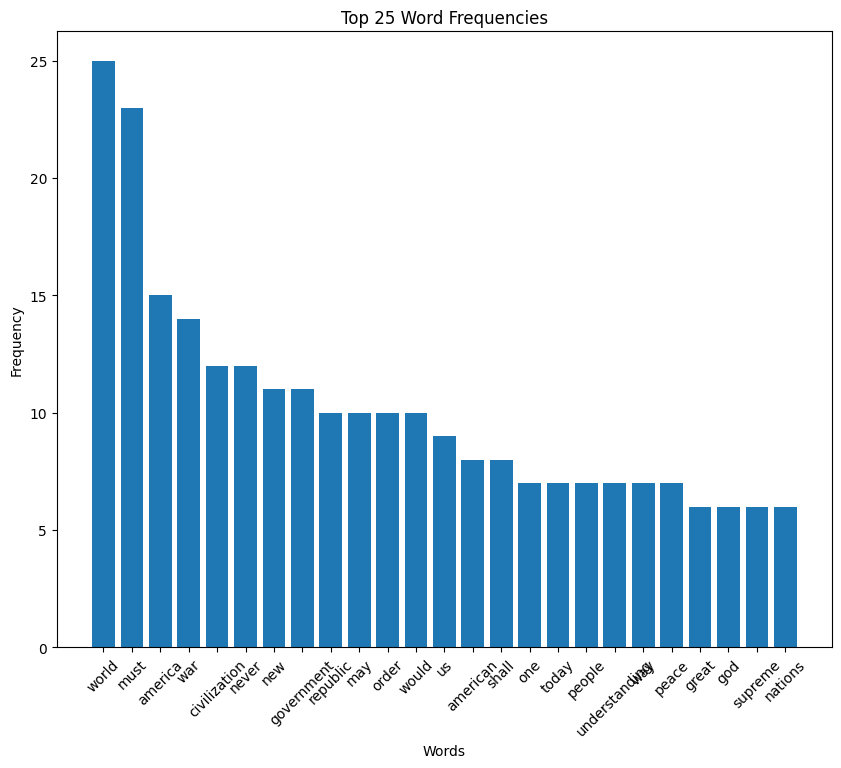
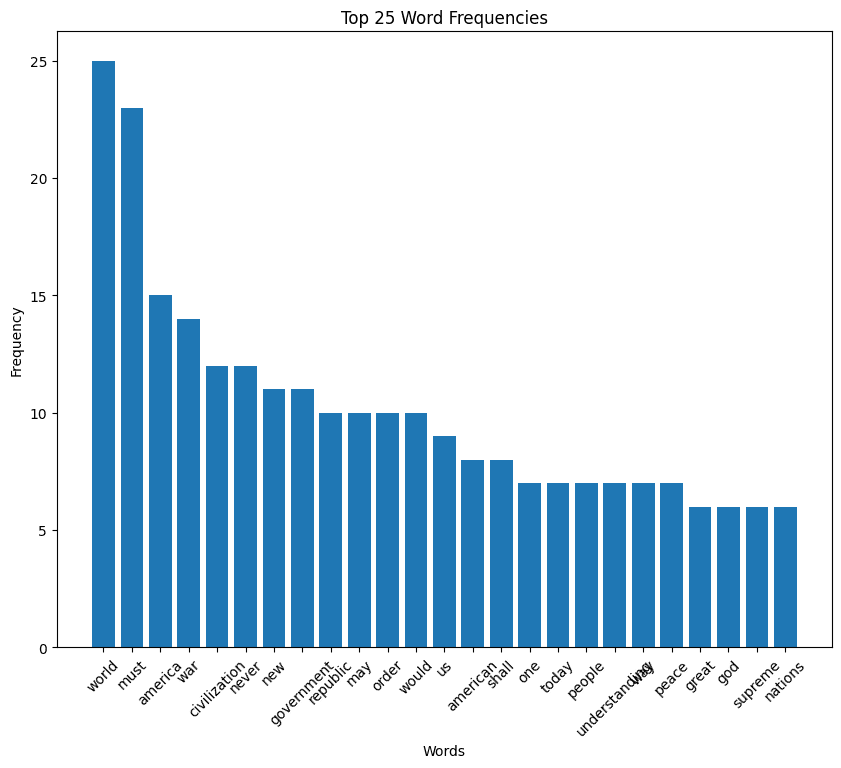
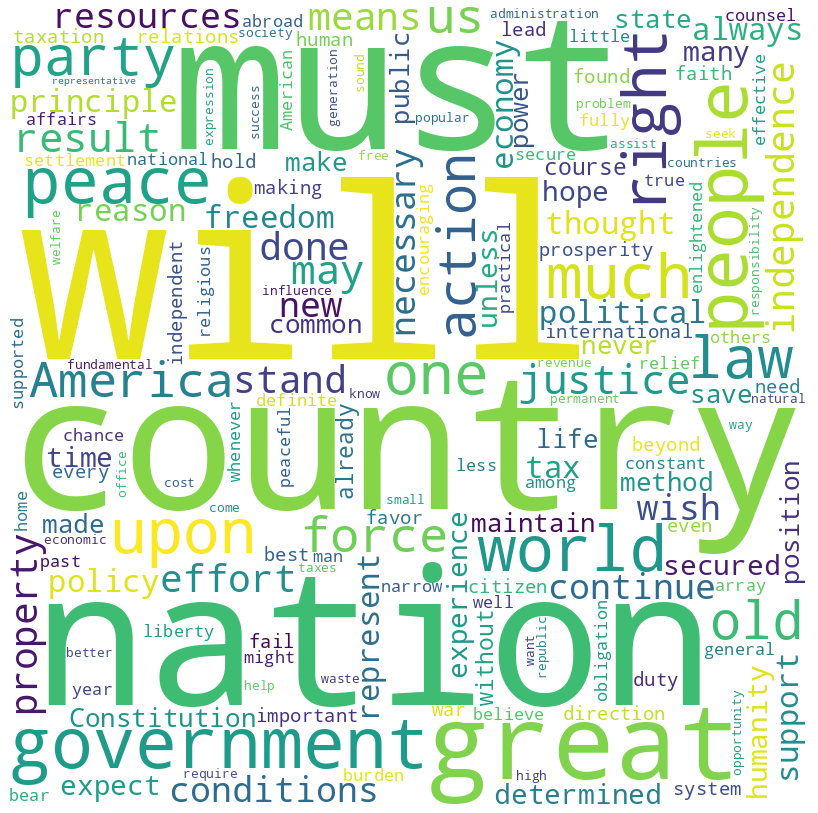
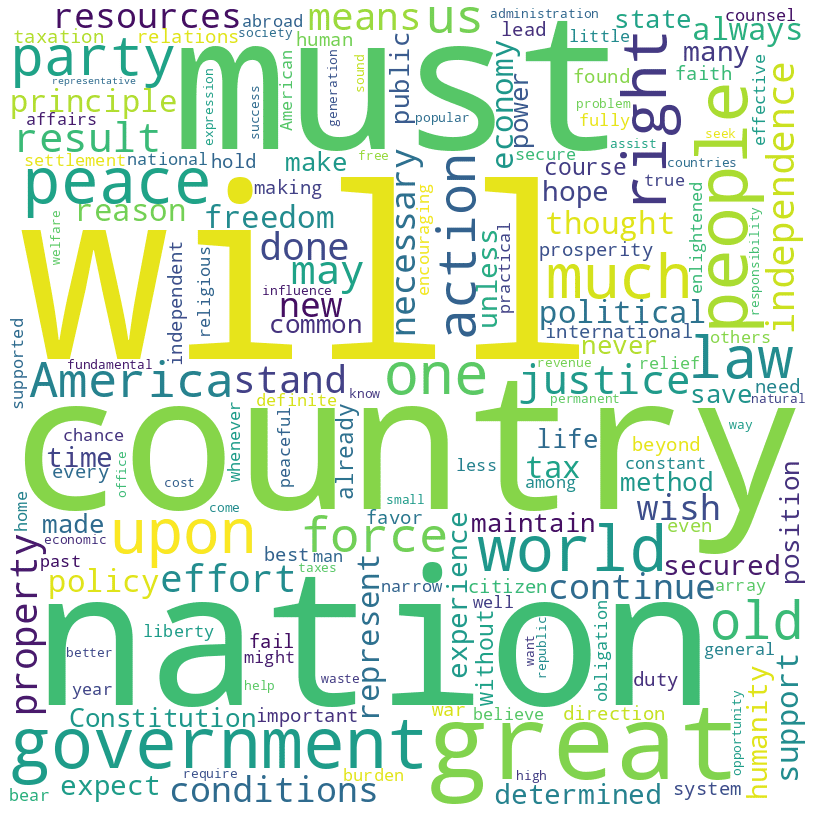
Calvin Coolidge inaugural address (1925)
Coolidge speech summary
Calvin Coolidge’s Inaugural Address in 1925 emphasizes a vision of America that champions peace, economic prudence, and adherence to constitutional principles. Coolidge reflects on the nation’s accomplishments and challenges, advocating for responsible governance, international cooperation without entanglement, and a strong but peaceful military stance.
He stresses the importance of fiscal responsibility, tax reform, and the role of government in supporting, not burdening, the citizenry. Coolidge calls for a united, distinctly American approach to progress, underscoring the need for moral integrity and the pursuit of justice and liberty at home and abroad.
For the full speech, you can read the entire text in my GitHub repository.
