Gerrymandering is a political tactic used to manipulate the boundaries of electoral districts to favor one political party over another. It’s essentially the opposite of what the Founders meant by representative democracy — voters are supposed to choose their representatives, and not the other way around.
The practice is named after Elbridge Gerry, a governor of Massachusetts who in 1812 approved a redistricting plan that created a district that resembled a salamander. The term “gerrymandering” combines the words “Gerry” and “salamander.”
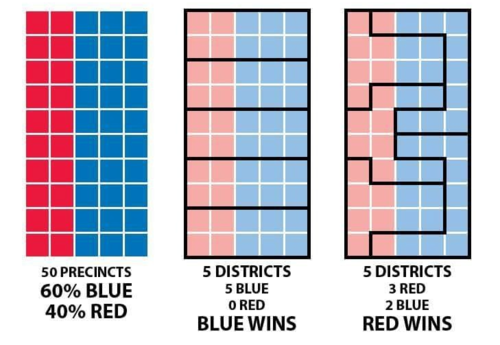
The objective of gerrymandering is to create “safe” districts for a particular political party or group by concentrating voters who are likely to support that party into a small number of districts, while diluting their votes in other districts. This is done by drawing district boundaries in a way that groups together like-minded voters or separates them from voters who are likely to vote for the opposing party. It’s a way of cherry-picking one’s constituents, and manipulating the outcome unfairly in your favor — with one net effect being the dilution of the voting rights of your opposition.
Gerrymandering is typically carried out by state legislatures, who have the authority to redraw electoral district boundaries every ten years after the release of the Census data. The redistricting process is supposed to ensure that each district has roughly the same number of residents, but lawmakers often use this opportunity to manipulate the boundaries in a way that benefits their party.
Partisan and racial gerrymandering
There are two main types of gerrymandering: partisan gerrymandering and racial gerrymandering. Partisan gerrymandering is when district boundaries are drawn in a way that benefits one political party over another. Racial gerrymandering is when district boundaries are drawn in a way that dilutes the voting power of racial minorities — which, in turn, tends to help the Republican Party and hurt the Democratic Party.
Partisan gerrymandering can be carried out in several ways. One common method is “packing,” which involves drawing district boundaries so that a high concentration of voters who support one party are all in one district. This leaves other districts with fewer voters who support that party, making it easier for the opposing party to win those districts. Another method is “cracking,” which involves breaking up a concentration of voters who support one party by drawing district boundaries so that they are spread out across multiple districts. This dilutes their voting power and makes it harder for them to win any of those districts.
Racial gerrymandering is usually carried out to dilute the voting power of racial minorities, particularly African Americans and Hispanics. This is done by drawing district boundaries that split up minority communities and dilute their voting power by spreading them across multiple districts. Racial gerrymandering is illegal under the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which prohibits discrimination on the basis of race.
Effects of gerrymandering
The effects of gerrymandering can be significant. By manipulating district boundaries, lawmakers can create a situation where one party has a significant advantage over the other, making it easier for them to win elections. This can lead to a lack of political competition, which can make it harder for voters to hold their elected officials accountable. In other words, gerrymandering can lead to increased corruption in government at all levels.
Gerrymandering also has the potential to create a lack of diversity in government. By concentrating voters of a particular political party or race into a small number of districts, lawmakers can create a situation where the views and interests of some voters are not represented in government. This can lead to a situation where elected officials are not truly representative of their constituents — which is the essence of the American Dream.
Efforts to combat gerrymandering have included legal challenges to redistricting plans, the use of independent redistricting commissions, and the adoption of alternative voting systems like ranked-choice voting. Despite these efforts, gerrymandering remains a significant issue in many states, and its effects can be seen in elections at all levels of government, from school boards to Congress to the White House.
Comments are closed.