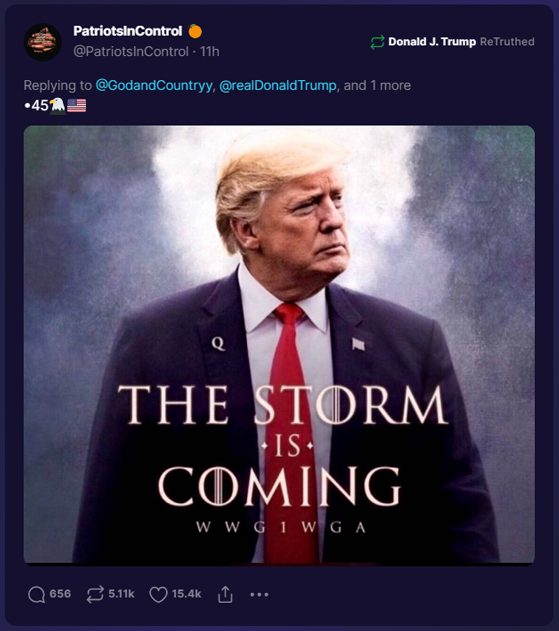
The “wallpaper effect” is a phenomenon in media, propaganda, and disinformation where individuals become influenced or even indoctrinated by being continuously exposed to a particular set of ideas, perspectives, or ideologies. This effect is akin to wallpaper in a room, which, though initially noticeable, becomes part of the unnoticed background over time.
The wallpaper effect plays a significant role in shaping public opinion and individual beliefs, often without the conscious awareness of the individuals affected.
Origins and mechanisms
The term “wallpaper effect” stems from the idea that constant exposure to a specific type of media or messaging can subconsciously influence an individual’s perception and beliefs, similar to how wallpaper in a room becomes a subtle but constant presence. This effect is potentiated by the human tendency to seek information that aligns with existing beliefs, known as confirmation bias. It leads to a situation where diverse viewpoints are overlooked, and a singular perspective dominates an individual’s information landscape.
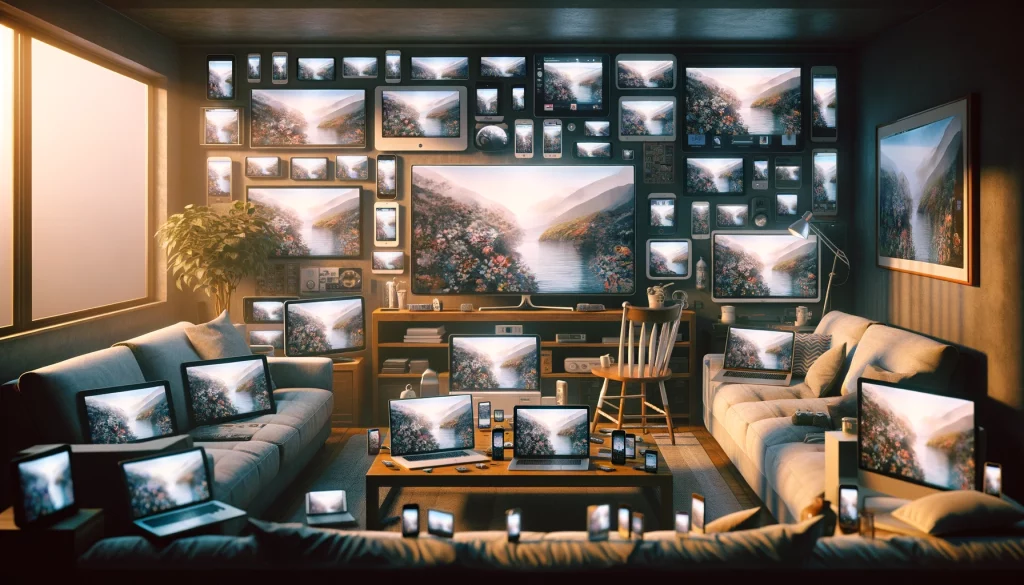

Media and information bubbles
In the context of media, the wallpaper effect is exacerbated by the formation of information bubbles or echo chambers. These are environments where a person is exposed only to opinions and information that reinforce their existing beliefs.
The rise of digital media and personalized content algorithms has intensified this effect, as users often receive news and information tailored to their preferences, further entrenching their existing viewpoints. Even more insidiously, social media platforms tend to earn higher profits when they fill users’ feeds with ideological perspectives they already agree with. Even more profitable is the process of tilting them towards more extreme versions of those beliefs — a practice that in other contexts we call “radicalization.”
Role in propaganda and disinformation
The wallpaper effect is a critical tool in propaganda and disinformation campaigns. By consistently presenting a specific narrative or viewpoint, these campaigns can subtly alter the perceptions and beliefs of the target audience. Over time, the repeated exposure to these biased or false narratives becomes a backdrop to the individual’s understanding of events, issues, or groups, often leading to misconceptions or unwarranted biases.
Psychological impact
The psychological impact of the wallpaper effect is profound. It can lead to a narrowing of perspective, where individuals become less open to new information or alternative viewpoints. This effect can foster polarized communities and hyper partisan politics, where dialogue and understanding between differing viewpoints become increasingly difficult.
Case studies and examples
Historically, authoritarian regimes have used the wallpaper effect to control public opinion and suppress dissent. By monopolizing the media landscape and continuously broadcasting their propaganda, these regimes effectively shaped the public’s perception of reality.
In contemporary times, this effect is also seen in democracies, where partisan news outlets or social media algorithms create a similar, though more fragmented, landscape of information bubbles.
Counteracting the wallpaper effect
Counteracting the wallpaper effect involves a multifaceted approach. Media literacy education is crucial, as it empowers individuals to critically analyze and understand the sources and content of information they consume.
Encouraging exposure to a wide range of viewpoints and promoting critical thinking skills are also essential strategies. Additionally, reforms in digital media algorithms to promote diverse viewpoints and reduce the creation of echo chambers can help mitigate this effect.
Implications for democracy and society
The wallpaper effect has significant implications for democracy and society. It can lead to a polarized public, where consensus and compromise become challenging to achieve. The narrowing of perspective and entrenchment of beliefs can undermine democratic discourse, leading to increased societal divisions and decreased trust in media and institutions.
The wallpaper effect is a critical phenomenon that shapes public opinion and belief systems. Its influence is subtle yet profound, as constant exposure to a specific set of ideas can subconsciously mold an individual’s worldview. Understanding and addressing this effect is essential in promoting a healthy, informed, and open society. Efforts to enhance media literacy, promote diverse viewpoints, and reform digital media practices are key to mitigating the wallpaper effect and fostering a more informed and less polarized public.