Coolidge speech word cloud
Coolidge speech histogram
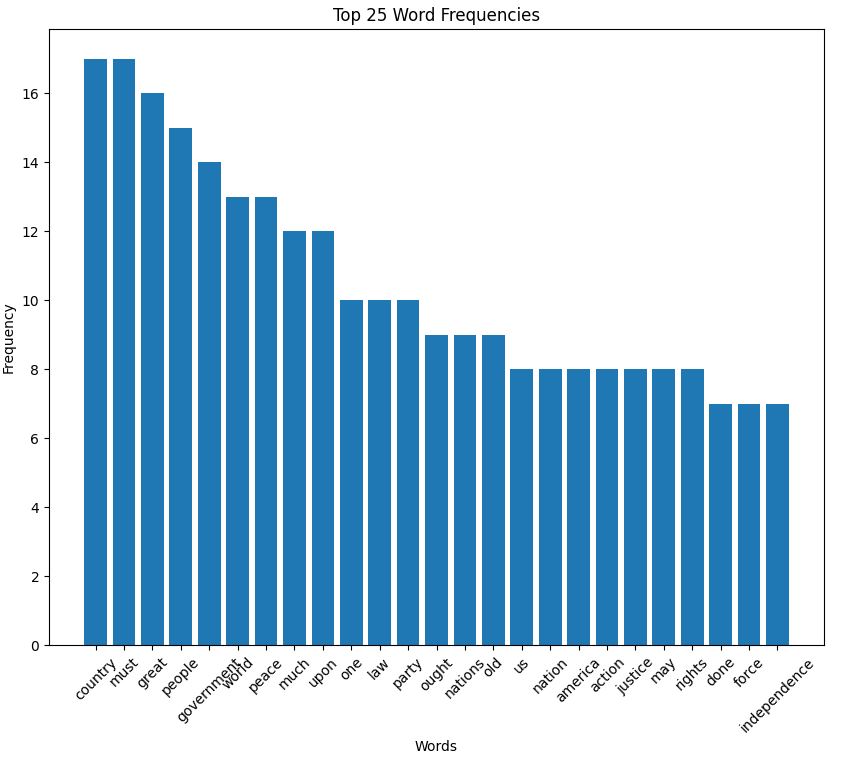
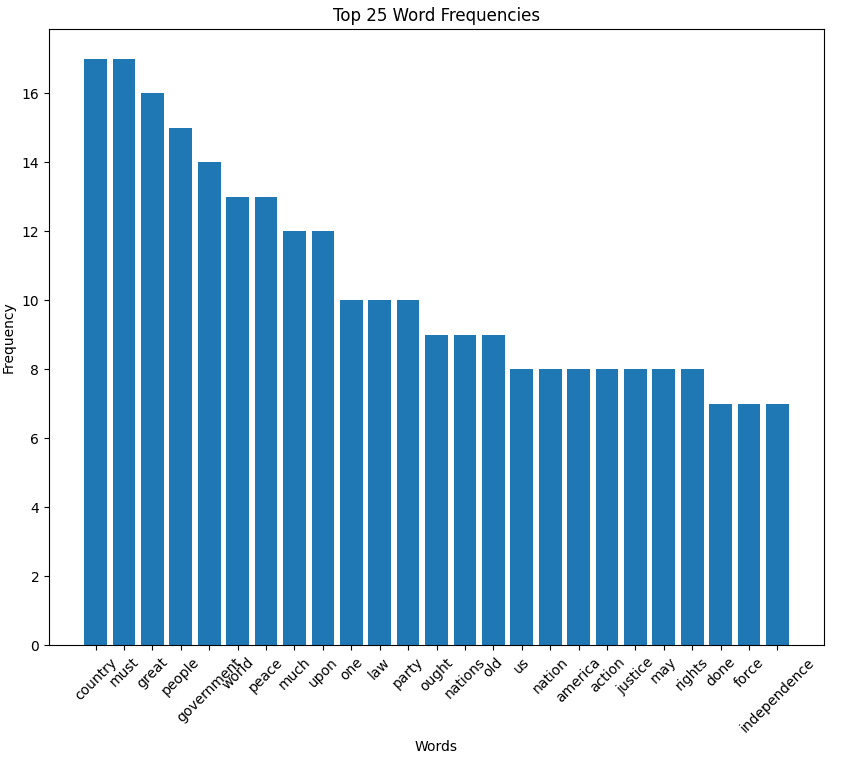
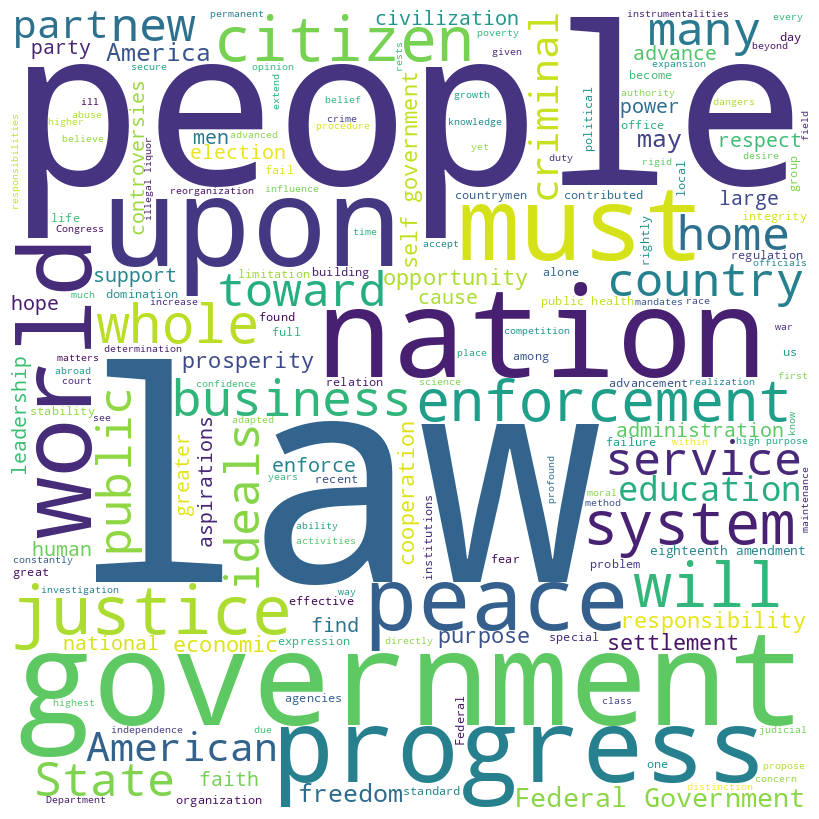
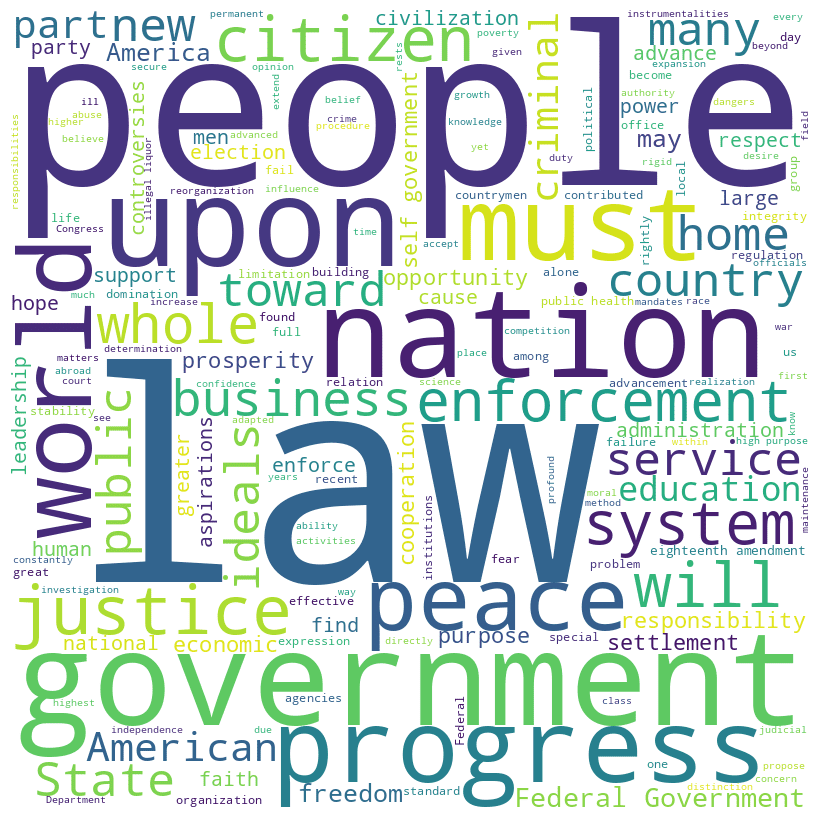
Herbert Hoover inaugural address (1929)
Hoover speech summary
Herbert Hoover’s inaugural address from March 4, 1929, emphasizes his commitment to American ideals and governance under the guidance of Providence. He discusses the nation’s progress post-World War I, highlighting the importance of law enforcement, judicial reform, and the enforcement of the 18th Amendment.
Hoover also addresses the relationship between government and business, advocating for regulation over ownership, and underscores the role of education, public health, and international peace in national prosperity. He calls for national unity and cooperation to address the challenges facing the United States, seeking divine assistance in his service to the country.
Hoover speech word cloud
Hoover speech histogram
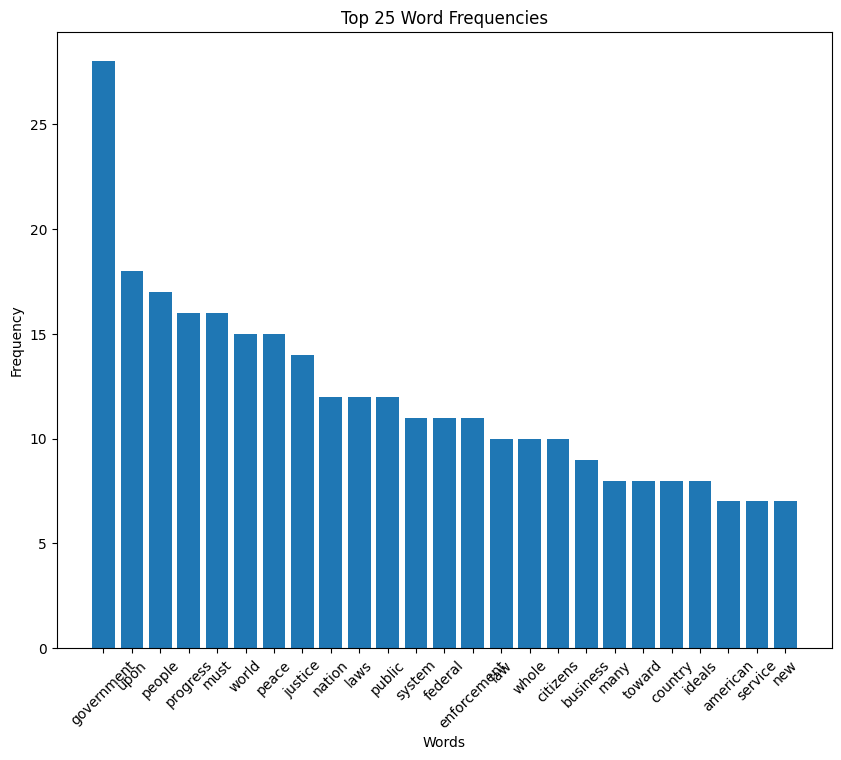
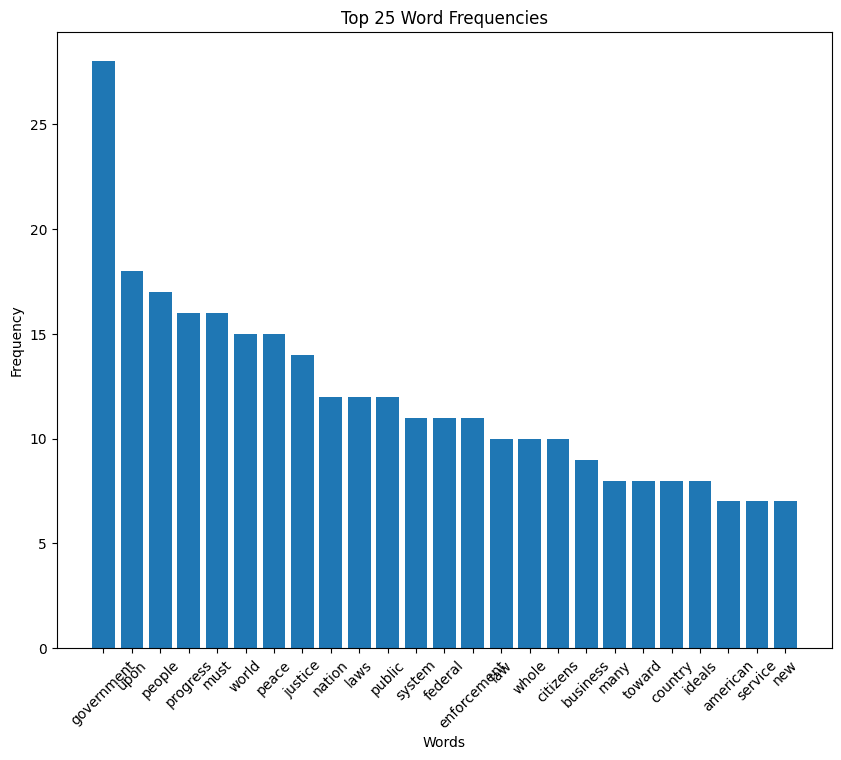
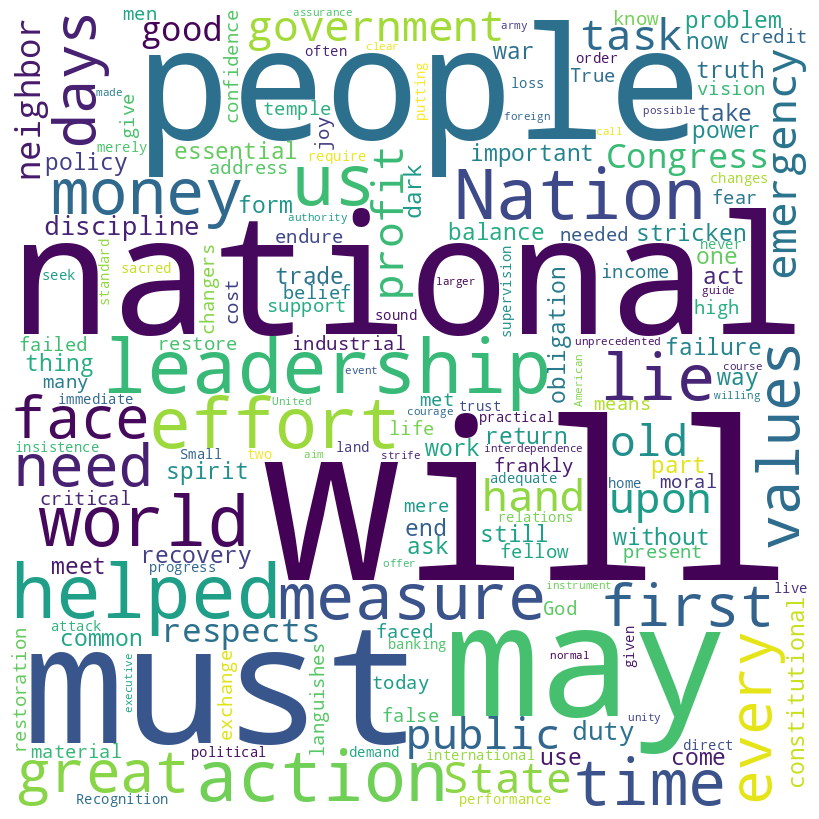
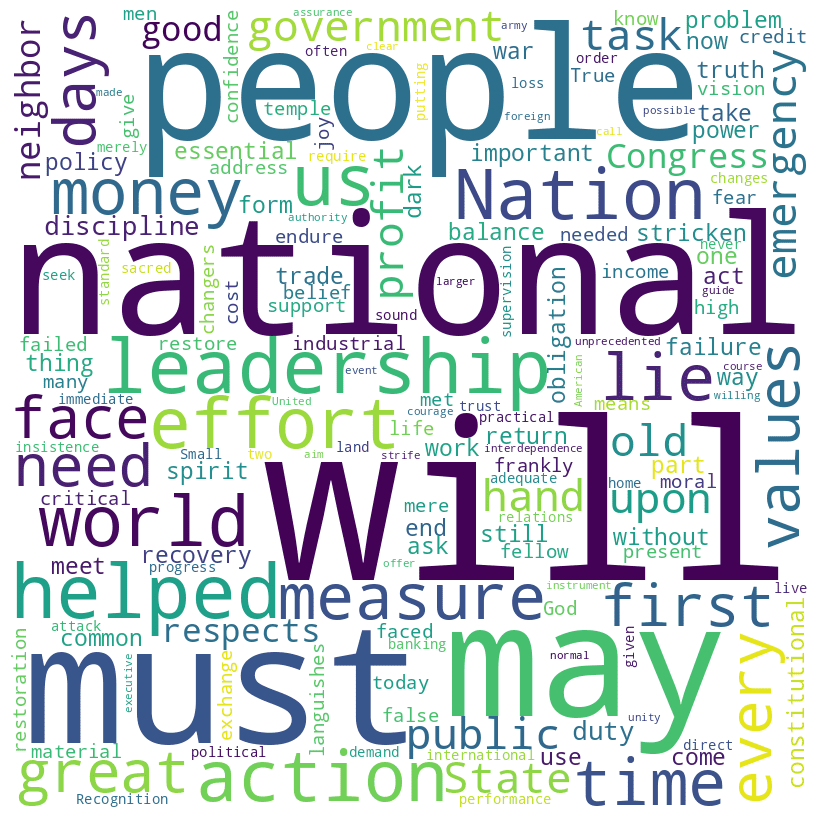
Franklin D. Roosevelt’s first inaugural address (1933)
FDR speech summary
Franklin D. Roosevelt‘s (FDR) 1933 inaugural speech emphasized a message of hope and resilience amid the Great Depression. He famously stated, “the only thing we have to fear is fear itself,” urging unity and action against economic challenges.
Roosevelt criticized financial practices, calling for ethical banking and investment, and outlined his New Deal plan to revive the economy by increasing employment, regulating banking, and boosting agricultural prices. He advocated for a balanced national economy and international trade, underlining the importance of government action and collective effort towards recovery and prosperity.
FDR speech word cloud
FDR speech histogram
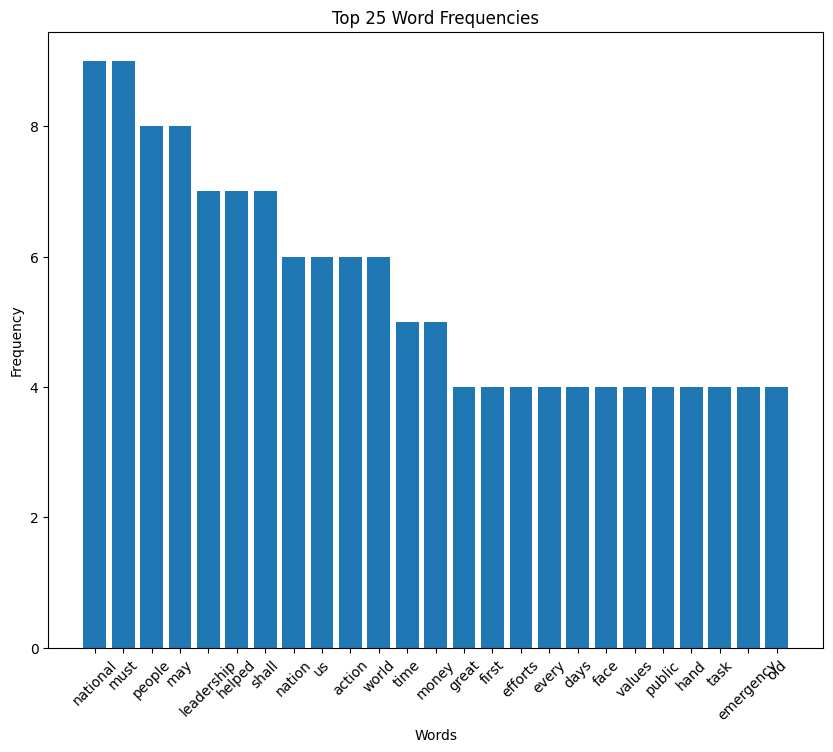
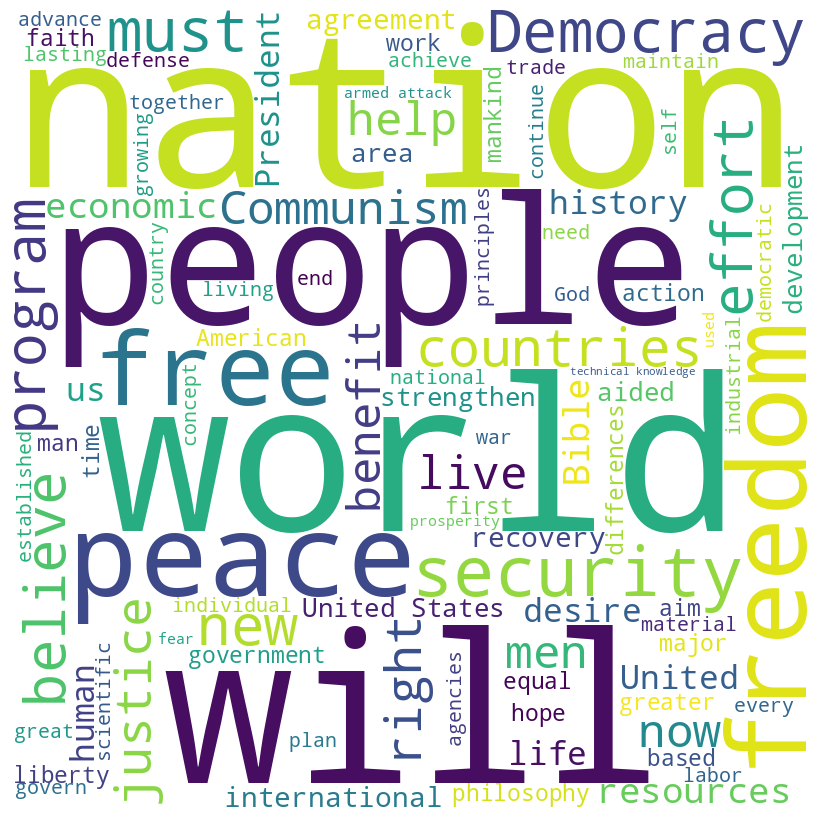
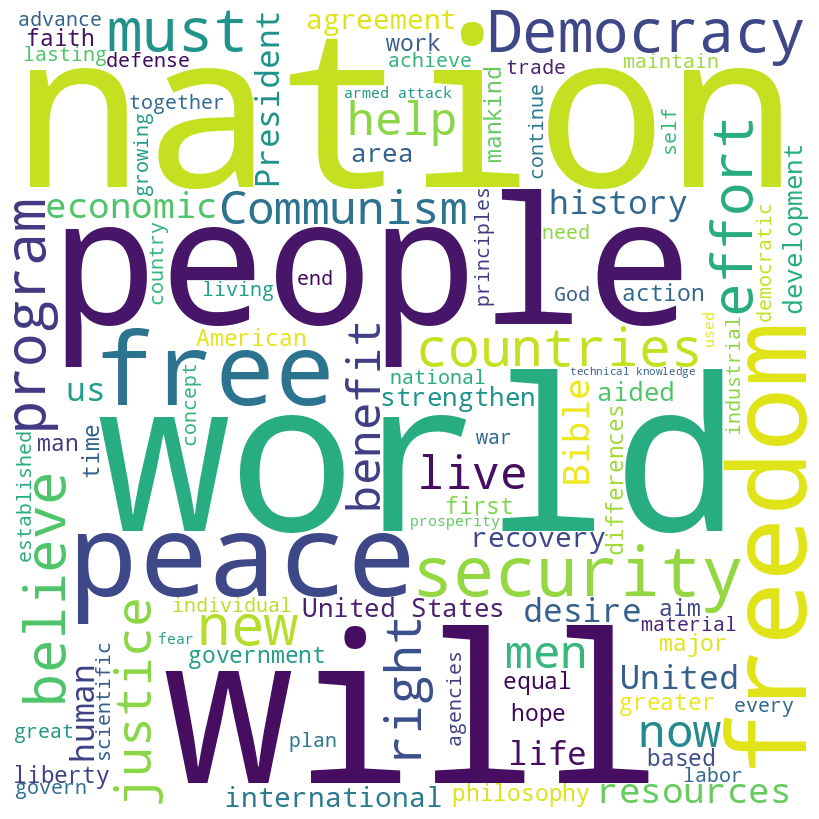
Harry S. Truman inaugural address (1949)
Truman speech summary
In his 1949 inaugural address, President Harry Truman outlines his vision for America’s role in the world, emphasizing the need for peace, democracy, and economic recovery. He addresses the challenges of communism, advocates for the United Nations, and calls for a global effort to aid underdeveloped nations.
Truman’s speech reflects his commitment to freedom, justice, and international cooperation, aiming to secure a prosperous and peaceful future for all. You can read the full text on GitHub.
Truman speech word cloud
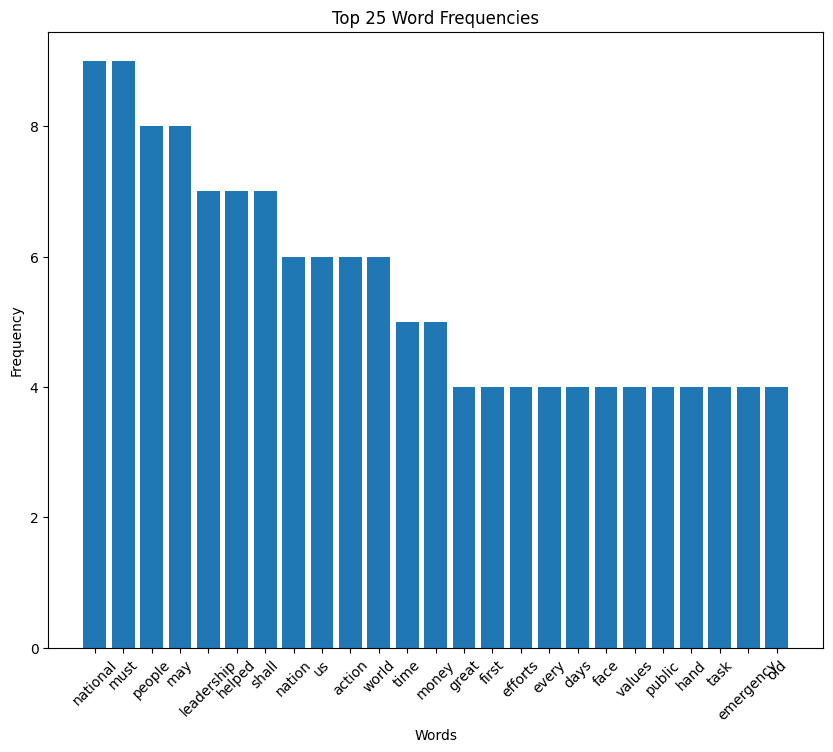
Truman speech histogram
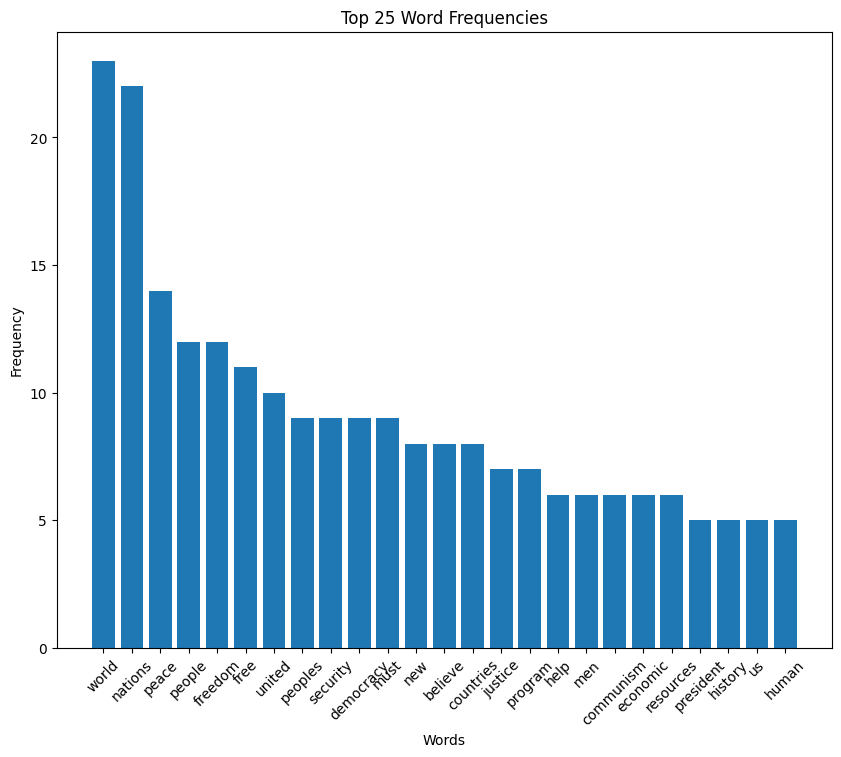
Dwight D. Eisenhower inaugural address (1953)
Eisenhower speech summary
In his inaugural address on January 20, 1953, President Dwight D. Eisenhower emphasizes the importance of faith, freedom, and mutual respect among nations. He acknowledges the challenges of the era, including the rise of new nations and the threats posed by technological advancements to human life.
Eisenhower advocates for peace, unity, and the defense of freedom, outlining principles of statesmanship aimed at promoting global security and prosperity. He stresses the role of every citizen in upholding these values and contributing to the strength and well-being of America and the world.
You can read the full text of the speech on GitHub.
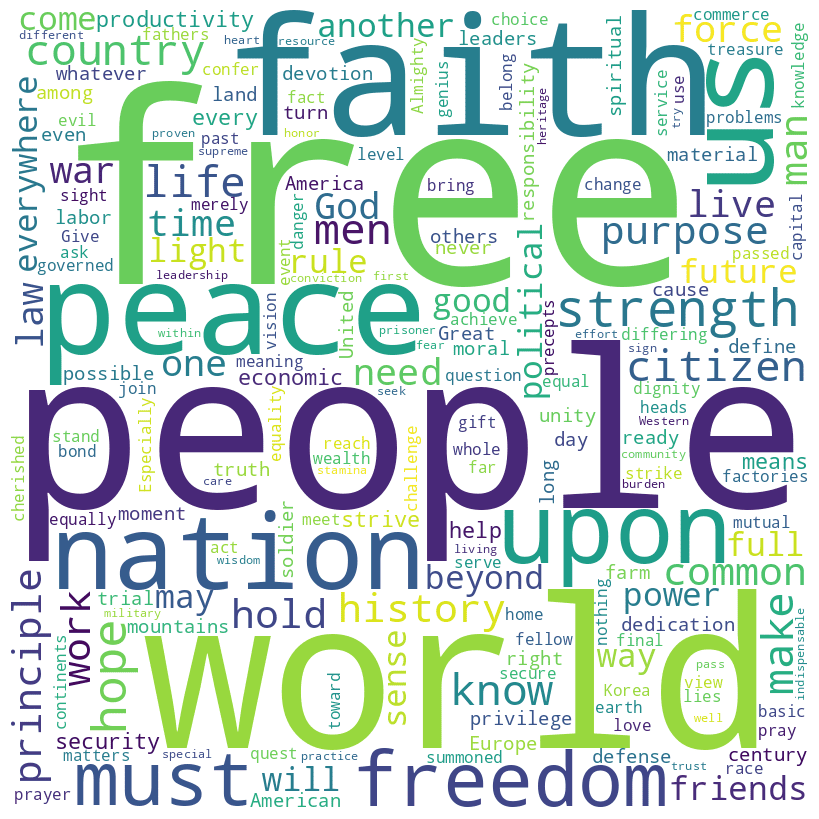
Eisenhower speech word cloud

Eisenhower speech histogram
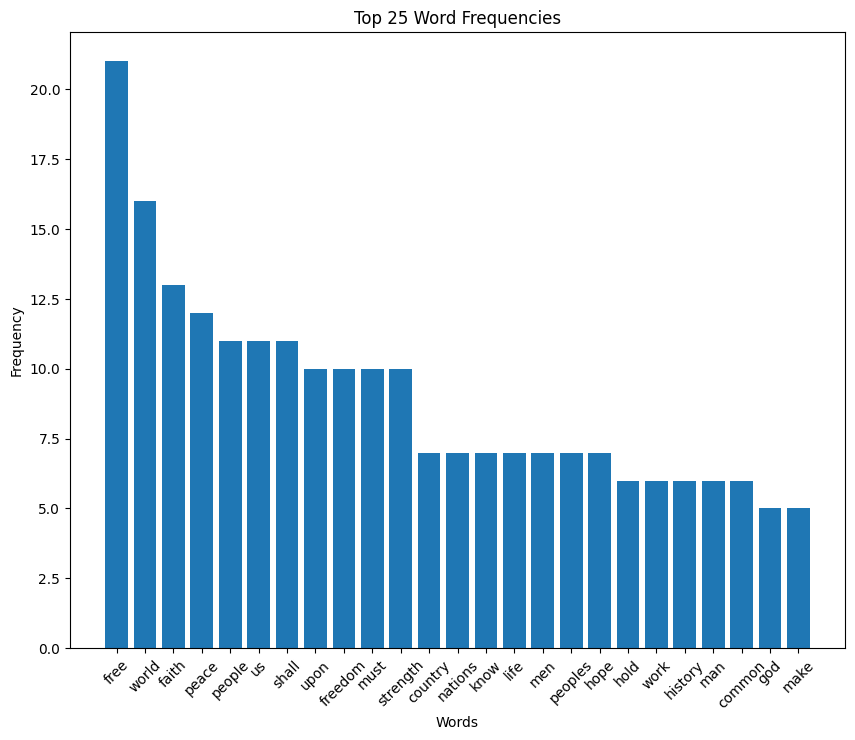
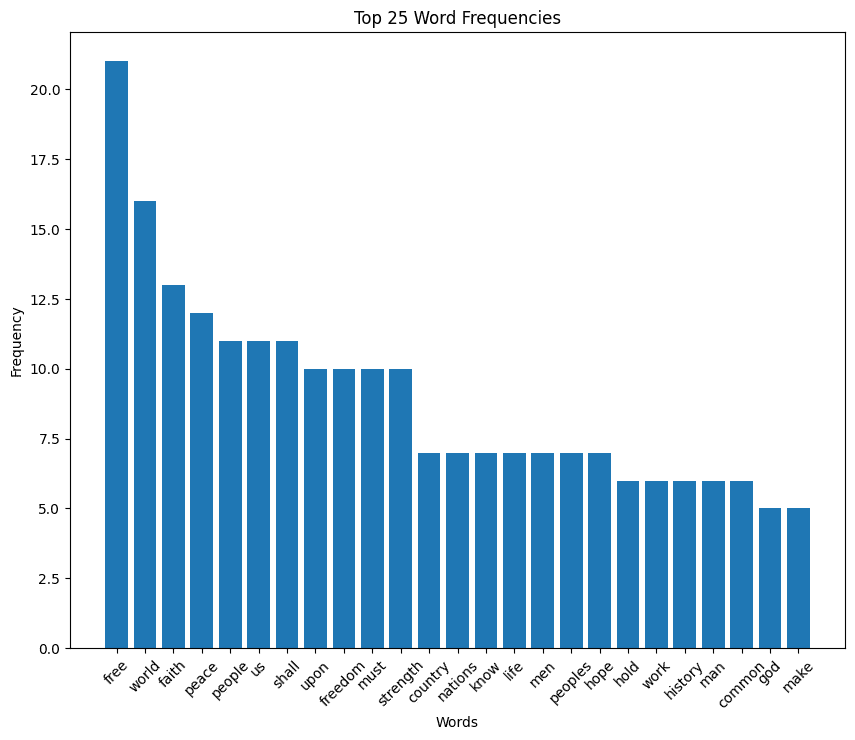
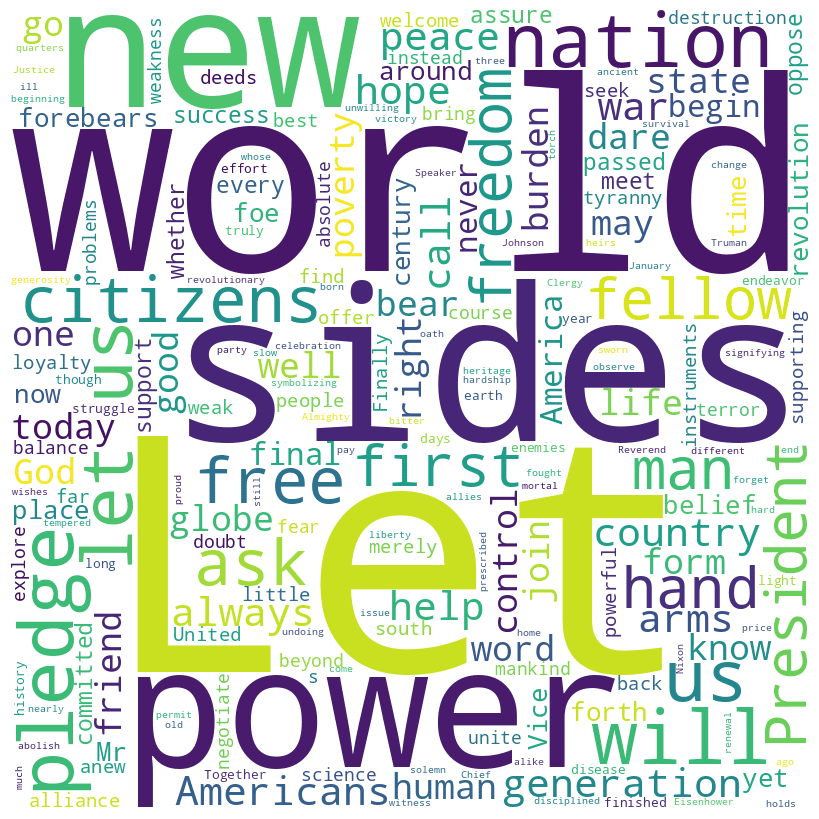
John F. Kennedy inaugural address (1961)
JFK speech summary
John F. Kennedy‘s inaugural address, delivered on January 20, 1961, emphasizes the importance of liberty and global unity against common enemies like tyranny, poverty, disease, and war. Kennedy calls for a new generation of Americans to bear the responsibility of leading the nation towards these ideals, stressing the importance of collaboration and mutual support among nations.
He famously urges Americans to contribute to their country and citizens worldwide to work together for the freedom of all humanity. This speech is a powerful call to action, advocating for peace, cooperation, and a better future for everyone.
You can read the full text of JFK’s inaugural address on GitHub.
JFK speech word cloud

JFK speech histogram
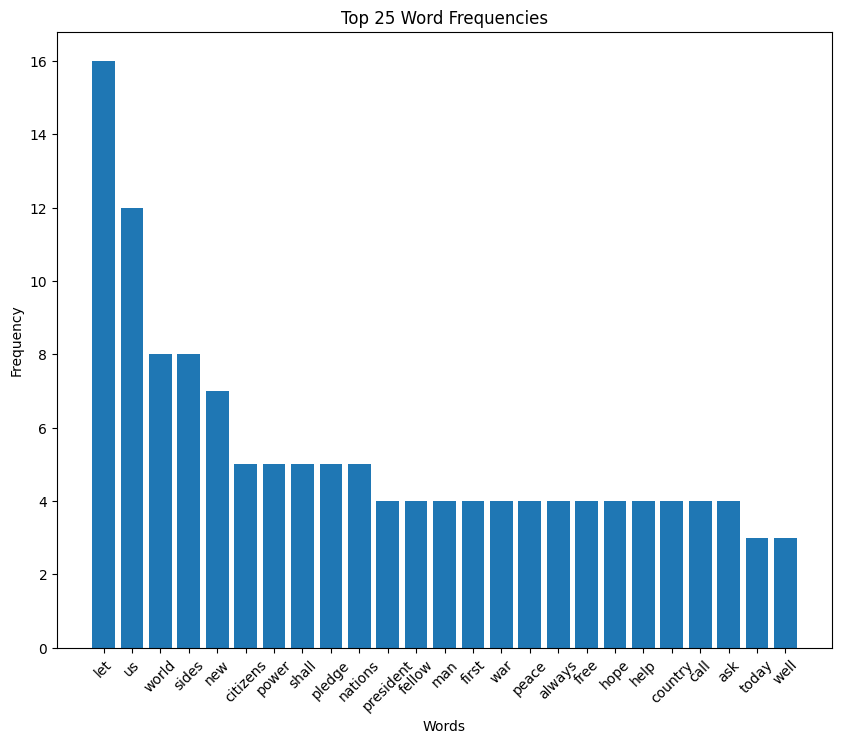
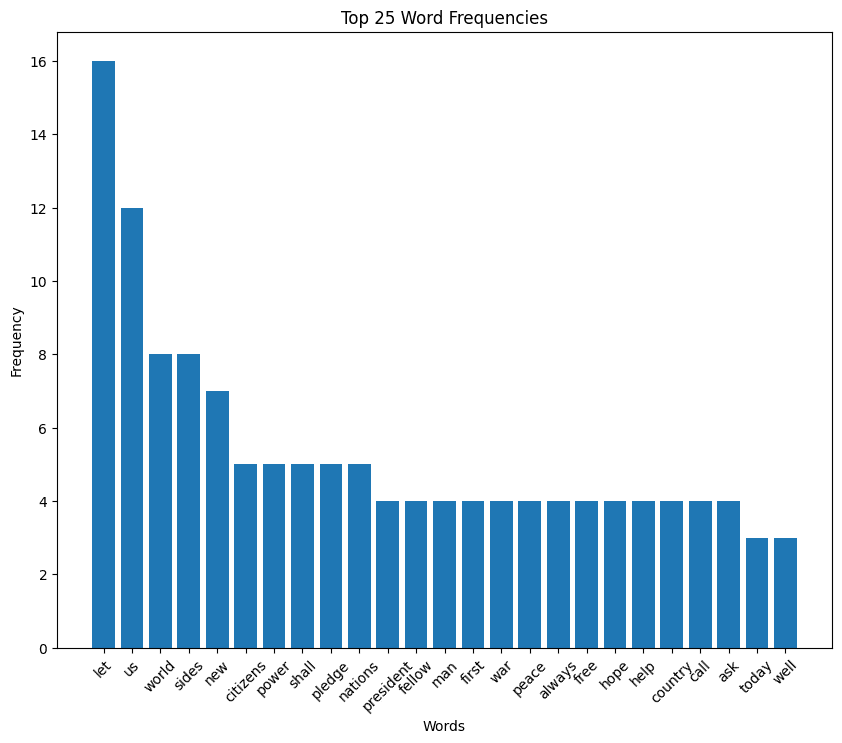
Lyndon B. Johnson (LBJ) inaugural address (1965)
LBJ speech summary
Lyndon Johnson’s 1965 inaugural speech emphasizes unity, justice, and the pursuit of progress amidst rapid change. He speaks of a covenant with justice and liberty at its core, reflecting on America’s role in global liberation and the importance of adapting to change without succumbing to division.
Johnson highlights the need for collective effort to overcome challenges, advocating for a nation united in purpose and action. His vision for America includes a commitment to justice, liberty, and the collective pursuit of a better society.
Having been elected by the people after assuming the office following John F. Kennedy‘s assassination, Johnson felt a mandate behind him to continue the civil rights work begun by JFK, Martin Luther King, Bobby Kennedy, Medgar Evers, and others — as a way of honoring their memory and doing the right thing at the same time.
You can read the full text of LBJ’s speech on my GitHub.
LBJ speech word cloud
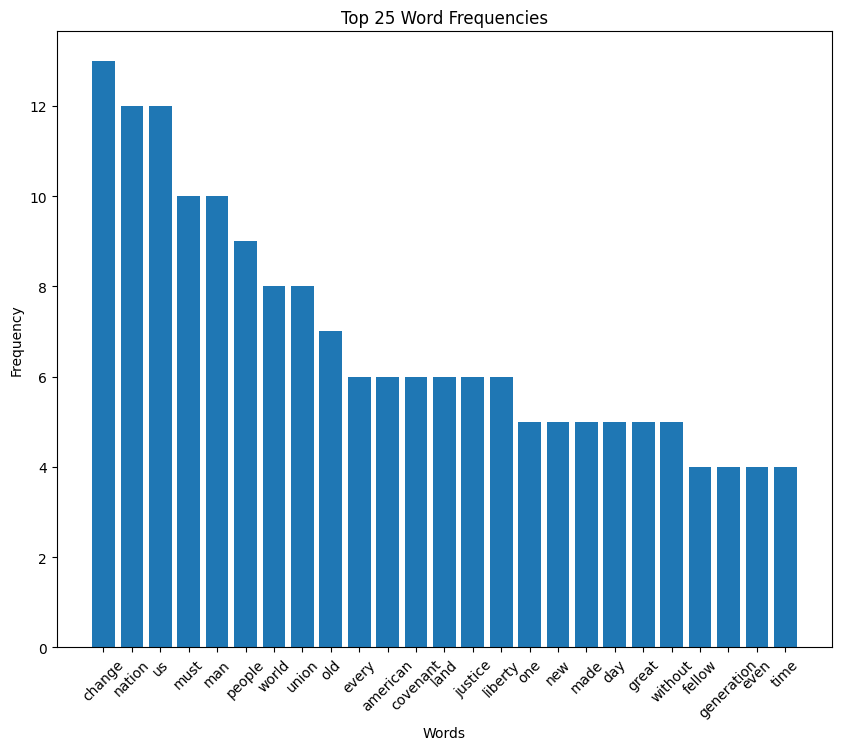
LBJ speech histogram
Richard Nixon inaugural address (1969)
Nixon speech summary
Richard Nixon‘s inaugural speech in 1969 emphasized unity, peace, and the potential for human progress. He portrayed the era as a pivotal moment for shaping the future, underlining the importance of peace, both domestically and globally.
Nixon called for cooperation beyond government efforts, engaging the American people in addressing national and global challenges. He stressed the need for understanding and cooperation among nations and highlighted the role of America as a peacemaker in the world. The speech reflected an optimistic vision for America’s role in fostering global peace and prosperity.
For the full text of the address, you can visit my GitHub repository.
Nixon speech word cloud
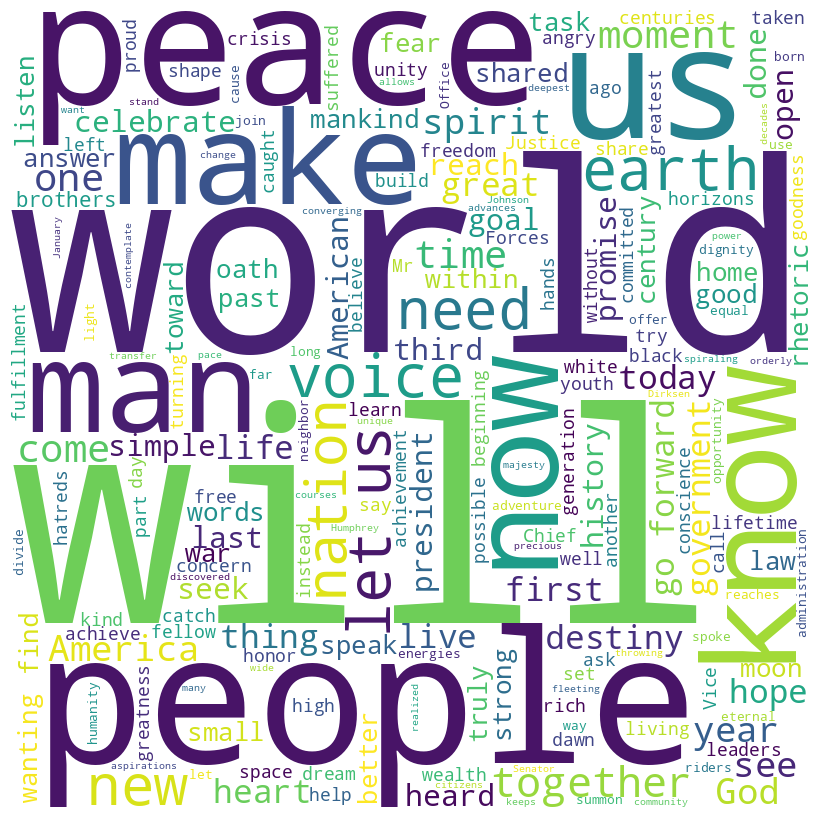
Nixon speech histogram
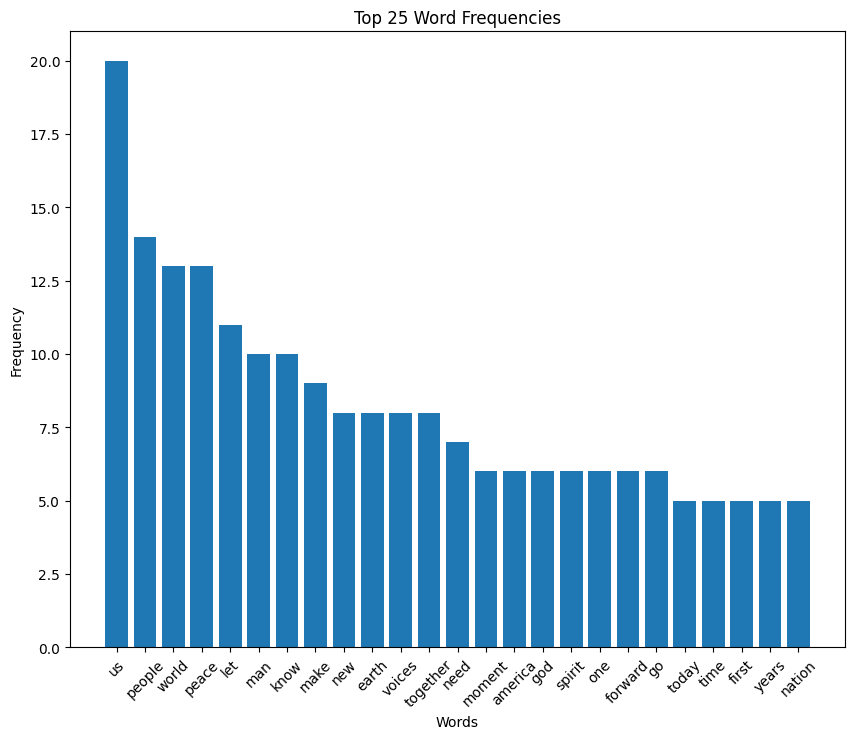
Gerald Ford inaugural address (1974)
Ford speech summary
Gerald Ford’s inaugural address emphasizes unity and the need for collective progress in the wake of President Nixon‘s resignation. Acknowledging his ascension to the presidency under unprecedented circumstances, Ford calls for national healing and support from American citizens, despite not being elected through a traditional vote.
He pledges honesty, transparency, and dedication to serving all Americans, aiming to restore trust in government and promote peace both domestically and internationally. Ford also asks for prayers for himself and Richard Nixon, highlighting the importance of forgiveness and reconciliation in moving forward.
You can read the full text of Ford’s inaugural address on my GitHub.
Ford speech word cloud
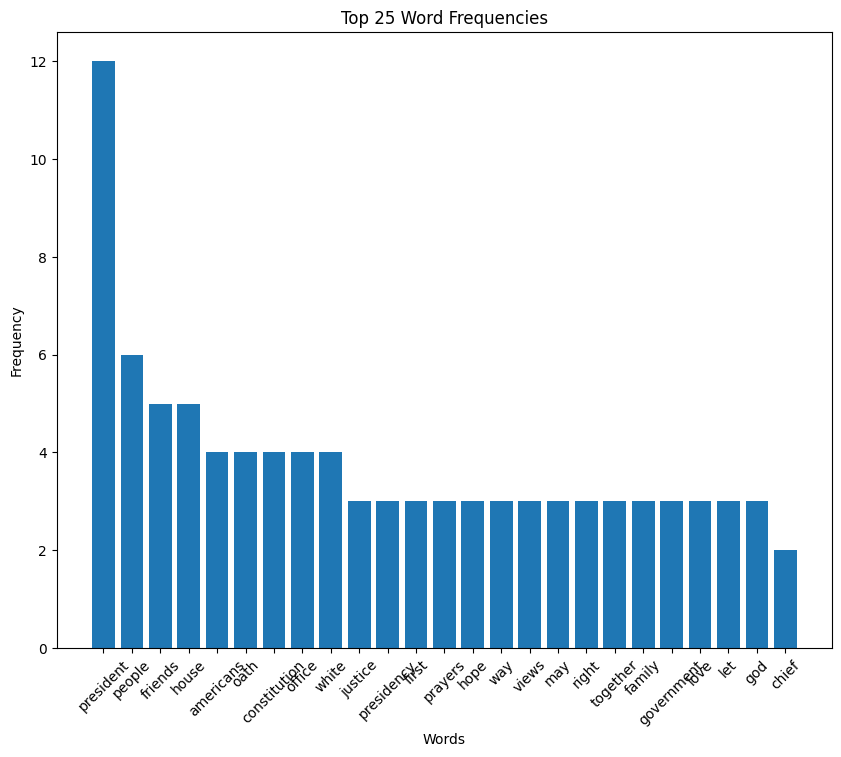
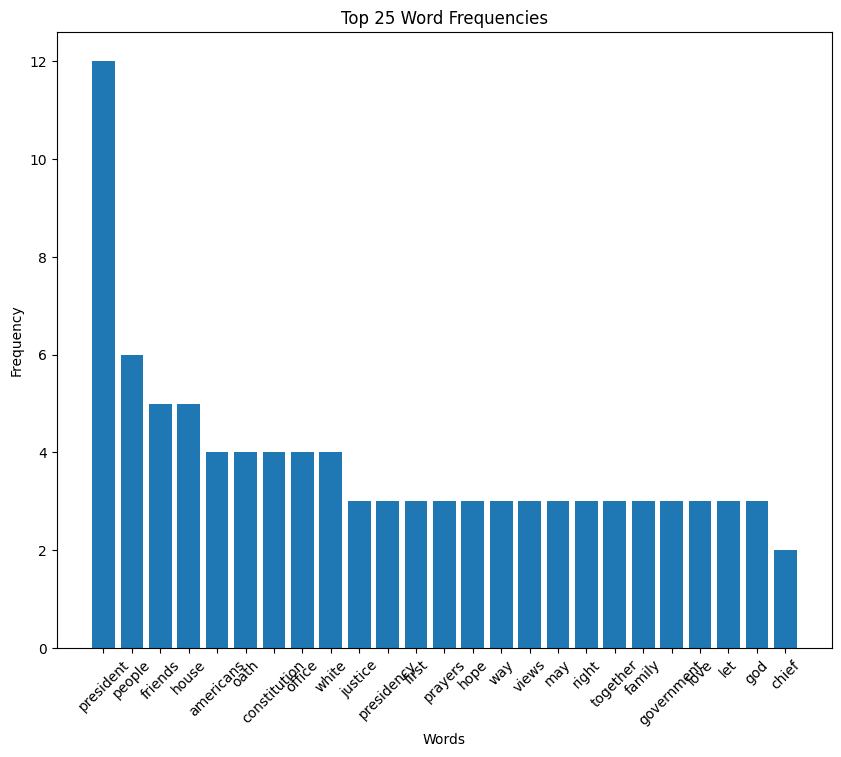
Ford speech histogram
Jimmy Carter inaugural address (1977)
Carter speech summary
In his 1977 inaugural address, President Jimmy Carter emphasized a new beginning for the United States, focusing on unity, trust, and a return to the country’s foundational principles of freedom, spirituality, and human rights. He called for a collective effort to overcome challenges, stressing the importance of humility, justice, and service to others as outlined in his faith.
Carter also highlighted the need for a strong, compassionate government and a commitment to peace and human dignity globally, aspiring to lead by example rather than intimidation, with a vision for a world free of nuclear weapons. You can read the full text of Carter’s inaugural address on my GitHub.
Carter speech word cloud
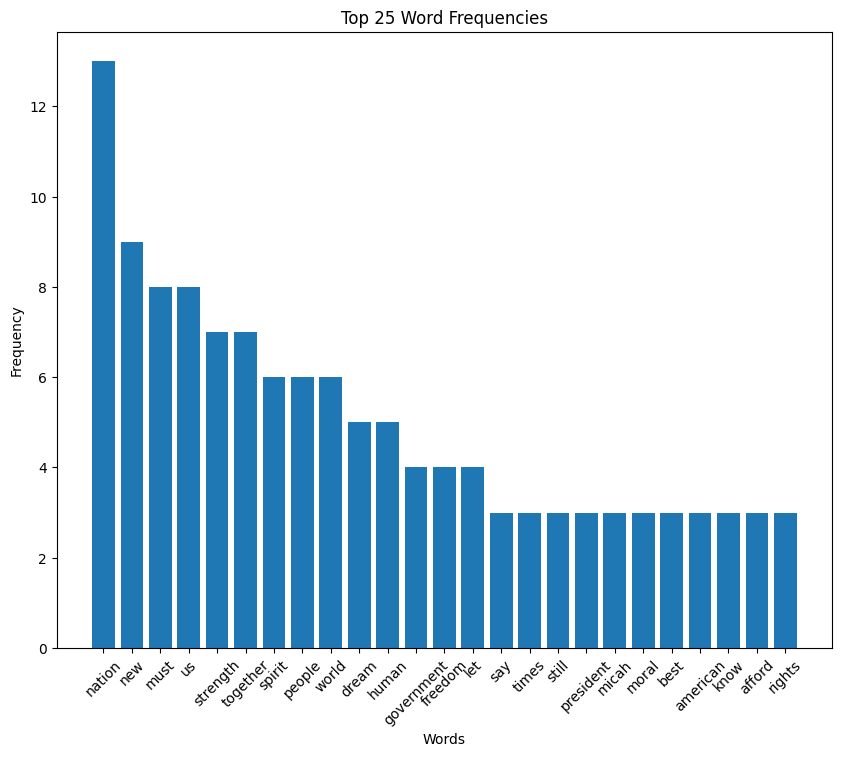
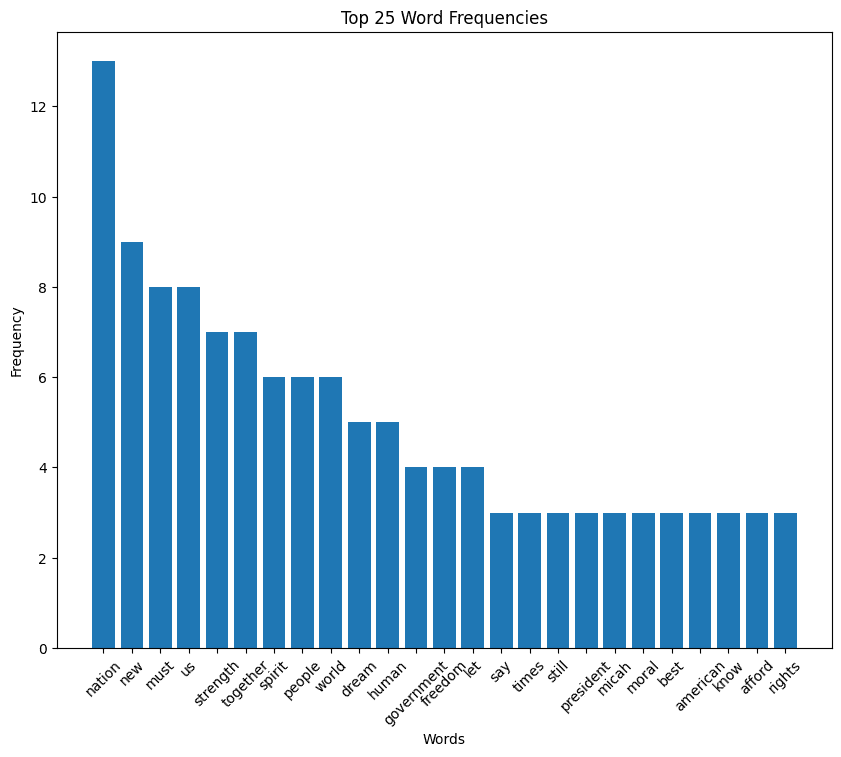
Carter speech histogram
Ronald Reagan inaugural address (1981)
Reagan speech summary
Ronald Reagan’s 1981 inaugural address emphasizes a return to individual liberty, reduced government intervention, and economic rejuvenation as pivotal to America’s future. He critiques the prevailing economic difficulties, attributing them to excessive government size and spending, while advocating for a smaller government that enables personal and national growth.
Reagan calls for unity and action to overcome these challenges, underlining the importance of faith, patriotism, and individual effort in achieving a prosperous, free society. He champions the American spirit, urging a collective effort towards national renewal and global leadership in freedom.
Reagan speech word cloud
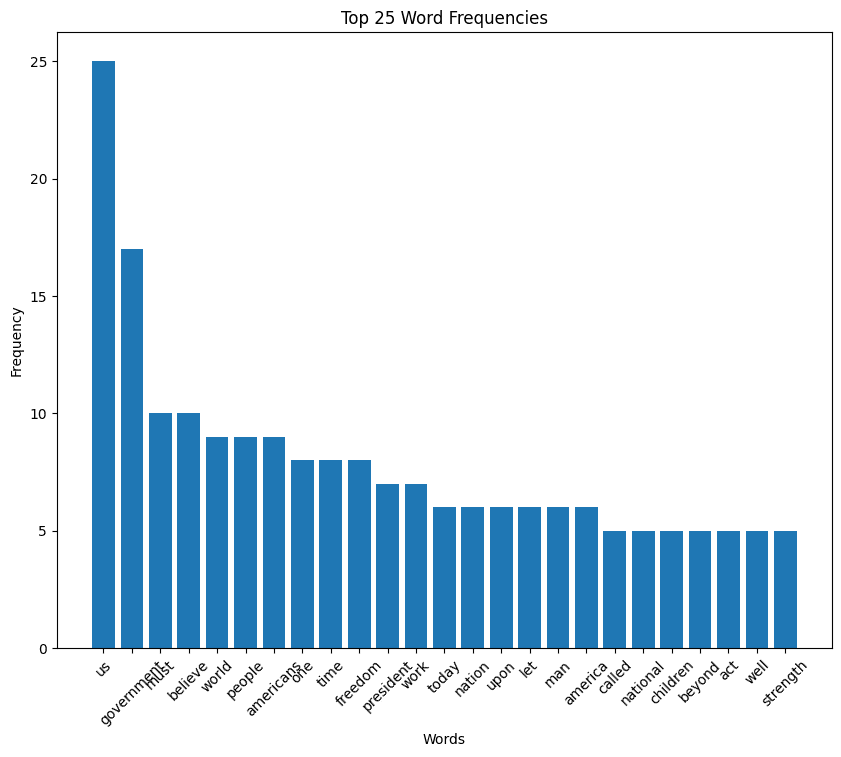
Reagan speech histogram
George H. W. Bush inaugural address (1989)
Bush speech summary
George H.W. Bush‘s inaugural address focuses on unity, service, and the promise of America. He celebrates the peaceful transition of power and democracy, calling on the principles of freedom, service to others, and the importance of community.
Bush emphasizes moving beyond materialism to leave a legacy of kindness, generosity, and civic duty for future generations. He highlights the end of the Cold War era, promoting global democracy, free markets, and cooperation between the executive and legislative branches. Bush calls for a new era of volunteerism and civic engagement, aiming to make America kinder and the world gentler.
You can read the full speech on my GitHub.
Bush speech word cloud
Bush speech histogram
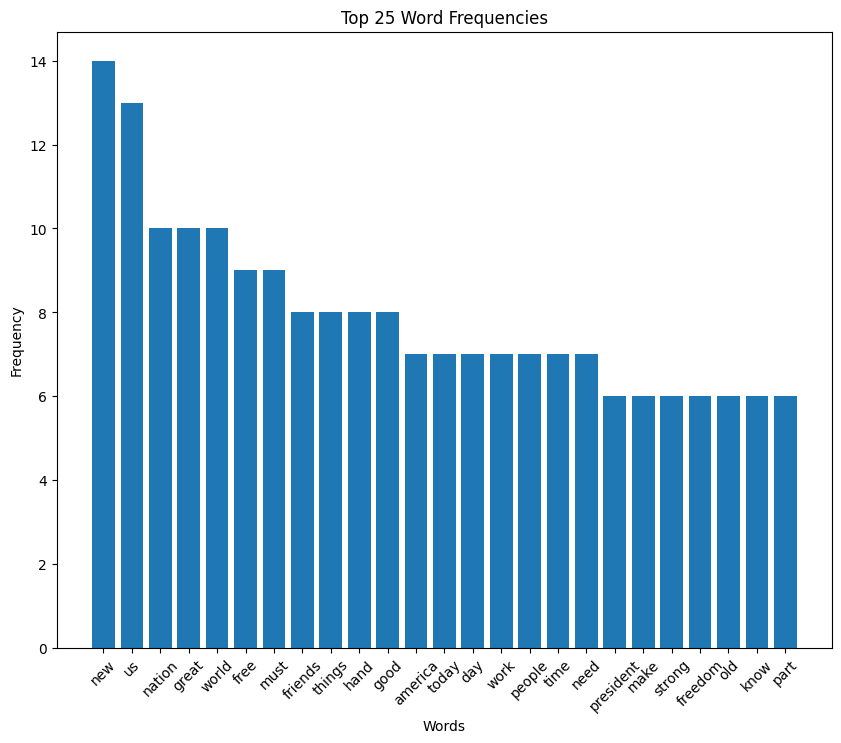
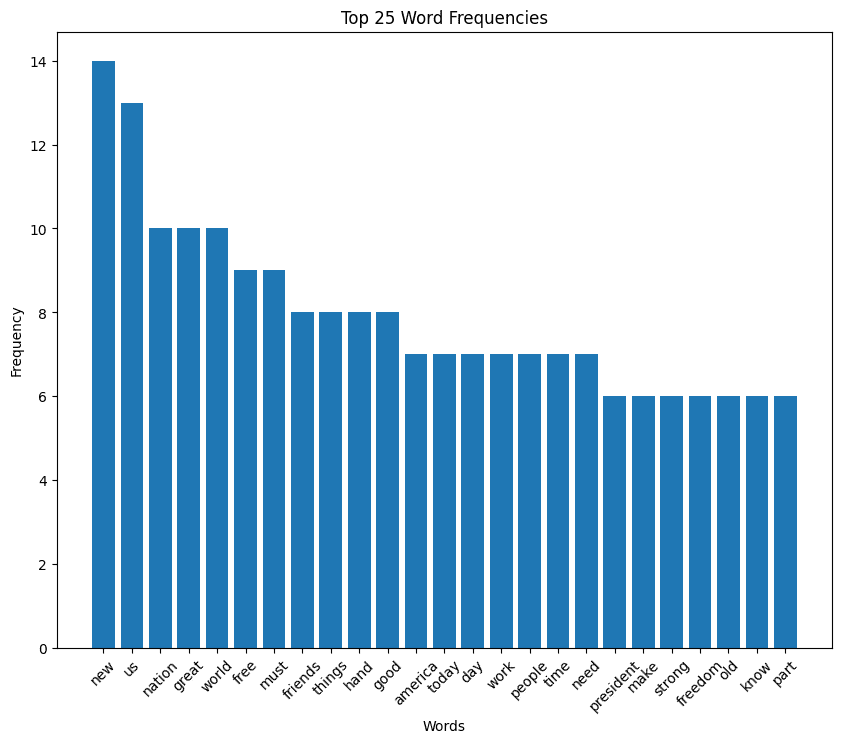
Bill Clinton inaugural address (1993)
Clinton speech summary
In his 1993 inaugural address, President Bill Clinton spoke of American renewal and the need for change to preserve the nation’s core ideals of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. He acknowledged the challenges and opportunities presented by a changing world, emphasizing the importance of embracing change as a friend, investing in the American people, and demanding responsibility from all citizens.
Clinton called for an end to political deadlock, a renewal of democracy, and active American leadership in global affairs, underscoring a collective responsibility towards future generations and the unity of the American spirit.
You can read the full text of Clinton’s speech in my GitHub historical documents repository.
Clinton speech word cloud

Clinton speech histogram
George W. Bush inaugural address (2001)
Bush speech summary
In his 2001 inaugural address, President George W. Bush emphasized the peaceful transition of power, the enduring spirit of American ideals, and the nation’s commitment to freedom, democracy, and compassion. He acknowledged America’s challenges and diversity, calling for unity, civility, and responsibility among citizens.
Bush pledged to address educational, economic, and social issues, stressing the importance of personal responsibility and community service. He invoked the notion of America being guided by a power greater than itself, affirming a commitment to make the nation more just and generous.
Bush speech word cloud
Bush speech histogram
Barack Obama inaugural address (2009)
Obama speech summary
Barack Obama’s inaugural speech emphasizes the importance of unity, responsibility, and the enduring spirit of the American people in the face of crises. Acknowledging the challenges of war, economic downturn, and environmental threats, he calls for collective action towards rebuilding and reform.
Highlighting the nation’s journey of perseverance and shared values, Obama advocates for a new era of responsibility and optimism, underpinned by a commitment to the ideals of freedom, equality, and opportunity for all. He underscores the role of citizenship in shaping a hopeful future, urging Americans to embrace their duties with confidence and determination.
For the full speech, you can visit my GitHub repository of inaugural speeches.
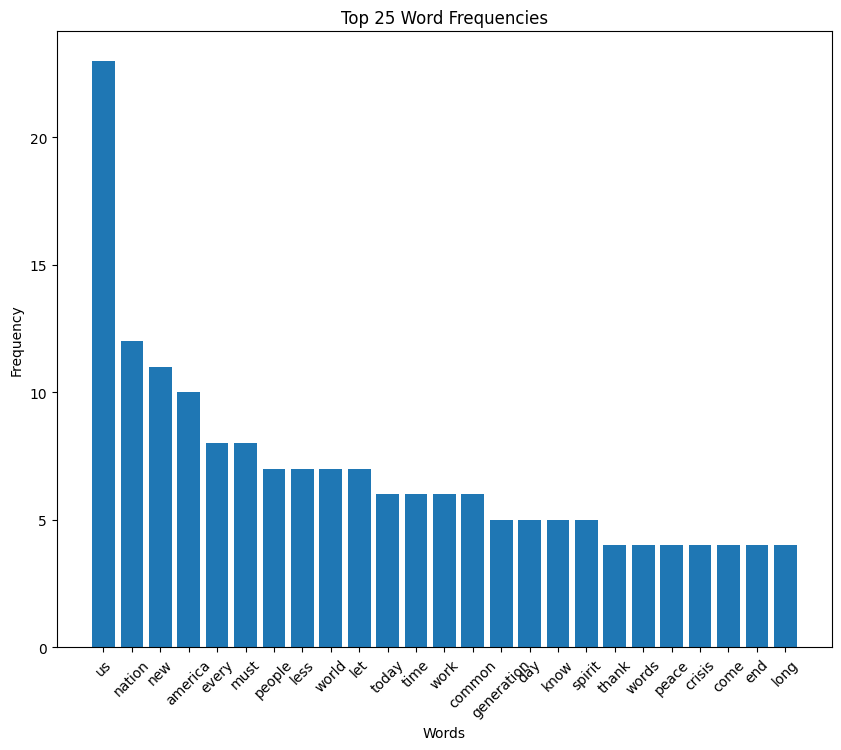
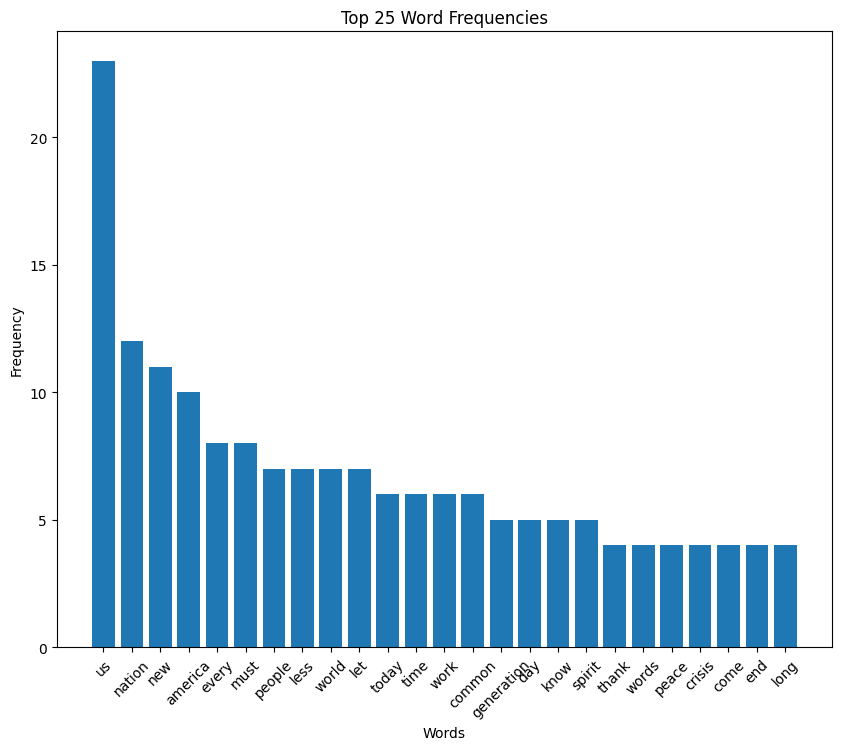
Obama speech word cloud
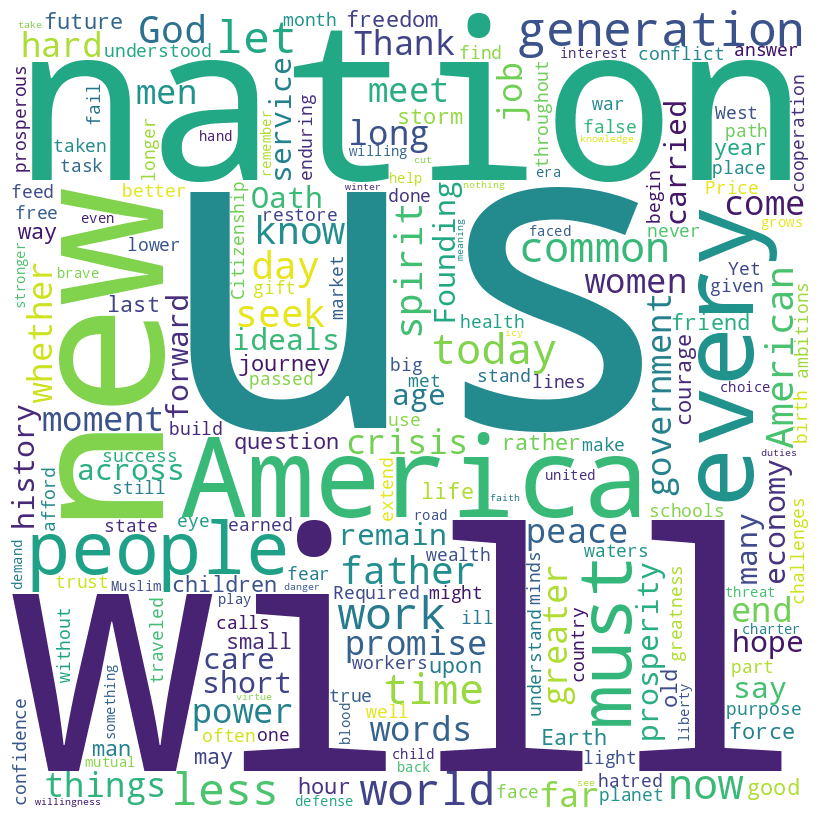
Obama speech histogram
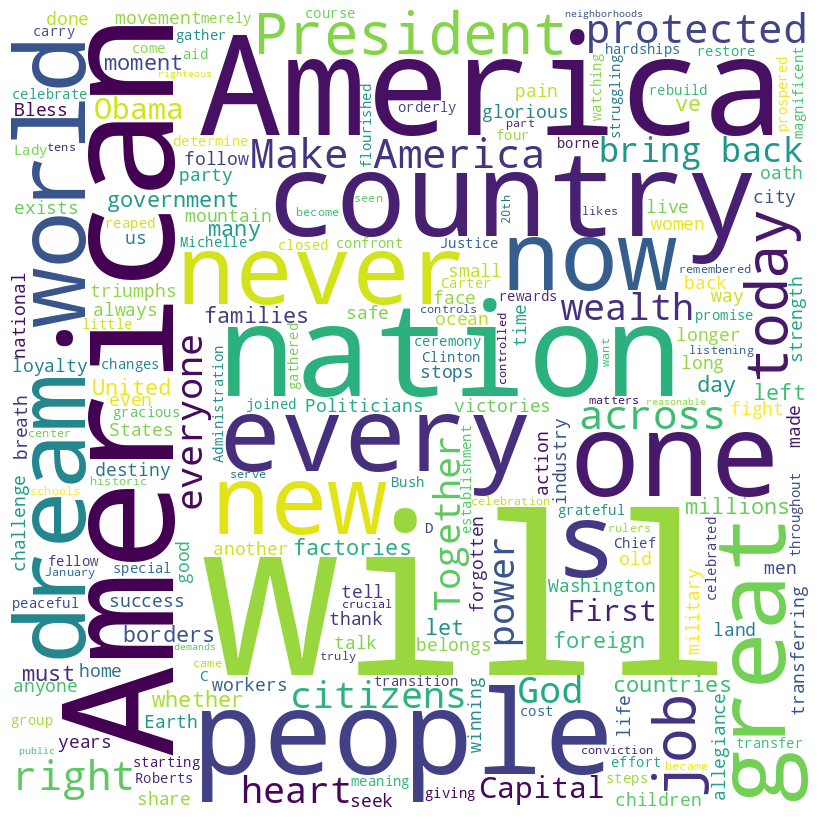
Donald Trump inaugural address (2017)
Trump speech summary
Donald Trump‘s inaugural speech emphasized a shift of power from Washington, D.C., to the American people, criticizing past administrations for neglecting them. He highlighted the struggles of ordinary Americans, promising job restoration, infrastructure improvement, and national security.
Trump called for unity and patriotism, aiming to eradicate radical terrorism and prioritize American interests in trade and foreign policy. He envisioned a prosperous future where America regains its strength, wealth, and pride, underlining this transition as a movement driven by the citizens’ voice.
For more details, you can read the full text of the speech in my GitHub repository.
Trump speech word cloud
Trump speech histogram
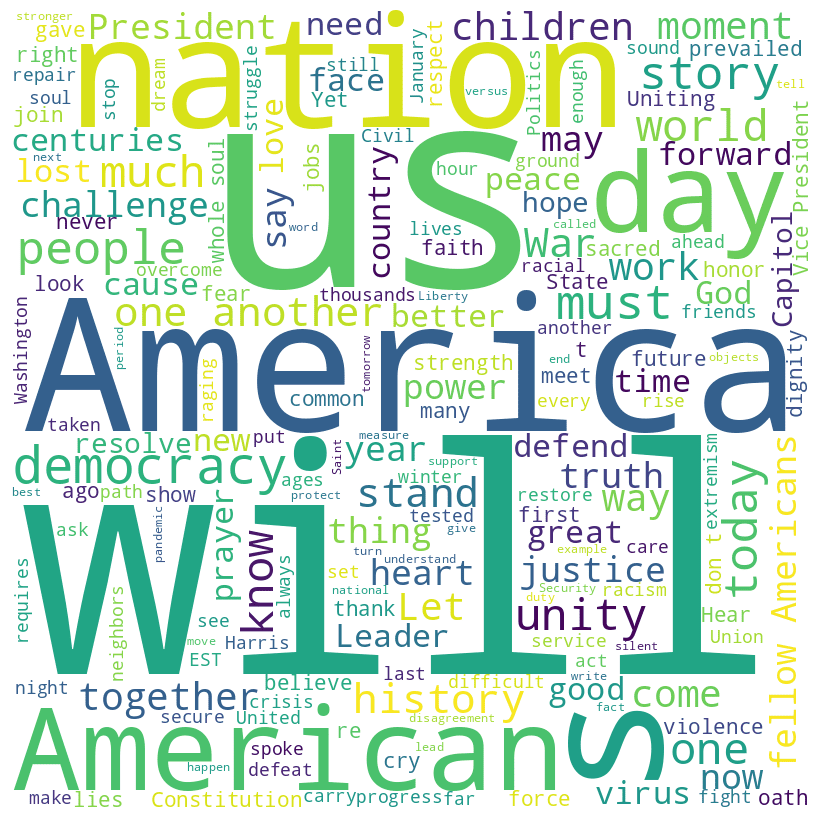
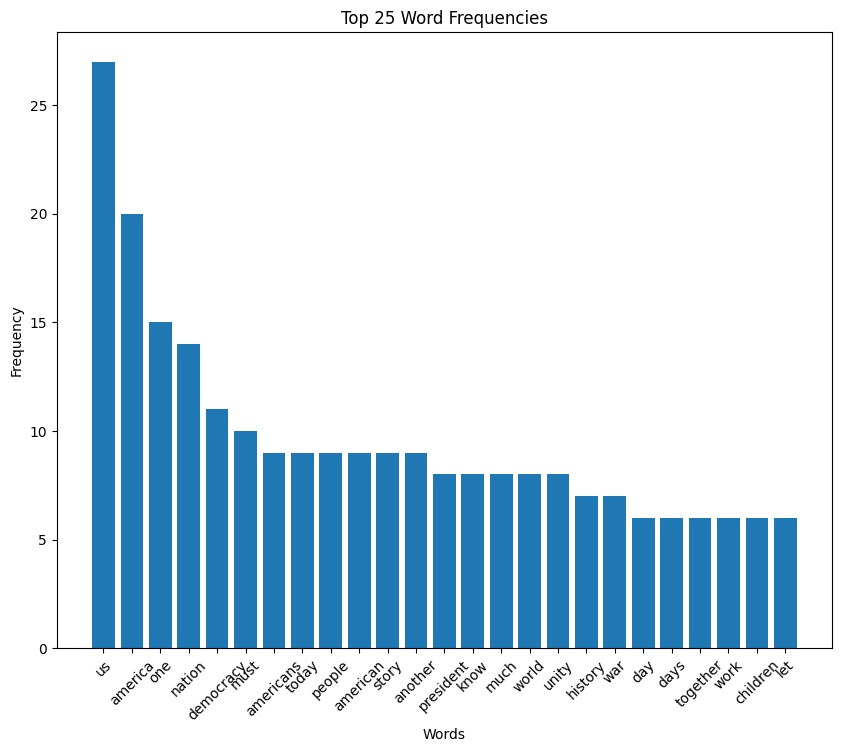
Joe Biden inaugural address (2021)
Biden speech summary
In his inaugural speech, President Joe Biden emphasized unity and resilience amidst national crises. He acknowledged the challenges America faces, including the covid-19 pandemic, racial injustice, climate change, and political extremism. Biden called for unity, asking Americans to come together to overcome these obstacles. He stressed the importance of democracy, which he described as precious and fragile, and celebrated its survival after the January 6 Capitol attack.
Biden promised to be a president for all Americans, including those who did not support him. He outlined his vision for healing and unity, asking everyone to join him in the cause of building a better nation. The speech also paid tribute to those who have suffered losses during the pandemic and called for a moment of silence.
Throughout his address, Biden conveyed a message of hope and determination, asserting that with unity, there is nothing America cannot do.
Biden speech word cloud
Biden speech histogram
Comments are closed.